Polyol composition containing fine particles dispersed therein, process for production of polymeric polyols, and process for production of polyurethane resins
A technology of polyol composition and manufacturing method, which is applied in the field of polyurethane resin manufacturing, can solve the problems of polymer polyol with high viscosity, uneconomical, expensive raw materials, etc., and achieve excellent mechanical strength, sufficiently small particle size, and narrow particle size distribution Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
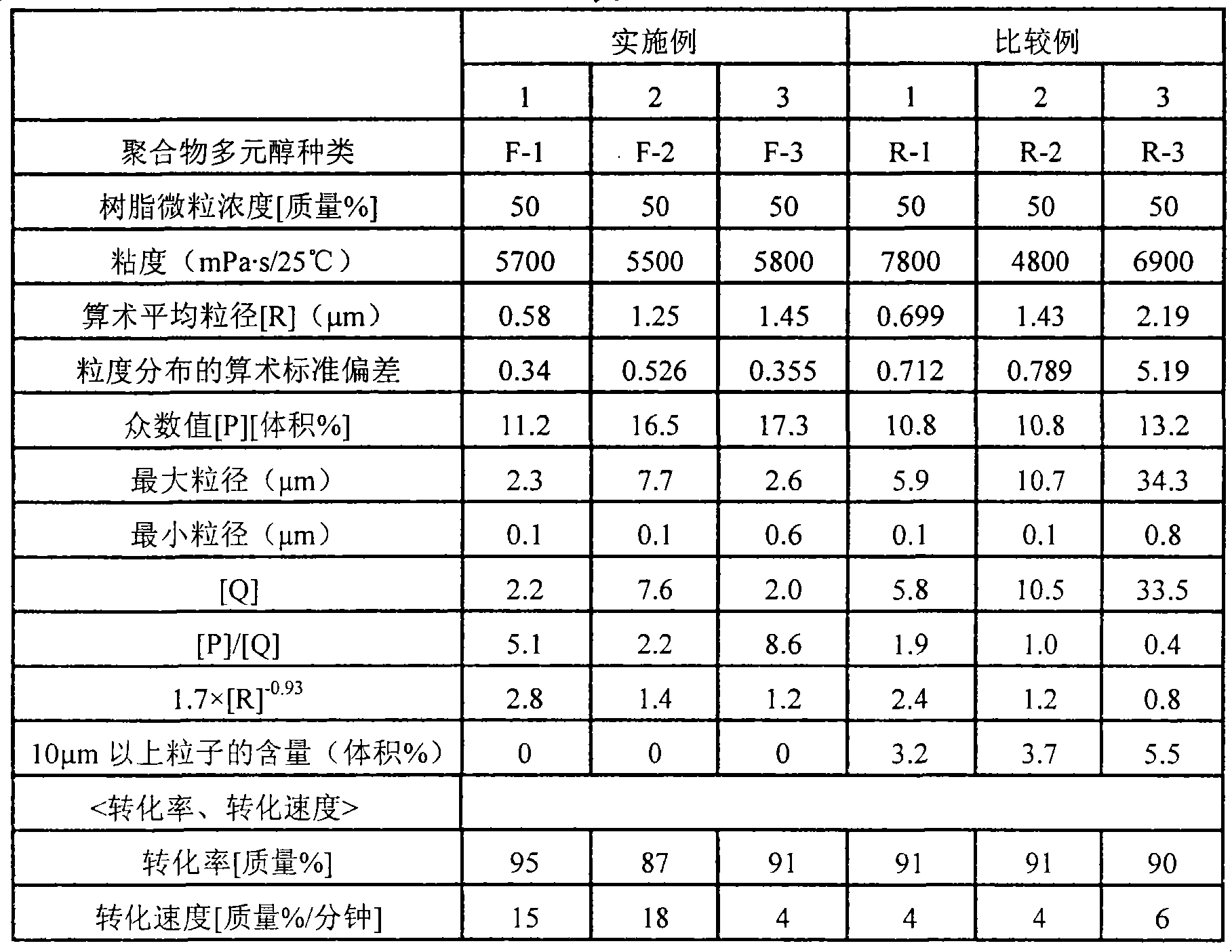
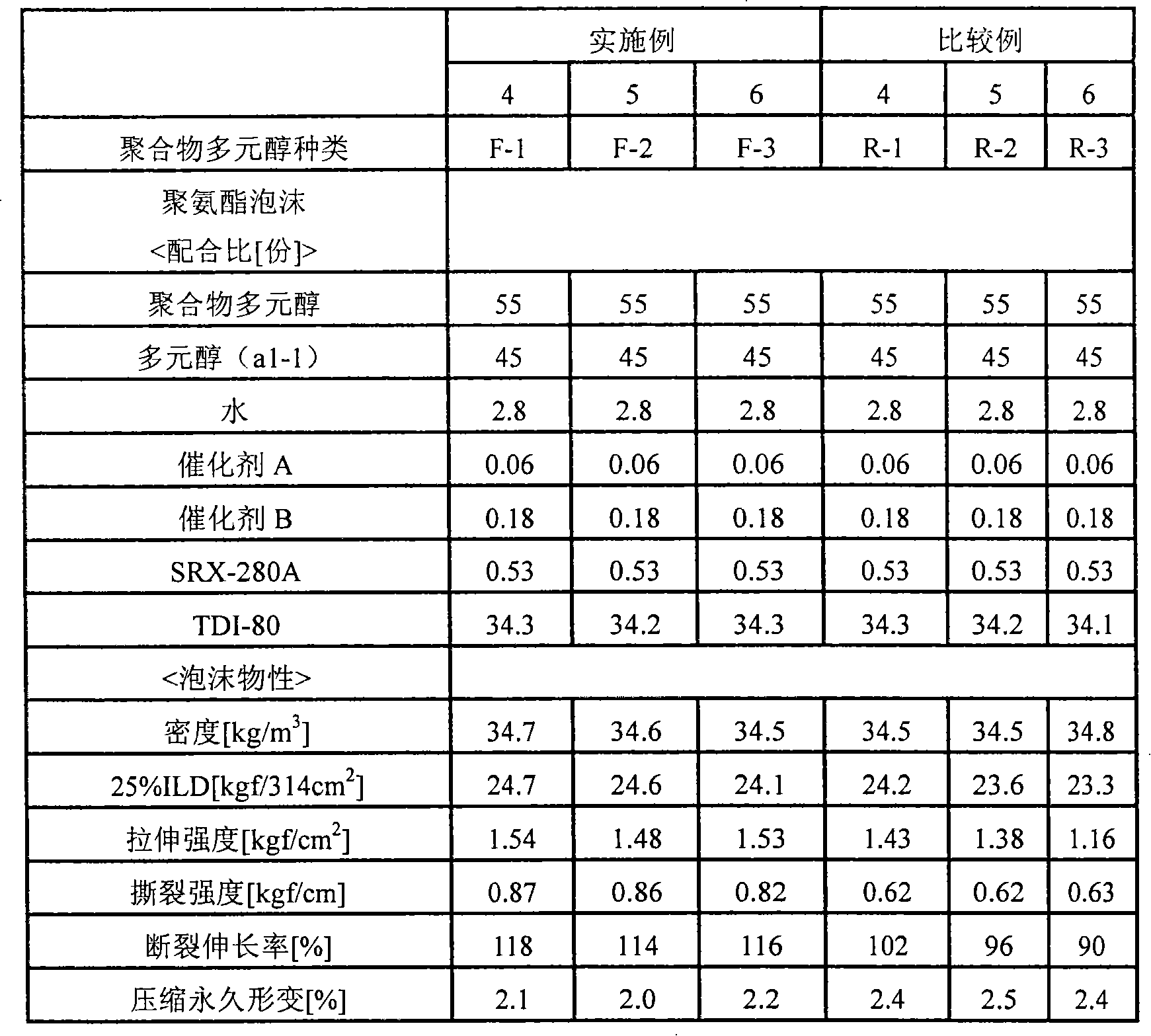
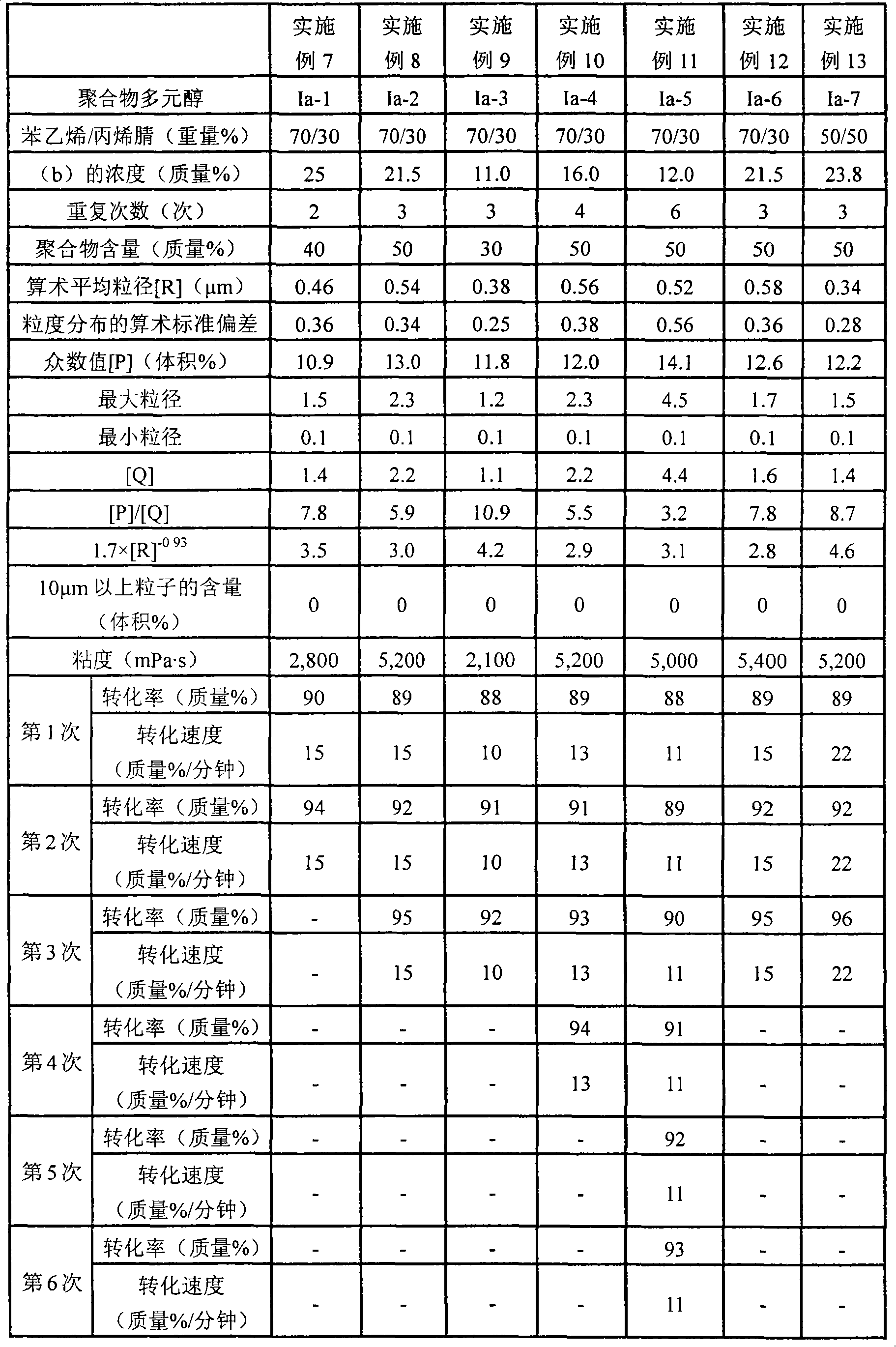
[0149] Hereafter, although an Example demonstrates this invention more concretely, this invention is not limited to this. Hereinafter, %, parts and ratio represent mass %, parts by mass and ratio by mass, respectively, unless otherwise specified.
[0150] The compositions, symbols, and the like of raw materials used in Examples and Comparative Examples are as follows.
[0151] (1) Polyol (a1)
[0152] Polyol (a1-1): Polyol obtained by adding glycerol in the order of PO-EO-PO, hydroxyl value = 56, internal EO unit content = 9%
[0153] Polyol (a1-2): Polyol obtained by adding to pentaerythritol in the order of PO-EO, hydroxyl value = 32, terminal EO unit content = 14%
[0154] (2) Dispersant (e)
[0155] e-1: Hydroxyl value = 20 obtained by linking 0.14 mol of polyol (a1-2) and 0.07 mol of 2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate via 0.16 mol of TDI, number of unsaturated groups / number of nitrogen-containing groups = 0.22 reactive dispersant [refer to US Patent No. 6,756,414 (correspond...
manufacture example -1
[0166] Production of Polymer Polyol Precursor (m1)
[0167] In a water-cooled jacketed pressure-resistant reaction vessel, add polyol (a1-1): 73 parts, acrylonitrile: 4.7 parts, styrene: 11 parts, allyl alcohol PO 2.2 mole adduct (the number average molecular weight is 186 ): 1 part, divinylbenzene: 0.05 parts, dispersant (e-1): 1.6 parts, xylene: 4.8 parts, and the temperature was adjusted to 107° C. under stirring. Radical polymerization initiator (k-1): 0.09 part, (k-2): 0.07 part was melt|dissolved in 3.2 parts of xylenes, and it press-injected into the said reaction container. After the initiator was charged, the polymerization started rapidly within 1 minute, and reached the maximum temperature of 160° C. in about 6 minutes. The polymer polyol precursor (m1) was obtained by aging at 140° C. for 30 minutes while removing the heat of polymerization. The conversion rate and the conversion rate were 78% and 13% by mass / min, respectively.
manufacture example -2
[0168] Production of polymer polyol precursor (m2)
[0169] Add polymer polyol precursor (m1): 100 parts, polyol (a1-1): 33 parts, acrylonitrile: 14 parts, styrene: 33 parts, allyl in a water-cooled jacketed pressure-resistant reaction vessel Alcohol PO 2.2 mole adduct: 3.3 parts, divinylbenzene: 0.14 parts, dispersant (e-1): 4.7 parts, xylene: 4.8 parts, and temperature was adjusted to 107° C. under stirring. Radical polymerization initiators (k-1): 0.24 parts and (k-2): 0.28 parts were dissolved in 3.2 parts of xylene, and then press-injected into the reaction container. After the initiator was charged, the polymerization started rapidly within 1 minute, and reached the maximum temperature of 160° C. in about 6 minutes. The polymer polyol precursor (m2) was obtained by aging at 140° C. for 30 minutes while removing the heat of polymerization. The conversion rate and the conversion rate were 84% and 14% by mass / min, respectively.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| transmittivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com