Process for preparing microbe oil
A technology for microbial oils and oil-producing microorganisms, which is applied in the fields of biofuels, fat production, and biological raw materials to achieve the effects of low production cost, reduced raw material cost, and wide application range.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
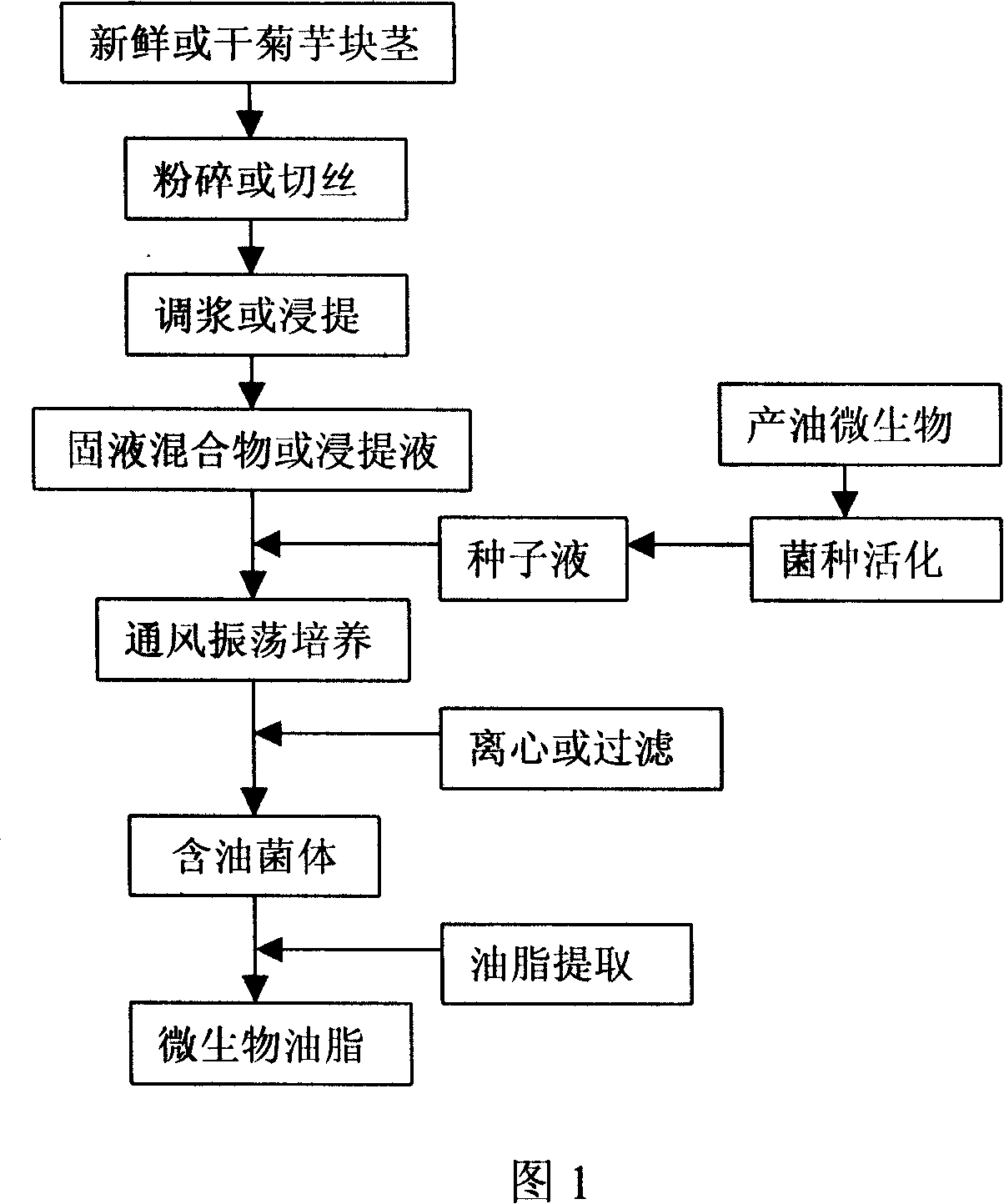
[0023] Follow the following process steps to prepare microbial oil successively:
[0024] A. Raw material pretreatment
[0025] Clean the fresh Jerusalem artichoke tubers, mix them with water at a mass volume ratio of 1:1, crush them with a juice extractor, and adjust the slurry to obtain a solid-liquid mixture. Adjust the initial pH to 3.0, and sterilize at 121° C. for 15 minutes before use.
[0026] B. Acquisition of oleaginous bacteria
[0027] Rhodosporidium toruloides (Rhodosporidium toruloides) AS 2.1389 seed solution (containing 10 6 ~10 8 Cells / mL) were inserted into the solid-liquid mixture prepared according to the above-mentioned process A according to the inoculum amount of 5%, cultured with shaking at 30°C and 200r / min for 5 days, and centrifuged at 5000rpm for 10min to collect the bacterial precipitate.
[0028] C. Oil extraction
[0029] Add 5mL of 4mol / L HCl per gram of bacteria, and digest the bacteria at 70°C for 30 minutes.
[0030] After cooling, add m...
Embodiment 2
[0032] Fresh Jerusalem artichoke tubers are crushed, mixed with water at a mass-volume ratio of 1:5, crushed with a juice extractor, and slurried to obtain a solid-liquid mixture, adjusted to an initial pH of 6.0, and sterilized at 121° C. for 15 minutes before use.
[0033] Lipomyces starkeyi AS2.1608 seed solution (containing 10 6 ~10 8 Cells / mL) were inserted into the solid-liquid mixture prepared according to the above-mentioned process A according to the inoculation amount of 20%, 30°C, 200r / min shaking culture for 5 days, and centrifuged at 5000rpm for 10min to collect the bacterial precipitate.
[0034] The oil extraction process is the same as in Example 1.
[0035] According to this process condition, 100g of fresh Jerusalem artichoke can obtain 2.8g of oil.
Embodiment 3
[0037] A. Raw material pretreatment
[0038] The dried Jerusalem artichoke tubers are crushed, mixed with water at a mass volume ratio of 1:3 to obtain a solid-liquid mixture, pH 7.0, and sterilized at 121° C. for 15 minutes before use.
[0039] B. Acquisition of oleaginous bacteria
[0040] Mortierella isabellina (Mortierella isabellina) AS3.3410 seed solution (containing 10 6 ~10 8spore cells / mL) were inserted into the solid-liquid mixture prepared according to the above-mentioned A process at an inoculum size of 10%, cultured with shaking at 37°C and 220r / min for 6 days, and centrifuged at 5000rpm for 10min to collect the bacterial precipitate.
[0041] The oil extraction process is the same as in Example 1.
[0042] According to this process condition, 100g dried Jerusalem artichoke can get 10.2g oil.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com