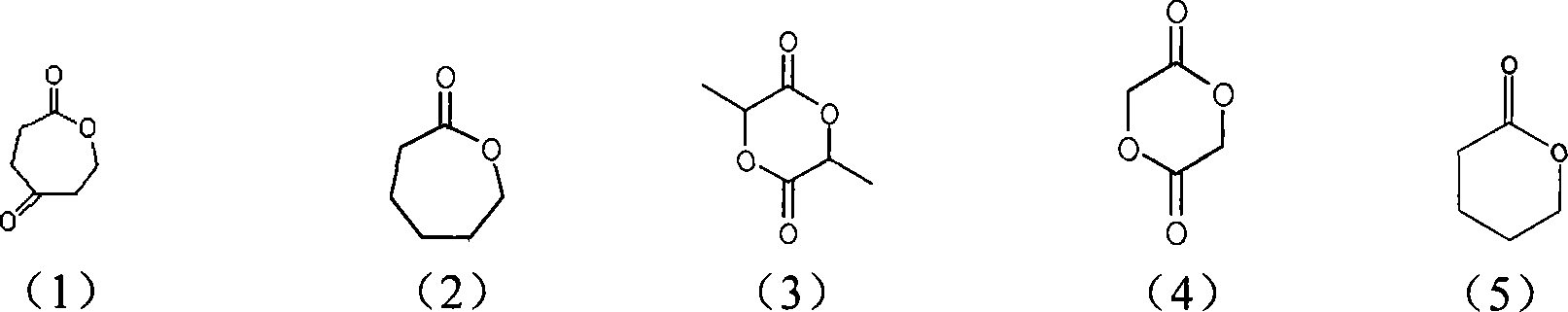
Epsilon-caprolactone polymer
A polymer and caprolactone technology, applied in the field of ε-caprolactone polymers, can solve the problems of low glass transition temperature, slow degradation rate, strong crystallinity, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
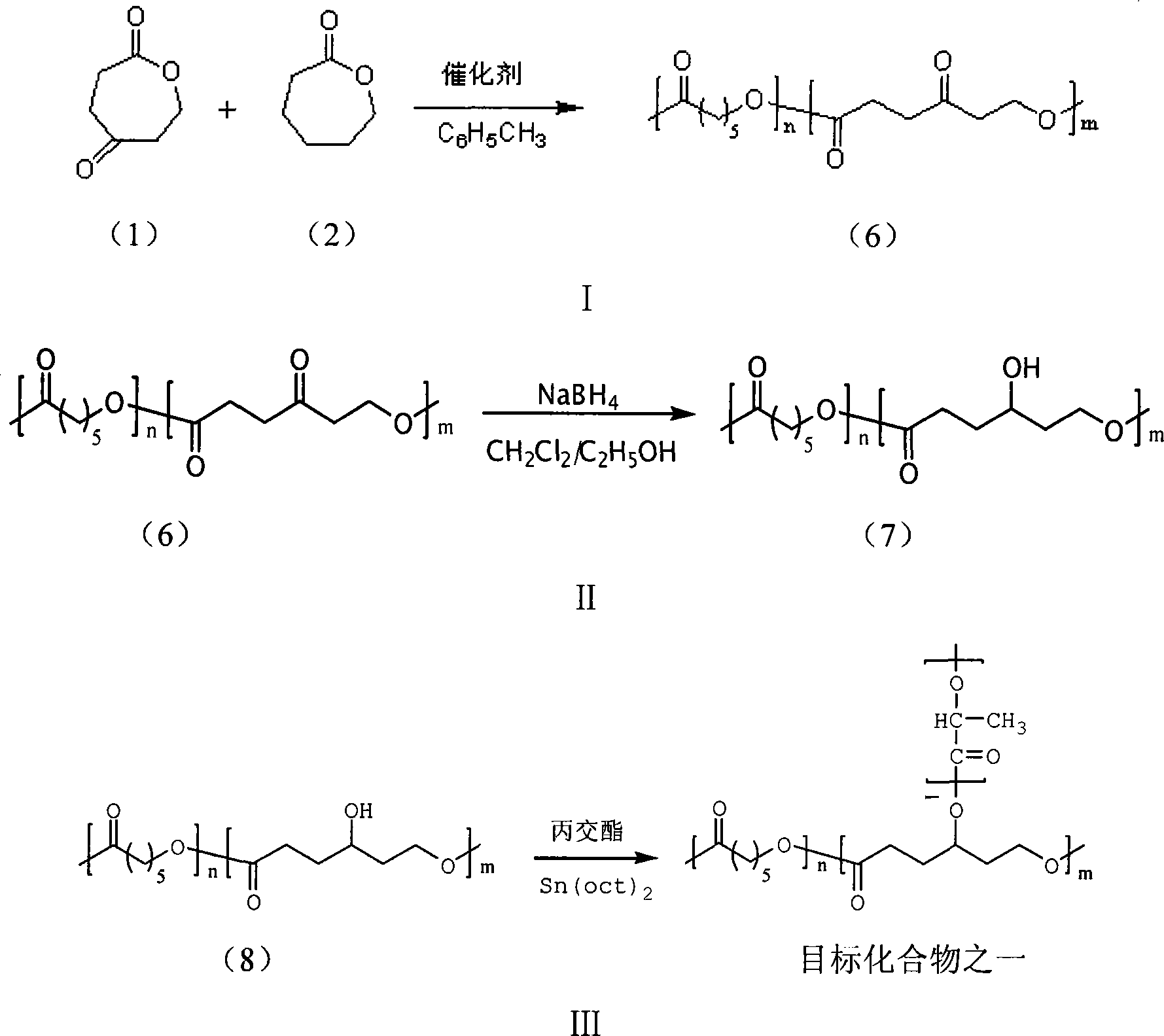
[0017] (1) Mix 4-carbonyl-ε-caprolactone (OPD) and caprolactone at a molar ratio of 1:2 and add them to the polymerization reactor, with 1% of the molar number of 4-carbonyl-ε-caprolactone The stannous isooctanoate is used as a catalyst, and dry toluene is used as a solvent, and the copolymer is obtained after reacting at 80° C. for 18 hours.
[0018] The H NMR spectrum of the obtained copolymer ( 1 H-NMR) analysis: with d-CHCl 3 as the solvent, TMS as the internal standard, and use the German AVANCE500MHz nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer to measure the hydrogen nuclear magnetic spectrum of the copolymer. COOCH 2 (δ=4.35, triplet), COCH 2 (δ=2.77, triplet), COOCH 2 (δ=4.08, triplet), COOCH 2 (δ=4.35, triplet) is the characteristic peak of the 4-carbonyl-ε-caprolactone structural unit in the polymer, COOCH 2 (δ=4.08, triplet) is the characteristic peak of the ε-caprolactone structural unit in the polymer, and can calculate 4-carbonyl-ε- in the polymer according to ...
Embodiment 2~3
[0026] 4-carbonyl-ε-caprolactone (OPD) and caprolactone are mixed at a molar ratio of 1:4 or 1:6 respectively and then added to the polymerization reactor, and can be obtained by the method of step (1) in Example 1 Copolymers with different molecular weights were analyzed by gel permeation chromatography (GPC). The molecular weight was calculated using a 244-type GPC tester from Waters Corporation of the United States, using tetrahydrofuran as the eluting solvent, and using polystyrene standard samples as the benchmark. The results are shown in Table 1
[0027] Table 1
[0028]
Embodiment 4~7
[0030] Only the molar ratio of reduction product to lactide in step (3) of Example 1 was changed (other conditions were the same as in Example 1). That is, the molar ratio of the reduction product to lactide is 1:40, 1:60, 1:80 or 1:100 respectively to obtain target objects with different molecular weights, and the resulting copolymer is analyzed by gel permeation chromatography (GPC). The 244 GPC tester of American Waters Company uses tetrahydrofuran as the eluting solvent, and the molecular weight calculation results are shown in Table 2 based on polystyrene standard samples.
[0031] Table 2
[0032]
instance number
Molar ratio of reduction product to lactide
M n a
×10 4
M w b
×10 4
The molecular weight distribution
(M w / M n )
1
4
5
6
7
1∶20
1∶40
1∶60
1∶80
1∶100
1.59
2.25
3.64
5.17
3.78
2.44 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com