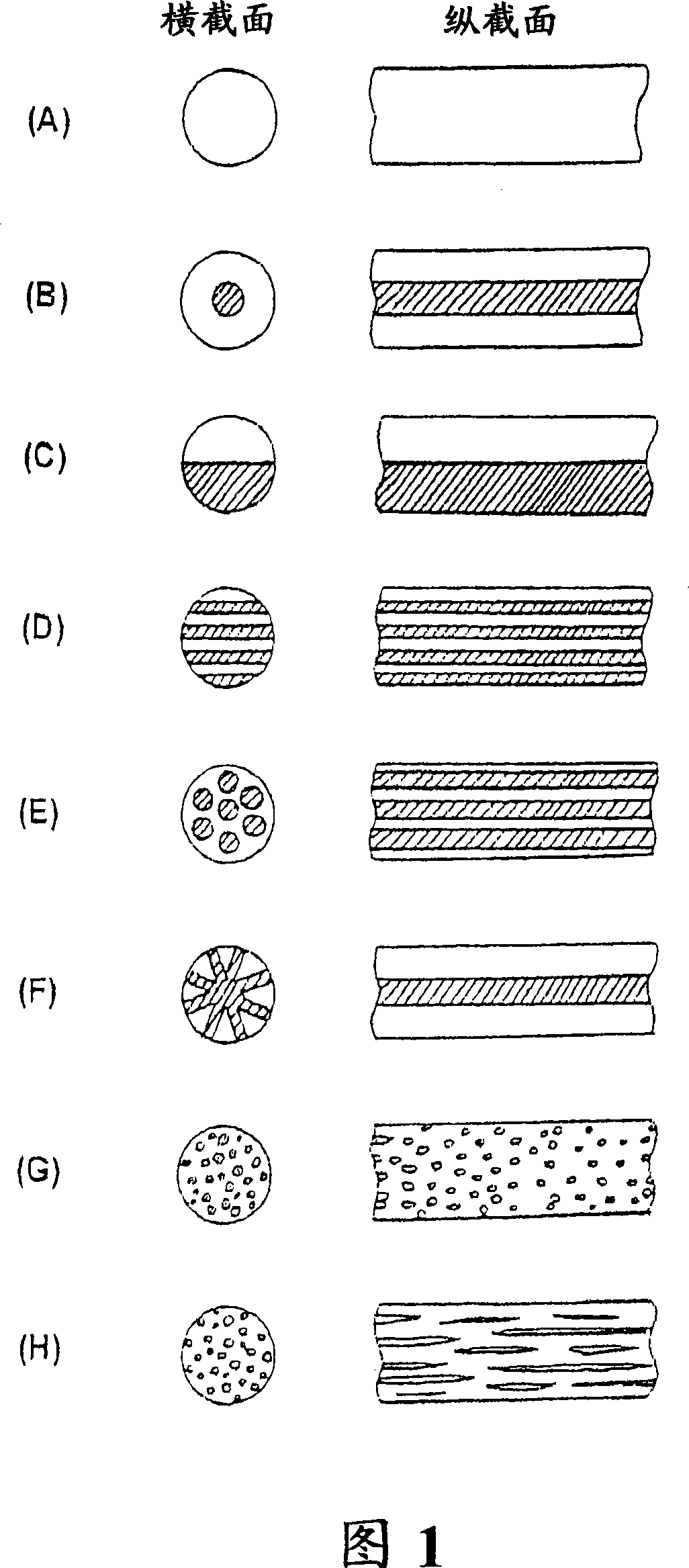
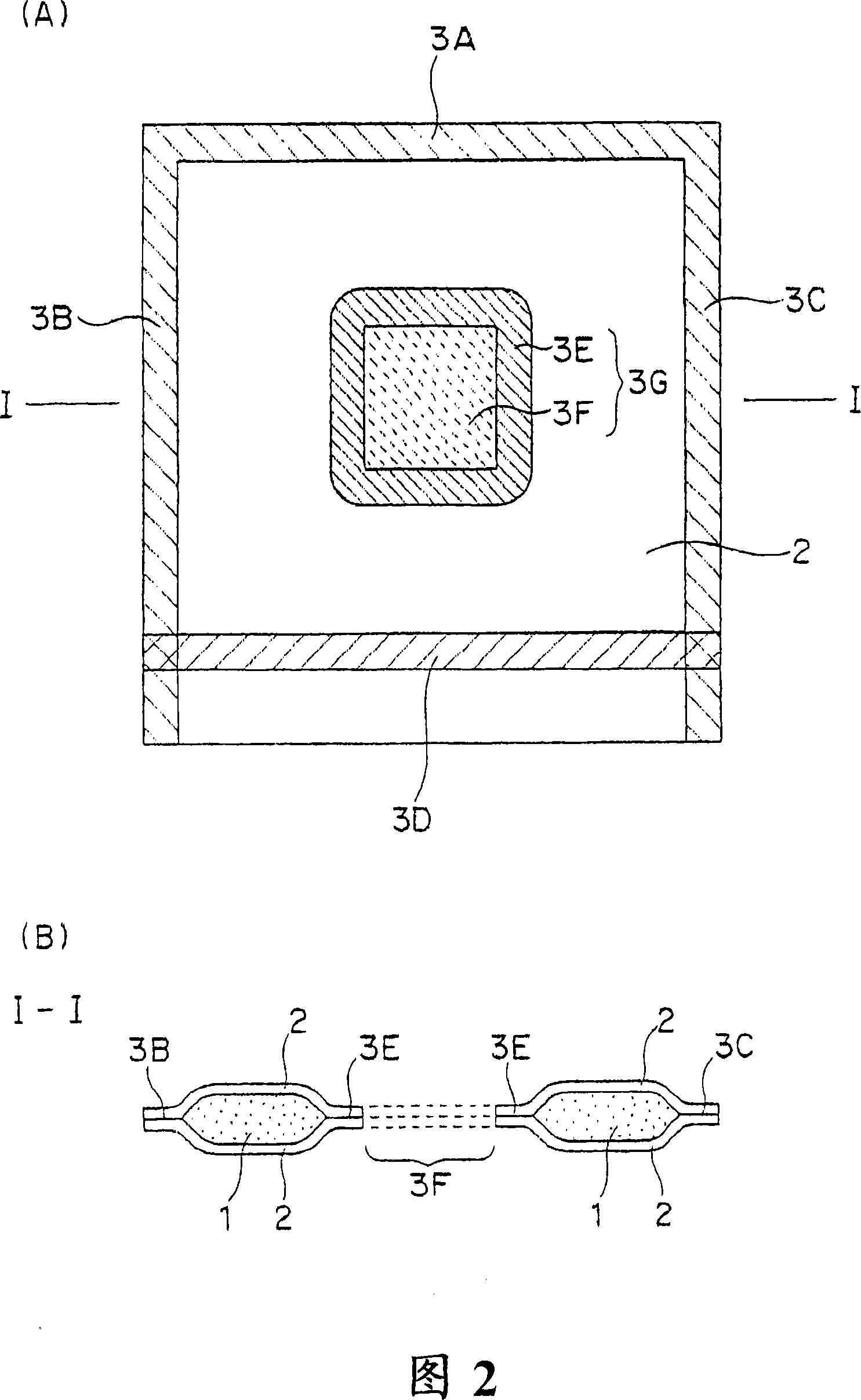
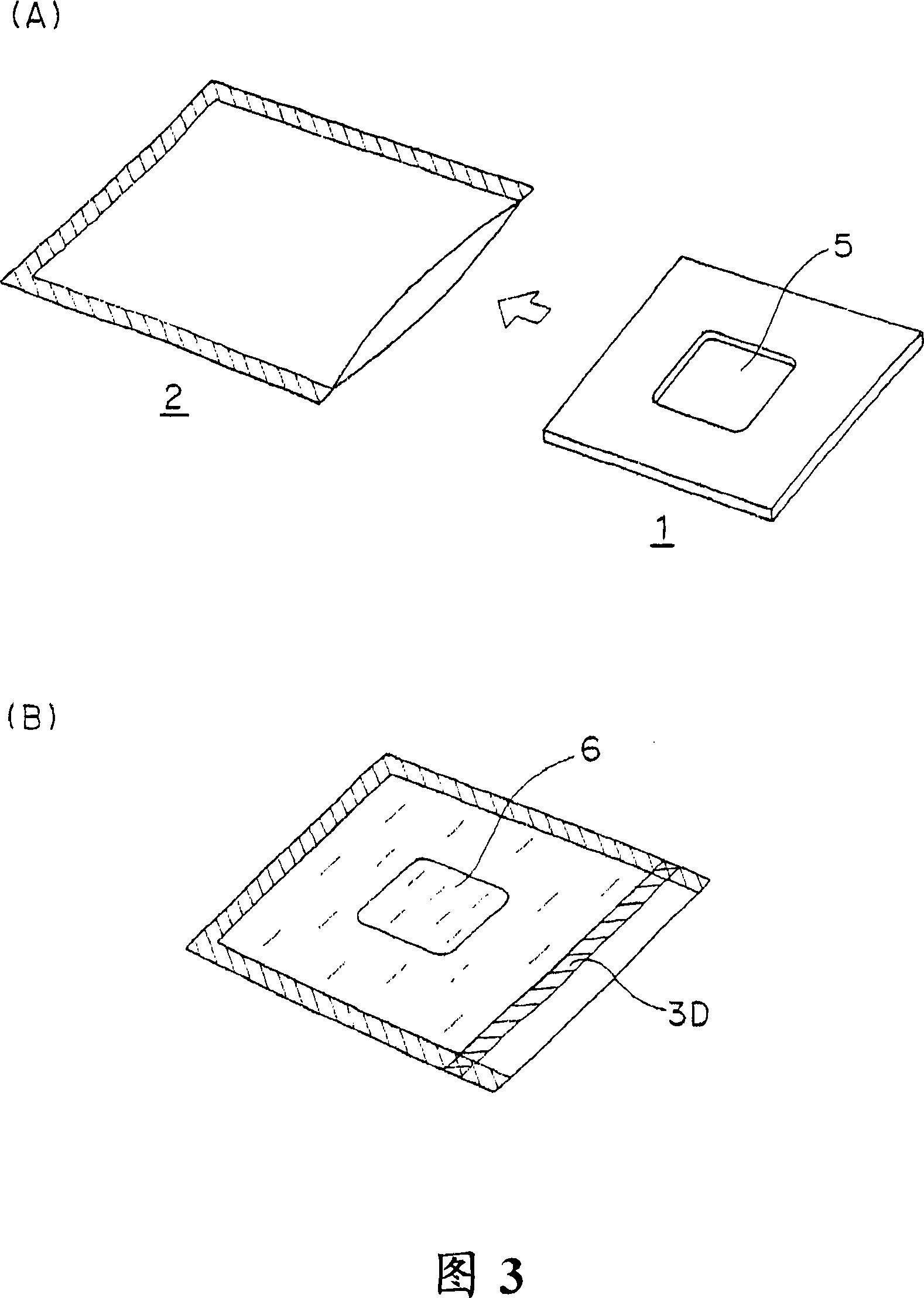
Vacuum heat insulation material
A technology of vacuum insulation materials and core materials, which is applied in heat exchange equipment, lighting and heating equipment, and pipeline protection through heat insulation, etc. It can solve the problems of reduced yield, low heat insulation, and reduced yield of vacuum insulation materials, and achieves Suppression of outgassing, excellent processability and handling, and excellent recyclability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment A
[0157]
[0158] The polyester fibers of Table 1 were used. All polyester fibers were polyethylene terephthalate fibers with a fiber length of 51 mm.
Embodiment A1
[0160] The polyester fibers in Table 1 were processed into sheets by a needle punching method. The weight per unit area of the sheet just after processing is 550g / m 2 . This sheet was cut into a size of 200 mm×200 mm, and dried at a temperature of 120° C. for 1 hour. Four dried sheets were laminated, and the laminated material was used as a core material, and inserted into an outer packaging material made of a gas barrier film having a four-layer structure of nylon, aluminum-deposited PET, aluminum foil, and high-density polyethylene. Simultaneously, a gas adsorbent (manufactured by Saesugetta Izu Corporation: COMBO) was inserted into an outer packaging material. Then, vacuum was evacuated with a vacuum device to make the internal pressure 0.01 Torr, and sealing was performed by thermal fusion. The resulting vacuum heat insulating material had a size of 200mm×200mm and a thickness of 10mm. The core material density of the obtained vacuum insulation material is 220kg / m 3...
Embodiment A2-A8
[0161]
[0162] A vacuum heat insulating material was obtained in the same manner as in Example A1 except that the type and amount of fibers used for the core material were changed as shown in Table 1. In Comparative Example A2, it was not necessary to process into a sheet, and the fibers in the form of cotton wool could be used as they were.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Average fiber diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com