Dry heat processing stabilizer for prothrombin complex or factor v a IX preparation
A technology of prothrombin and coagulation factor, applied in the field of medicine, can solve the problems of unsatisfactory protective effect, difficulty in meeting large-scale production, and difficulty in achieving the recovery rate of coagulation factor activity.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0007] Example 1: The protective effect of the stabilizer of the present invention on the prothrombin complex.
[0008] 1. Preparation of Prothrombin Complex
[0009] According to conventional methods, the frozen plasma or plasma supernatant from which cryoprecipitation was removed was adsorbed with anion resin DEAE-Sepharose A50 to prothrombin complex, and eluted with an eluent containing 2M NaCl and 0.02M trisodium citrate, and the obtained eluted The solution was desalted and concentrated by ultrafiltration with an ultrafiltration buffer solution containing 0.02M trisodium citrate, 0.6% NaCl, and pH 6.6-7.8 to obtain a concentrated solution of prothrombin complex.
[0010] 2. Add stabilizer to prepare prothrombin complex freeze-dried preparation (until dry heat treatment)
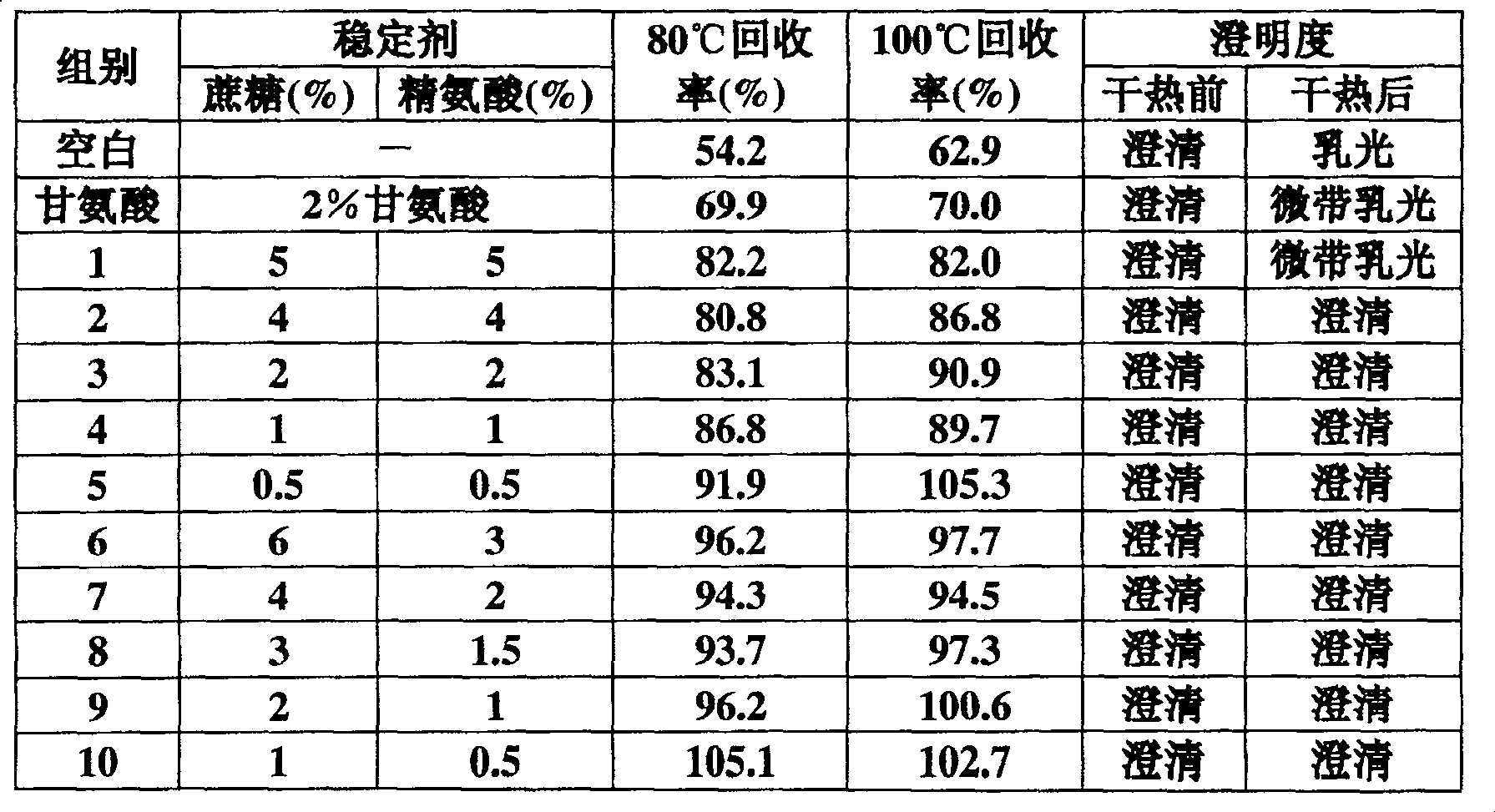
[0011] A stabilizer composed of sucrose and arginine in a certain ratio (see Table 1) was added to the prothrombin complex prepared above, sterilized, sub-packaged, and freeze-dried, then subjected to 8...
Embodiment 2
[0017] Embodiment 2: Arginine is to the protection test of coagulation factor IX preparation
[0018] Conventionally, the blood coagulation factor IX eluted from the heparin affinity chromatography Sepharose CL-6B column is desalted by ultrafiltration, and the resulting solution contains 100 IU / ml blood coagulation factor IX, and 1% arginine is added. After freeze-drying, it was subjected to dry heat treatment at 80°C / 72 hours and 100°C / 30 minutes respectively, and the potency of blood coagulation factor IX was detected before and after dry heat treatment, and the recovery rate of activity was calculated. Compared with the blank control, the recovery rate of the blank control coagulation factor IX without adding arginine was 50.9% (80°C / 72 hours) and 57.8% (100°C / 30 minutes), while the recovery rate of adding 1% arginine 90.8% (80°C / 72 hours) and 92.0% (100°C / 30 minutes), respectively. The results showed that the products with arginine as a stabilizer could effectively protec...
Embodiment 3
[0019] Embodiment 3: the protective test of sucrose to coagulation factor IX
[0020] According to the conventional method, the blood coagulation factor IX obtained from the elution of the heparin affinity chromatography Sepharose CL-6B column was concentrated by ultrafiltration, and the obtained concentrated solution contained 80IU / ml blood coagulation factor IX, added 1% sucrose, sterilized and freeze-dried, respectively passed through Dry heat treatment at 80°C / 72 hours and 100°C / 30 minutes, detect the activity of coagulation factor IX before and after dry heat treatment, and calculate the activity recovery rate. The coagulation factor IX recovery rate of the blank control was 59.4% (80°C / 72 hours) and 63.9% (100°C / 30 minutes) respectively, and the recovery rate of adding 1% sucrose was 92.9% (80°C / 72 hours) and 94.7% % (100°C / 30 minutes). The results showed that the preparation with sucrose as a stabilizer could effectively protect coagulation factor IX during dry heat tr...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com