Coating blade for processing cast iron
A technology of coating inserts and coatings, applied in the direction of layered products, etc., can solve the problems of the overall performance limitation of the tool and the lack of gradient structure, achieve green and environmentally friendly dry cutting, avoid the decline of strength and toughness, and improve the cutting edge. the effect of strength
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
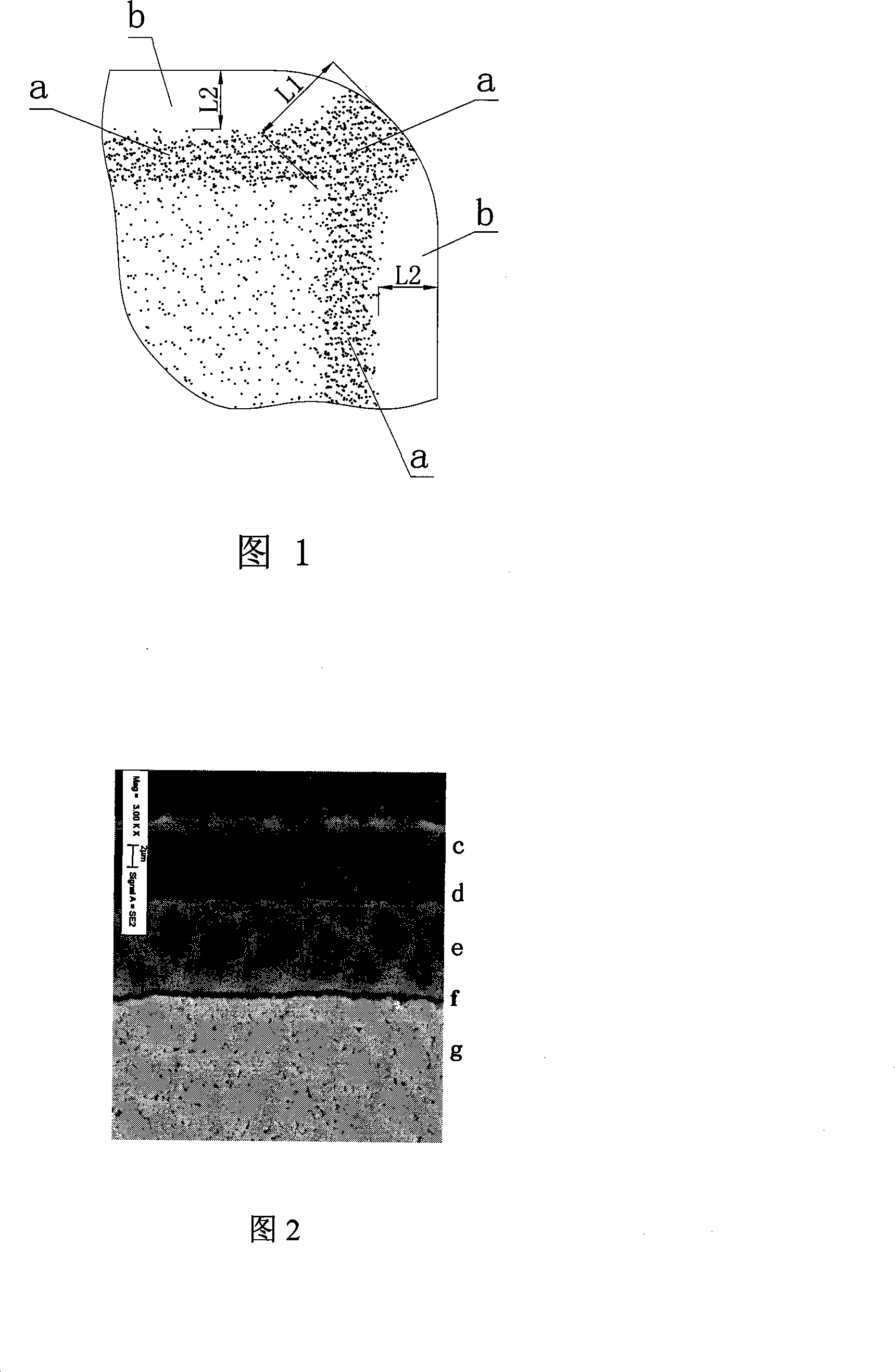
[0032] A coated insert according to the invention, comprising a hard phase based on tungsten carbide (WC) and a binding phase based on cobalt (Co), by adding a small amount of nitrogen-containing cubic compounds or consisting of these cubic compounds Solid solution, and the powder mixture is pressed, and the cemented carbide tool is sintered by gradient sintering technology (sintered at 1440°C, cooled under a de-N atmosphere after high temperature sintering), and a layer of bonding phase is formed on the surface of the cemented carbide substrate enriched surface zone, forming a layer of cubic phase enriched zone under the binder phase enriched surface zone. The thickness L2 of the bonding phase-enriched surface region b is 50 μm, and the content of Co in the bonding phase-enriched surface region is 1.2 times the nominal content of Co in the cemented carbide matrix; by using chamfering, Rounding and other treatments remove the bonded phase-enriched surface area on the surface o...
Embodiment 2
[0040] The preparation method of the matrix in this example is the same as in Example 1, and the components and content of the prepared blade matrix are the same as those in Example 1, but by controlling the gradient sintering process, a 20 μm thick binder phase enriched surface area is formed on the surface of the matrix , the content of Co in the bonding phase-rich surface area is 1.3 times the nominal content of Co in the cemented carbide matrix; through chamfering and rounding, a bonding phase rich in L2 = 20 μm thick is formed on both sides of the cutting edge The surface area b is concentrated, and the middle fan-shaped part exposes the cubic phase enrichment area a with good high temperature performance (as shown in Figure 1). The thickness L1 of the cubic phase enrichment area is 40 μm, and the content of the cubic phase compound is the cubic phase in the matrix 1.45 times the nominal content of the compound.
[0041] The substrate g is coated according to the process ...
Embodiment 3
[0043] The preparation method of the substrate in this example is the same as that in Example 1, and the composition of the prepared cemented carbide matrix includes: 5.5wt% Co, 3.5wt% Ti and Ta cubic carbonitride, and the balance is WC. On both sides of the cutting edge, there is a bonded phase enriched surface area b with a thickness of L2 = 35 μm, and the content of Co in the bonded phase enriched surface area b is 1.4 times the nominal content of Co in the cemented carbide matrix; and the middle fan-shaped part It is a cubic phase-enriched region a with good high-temperature performance. The thickness L1 of the cubic-phase-enriched region a is 70 μm, and the content of the cubic phase compound is 1.15 times the nominal content of the cubic phase compound in the matrix.
[0044] In this embodiment, the substrate is coated by the process method of Example 1 to obtain the same coating structure as that of Example 2.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| crystal size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com