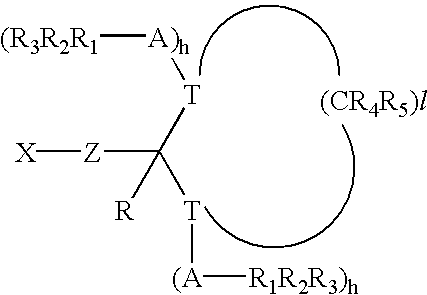
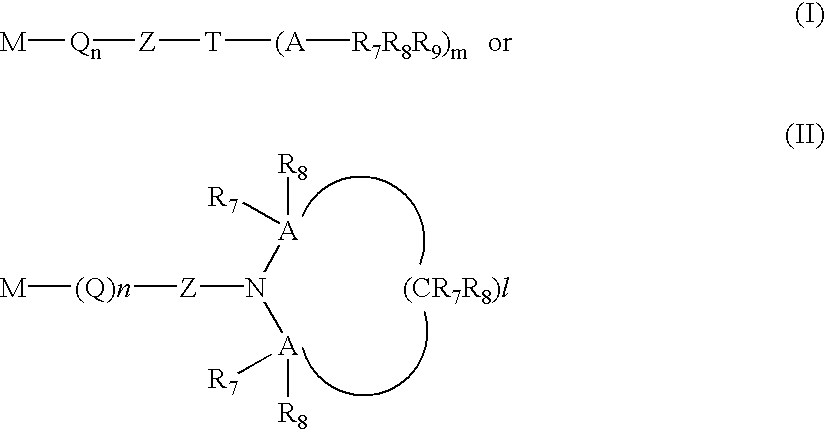
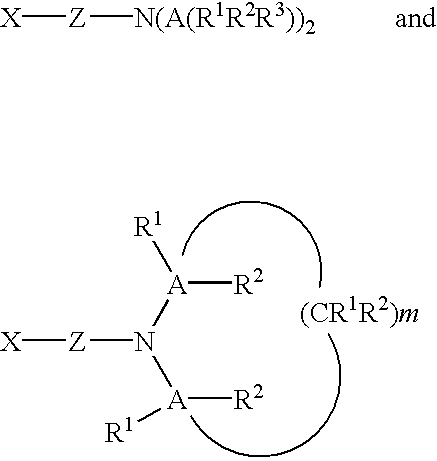
Compositions providing improved functionalization of terminal anions and processes for improved functionalization of terminal anions
a terminal anions and functionalization technology, applied in the field of compounding providing improved processes for improving the functionalization of terminal anions, can solve the problems of low capping efficiency, low efficiency of functionalization reactions, and inability to meet the requirements of low-temperature conditions on an industrial scale, so as to improve the functionalization efficiency of living polymer anions and the effect of increasing the efficiency of reactions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Preparation of Dimethylaminopropylpolystyrene
A 250 ml. glass reactor was equipped with two break-seal reagent ampoules, a sampling port attached with a Teflon® stopcock, an inlet tube fitted with a septum cap, and a magnetic stir bar. This reactor was flame sealed to a high vacuum line, and evacuated at 120° C. for 8 hours. The flask was refilled with dry argon, and allowed to cool to room temperature. The reactor was charged with purified benzene (90 ml.). S-butyllithium, 0.149 grams (2.3 mmole, 1.45 M in cyclohexane, 1.6 mL) was then added via syringe. Purified styrene monomer (9.30 grams, 89.3 mmoles) was added from a break-seal ampoule. The reaction mixture was kept for 6 hours at room temperature. The living poly(styryl)lithium was then transferred into an ampoule and the known amount of residual solution was terminated with degassed methanol from the last ampoule to obtain a base polymer sample. A second 250 ml. glass reactor was equipped with three break-seal reagent ampoules...
example 2
Preparation of Dimethylaminopropylpolyisoprene
A 250 ml. glass reactor was equipped with two break-seal reagent ampoules, a sampling port attached with a Teflon® stopcock, an inlet tube fitted with a septum cap, and a magnetic stir bar. This reactor was flame sealed to a high vacuum line, and evacuated at 120° C. for 8 hours. The flask was refilled with dry argon, and allowed to cool to room temperature. The reactor was charged with purified cyclohexane (90 ml.). S-Butyllithium, 0.149 grams (2.3 mmole, 1.45 M in cyclohexane, 1.6 mL) was then added via syringe. Purified isoprene monomer (9.00 grams, 132.1 mmoles) was added from a break-seal ampoule. The reaction mixture was kept for 6 hours at room temperature. The living poly(isoprenyl)lithium was then transferred into an ampoule and the known amount of residual solution was terminated with degassed methanol from the last ampoule to obtain a base polymer sample. A second 250 ml. glass reactor was equipped with three break-seal reagen...
example 3
Preparation of Alpha-Hydroxy-Omega-Dimethylaminopropylpolystyrene
A 500 ml. glass reactor was equipped with two break-seal reagent ampoules, a sampling port attached with a Teflon® stopcock, an inlet tube fitted with a septum cap, and a magnetic stir bar. This reactor was flame sealed to a high vacuum line, and evacuated at 120° C. for 8 hours. The flask was refilled with dry argon, and allowed to cool to room temperature. The reactor was charged with purified benzene (250 ml.). 3-(1,1-Dimethylethoxy)-1-propyllithium, chain extended with two equivalents of isoprene, 0.90 grams (3.5 mmole, 0.52 M in cyclohexane, 6.7 mL) was then added via syringe. Purified styrene monomer (28.15 grams, 89.3 mmoles) was added from a break-seal ampoule. The reaction mixture was kept for 6 hours at room temperature. The living poly(styryl)lithium was divided equally into three calibrated ampoules for reaction with the alkyl chlorides. The residual solution was terminated with degassed methanol from the l...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com