A kind of preparation method of die-casting zinc alloy with high hardness and high toughness
A high-toughness, zinc alloy technology, applied in the field of non-ferrous metal processing, can solve problems such as low hardness, poor toughness, and difficulty in meeting industrial needs, and achieve the effect of reducing toughness and increasing hardness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0046] First, put 261.45g of industrial pure zinc, 13.4g of industrial pure aluminum and 6g of Al-50Cu master alloy into a graphite crucible and heat and melt in a well-type electric furnace. The melting temperature is 650°C. Proper stirring is carried out after the alloy is completely melted. , let it stand for 5 minutes, wrap 0.15g of Mg in aluminum foil and dissolve it into the alloy liquid and stir it well. At the same time, 19g of Al-12.6Si master alloy was added to the alloy melt, mixed evenly to obtain Zn-11Al-1Cu-0.05Mg-0.8Si alloy melt, and finally poured into a room temperature metal mold to obtain a diameter of 12 mm. Impact specimens with a length of 80 mm.
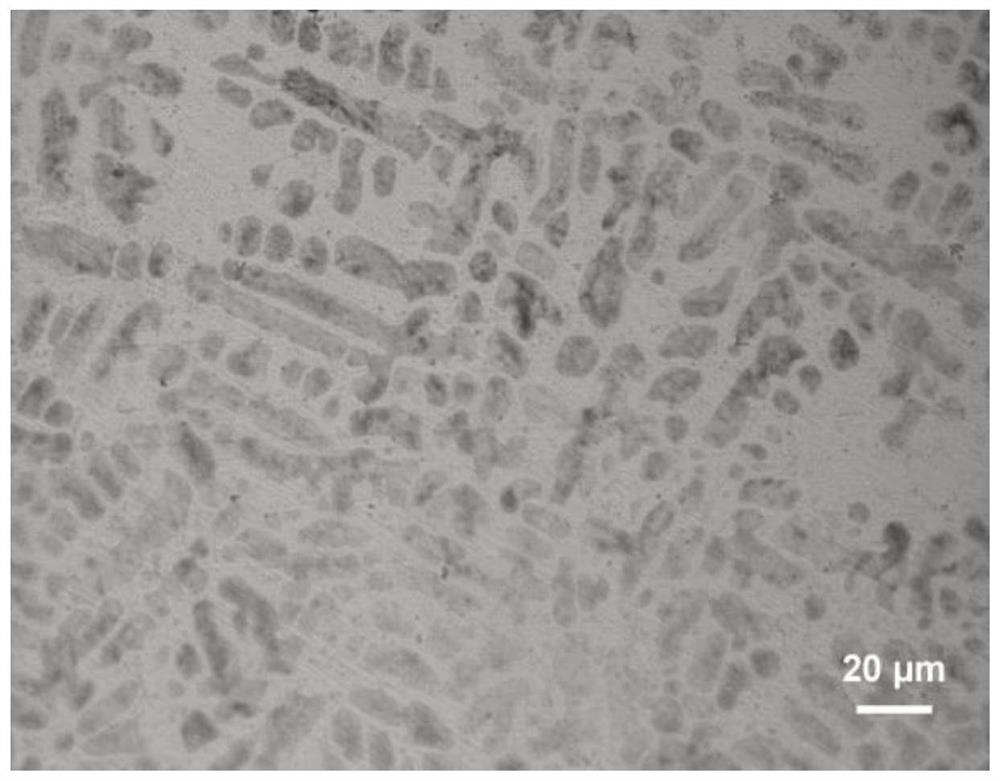
[0047] Figure 5 Be the microstructure of Zn-11Al-1Cu-0.05Mg alloy when Si content is 0.8wt.%, compare with comparative example 4 (as Figure 4 As shown), the size of the silicon phase in the alloy structure is significantly reduced.
[0048] Studies have shown that the impact toughness of Zn-11Al-1Cu-0.05M...
Embodiment 2
[0050] First, put 253.85g of industrial pure zinc, 13.4g of industrial pure aluminum and 6g of Al-50Cu master alloy into a graphite crucible and heat and melt in a well-type electric furnace. The melting temperature is 630°C. Proper stirring is carried out after the alloy is completely melted. , let it stand for 5 minutes, wrap 0.15g of Mg in aluminum foil and dissolve it into the alloy liquid and stir it well. At the same time, add 9.7g of Zn-3Ti master alloy into a graphite crucible, control the melting temperature at 540°C, then add 19g of Al-12.6Si alloy and semi-solid Zn-3Ti master alloy into the melt, mix well and pour into Impact specimens with a diameter of 12 mm and a length of 80 mm were obtained in metal molds at room temperature.
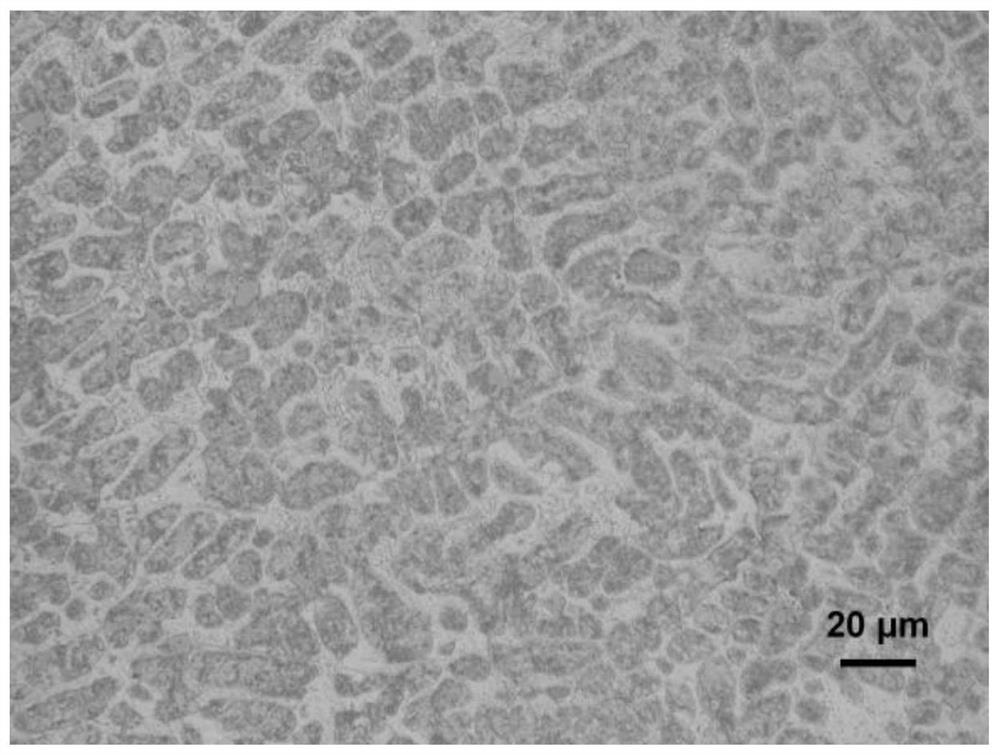
[0051] Image 6 When the Si content is 0.8%, the microstructure of the Zn-11Al-1Cu-0.05Mg alloy with a Ti content of 0.1wt.% is compounded, and it can be seen that the grains of the alloy are obviously finer than those without adding Ti...
Embodiment 3
[0054] First, put 233.85g of industrial pure zinc, 13.4g of industrial pure aluminum and 6g of Al-50Cu master alloy into a graphite crucible for heating and melting in a well-type electric furnace. The melting temperature is 650°C. Proper stirring is carried out after the alloy is completely melted. , let it stand for 5 minutes, wrap 0.15g of Mg in aluminum foil and dissolve it into the alloy liquid and stir it well. At the same time, add 29.1g of Zn-3Ti master alloy into another graphite crucible, control the melting temperature at 520°C, then add 19g of Al-12.6Si alloy and semi-solid Zn-3Ti master alloy into the alloy melt and mix well Afterwards, it was poured into a metal mold at room temperature to obtain an impact sample with a diameter of 12 mm and a length of 80 mm.
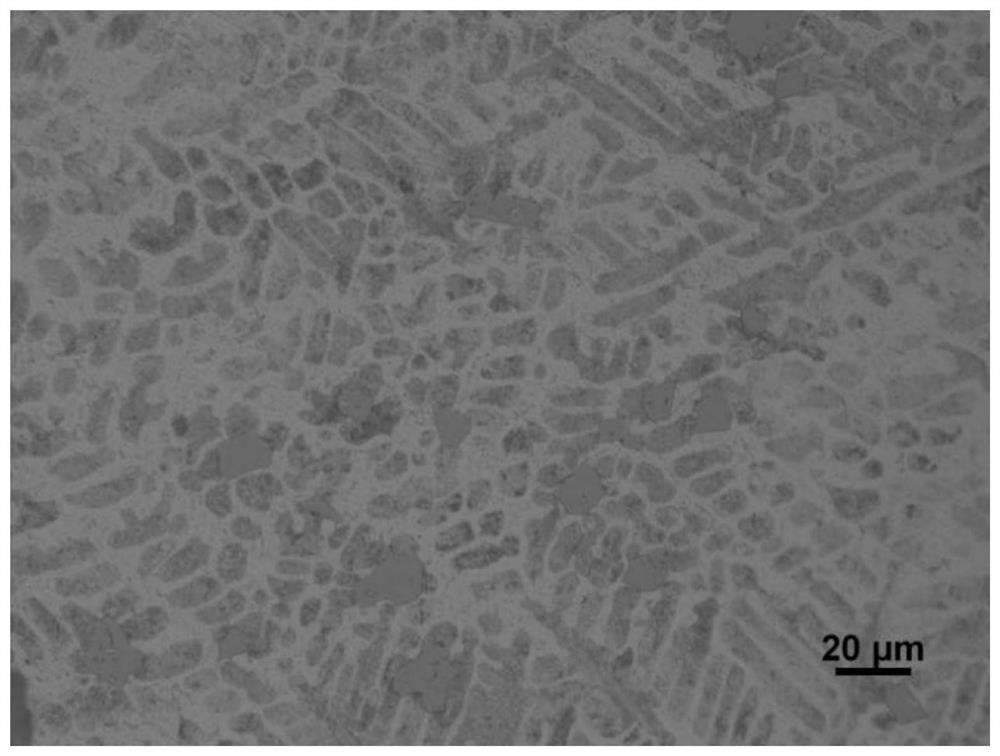
[0055] Figure 7 When the Si content is 0.8%, the microstructure of the Zn-11Al-1Cu-0.05Mg alloy with a Ti content of 0.3wt.% is added in combination. It can be seen that the microstructure of the alloy ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| hardness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| hardness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com