Method for hardening stainless steel and molten salt bath for realizing said method
A stainless steel, salt melting technology, applied in the field of hardened stainless steel, can solve the problems of high capital and energy cost, high equipment complexity, etc., to avoid equipment and energy consumption, easy to implement, and reduce adhesion loss.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
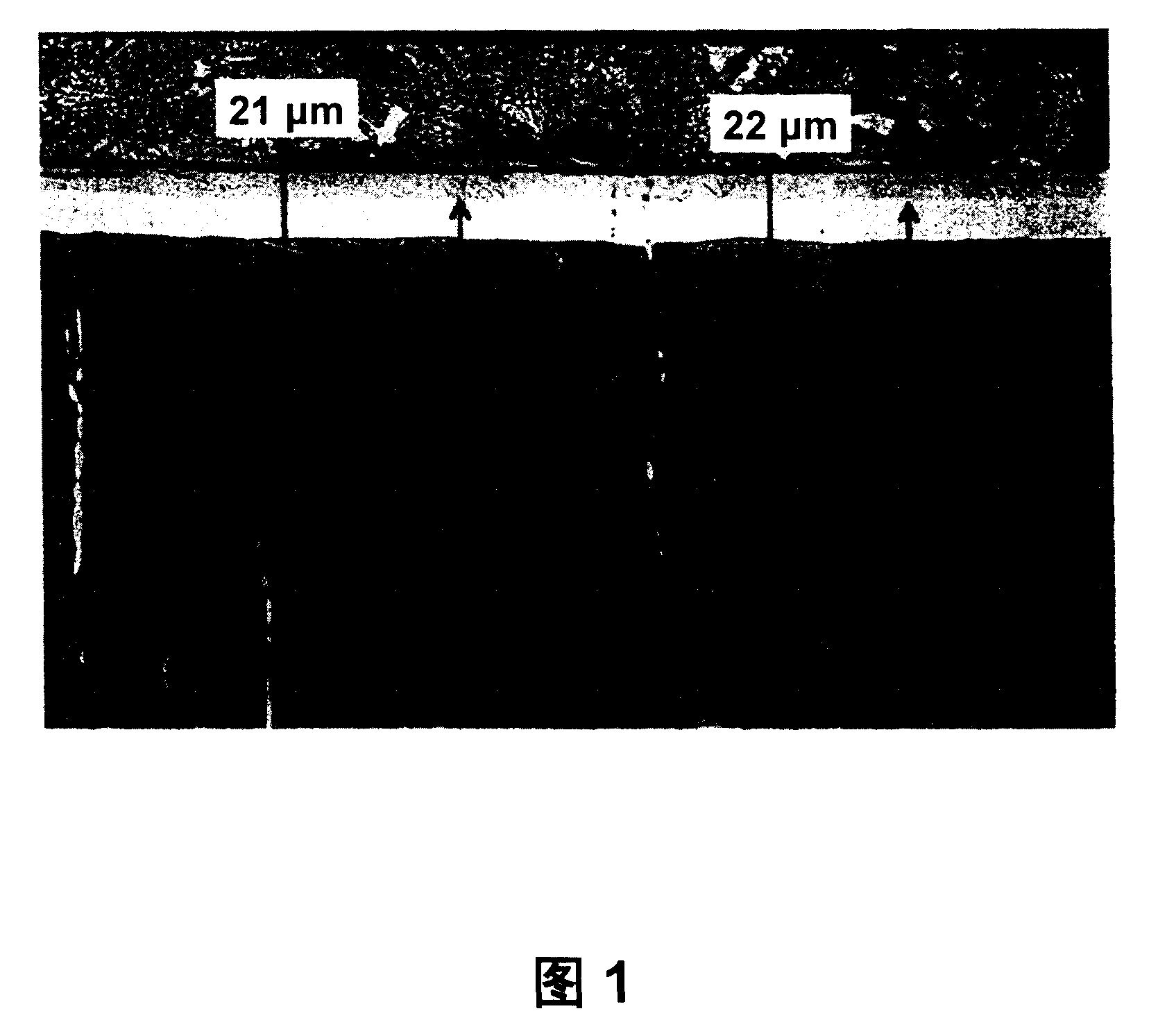
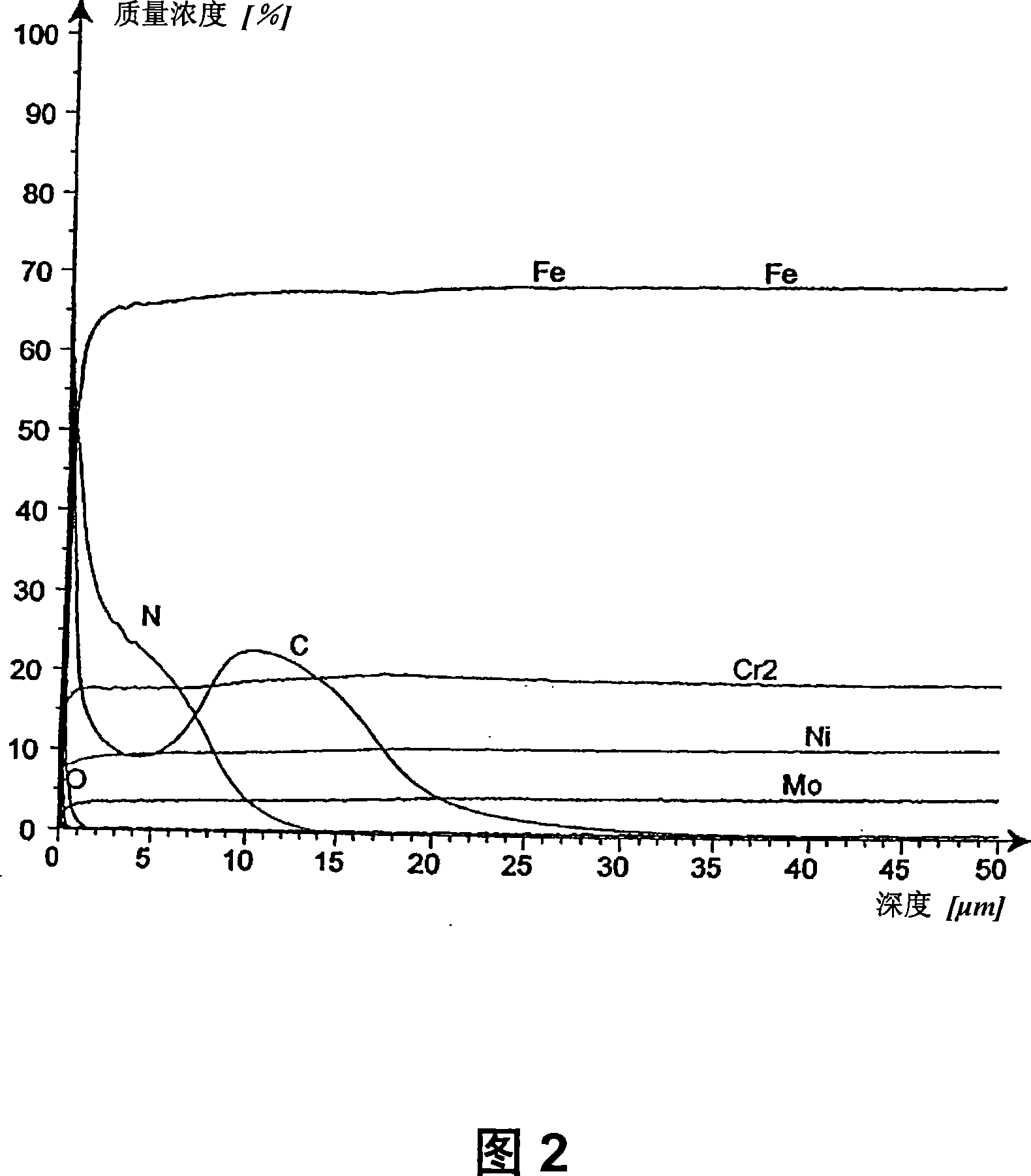
[0066] 42 kg dry potassium chloride, 34 kg dry lithium chloride and 20 kg dry barium chloride are weighed into a crucible made of refractory steel, eg raw material 1.4828, and mixed loosely. All salts must have a residual moisture of less than 0.3% by weight. The mixture was heated to 400°C to obtain a water clear melt. To this was slowly added 4 kg of potassium hexacyanoferrate(II) which had been dried in a muffle furnace at 140° C. for 12 hours before. When potassium hexacyanoferrate(II) was added, very small amounts of carbon were precipitated on the crucible walls and on the surface of the melt. Skim off the carbon with a sieve. There is then a water-clear melt which reaches an operating temperature of 400°C. 10 kg of workpieces made of stainless steel 1.4571 (raw material X6CrNiMoTi17-12.2) fixed on steel wires were immersed in the melt and exposed to the influence of the melt for 48 hours.
[0067] The result of this treatment is a 20 to 22 μm thick diffusion lay...
Embodiment 2
[0070] 43 kg dry potassium chloride, 30 kg dry lithium chloride, 17 kg dry strontium chloride and 3 kg dry barium chloride were weighed into a crucible made of high temperature resistant steel and mixed loosely. All salts must have a residual moisture of less than 0.3% by weight. The mixture was heated to 400°C to obtain a water clear melt. To this was slowly added 7 kg of potassium hexacyanoferrate(II) which had been dried in a muffle furnace at 140° C. for 12 hours before. There is then a water-clear melt down to the operating temperature of 370°C. 10 kg of workpieces made of stainless steel 1.4301 fixed on steel wires are immersed in the melt and exposed to the influence of the melt for 24 to 48 hours.
[0071] Depending on the treatment time, this treatment results in a 10 to 25 μm thick diffusion layer on the surface of the treated components and samples, which is visible metallographically by cross-grinding and etching with the etchant V2A-Beize.
Embodiment 3
[0073] In a crucible made of refractory steel, 37 kg dry potassium chloride, 26 kg dry lithium chloride and 17 kg dry strontium chloride were weighed and mixed loosely. All salts must have a residual moisture of less than 0.3% by weight. The mixture was heated to 400°C to obtain a water clear melt. 10kg KCN and 10kg NaCN were slowly added thereto. The formed melt reaches an operating temperature of 400 to 410°C. 10 kg of workpieces made of stainless steel 1.4301 fixed on steel wires are immersed in the melt and exposed to the influence of the melt for 24 hours.
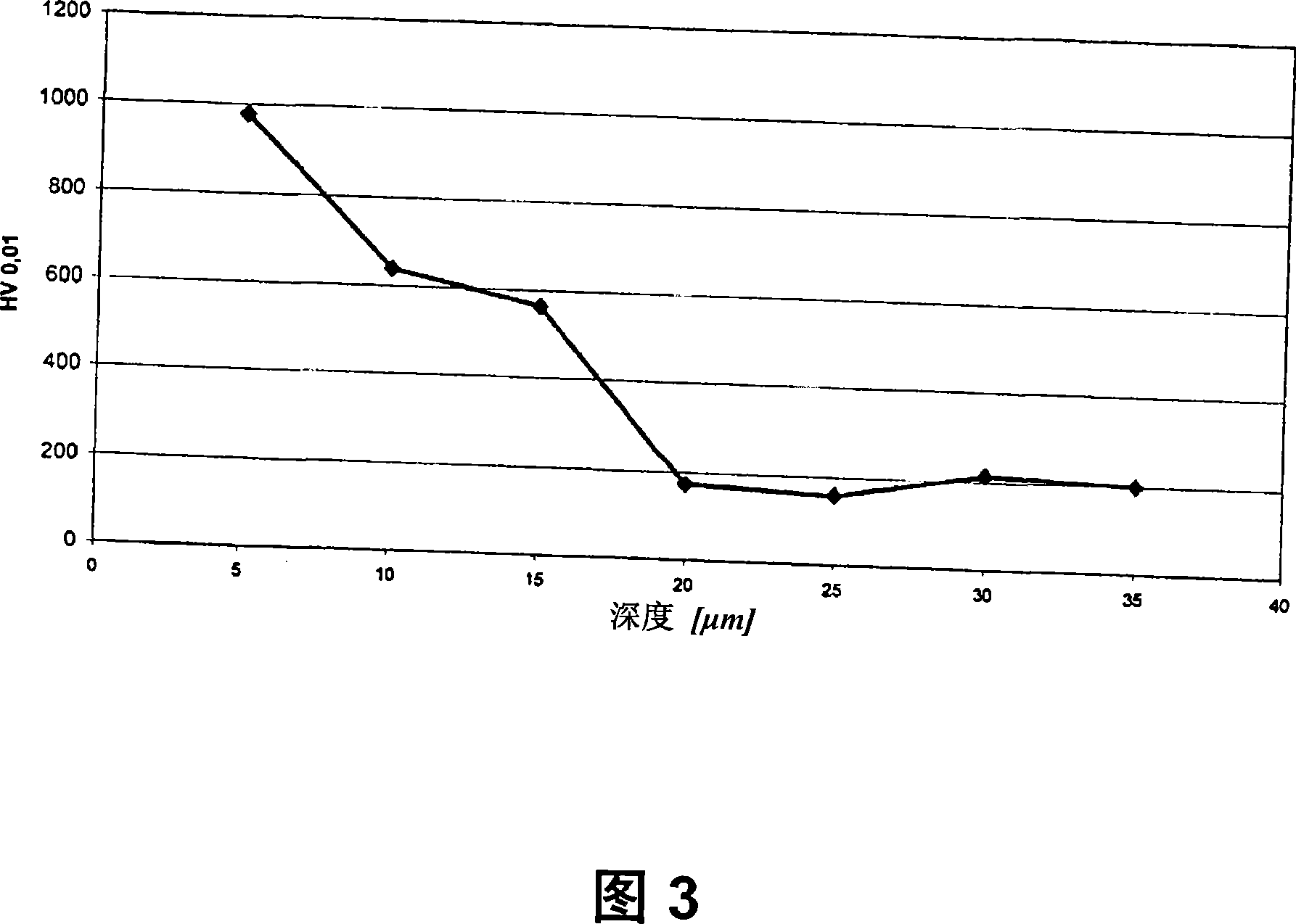
[0074] The result of this treatment is an approximately 10 μm thick diffusion layer on the surface of the treated components and samples, which is visible metallographically by cross-grinding and etching with the etchant V2A-Beize. The hardness of this layer was measured to be 620 HV (0.5).
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| hardness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com