Glutamic acid extracting technique
An extraction process, glutamic acid technology, applied in the field of glutamic acid extraction process, can solve problems such as poor extraction rate of glutamic acid and product quality, high treatment cost, and large amount of acid and alkali, so as to achieve good product quality and reduce sewage The effect of processing costs and reducing production costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
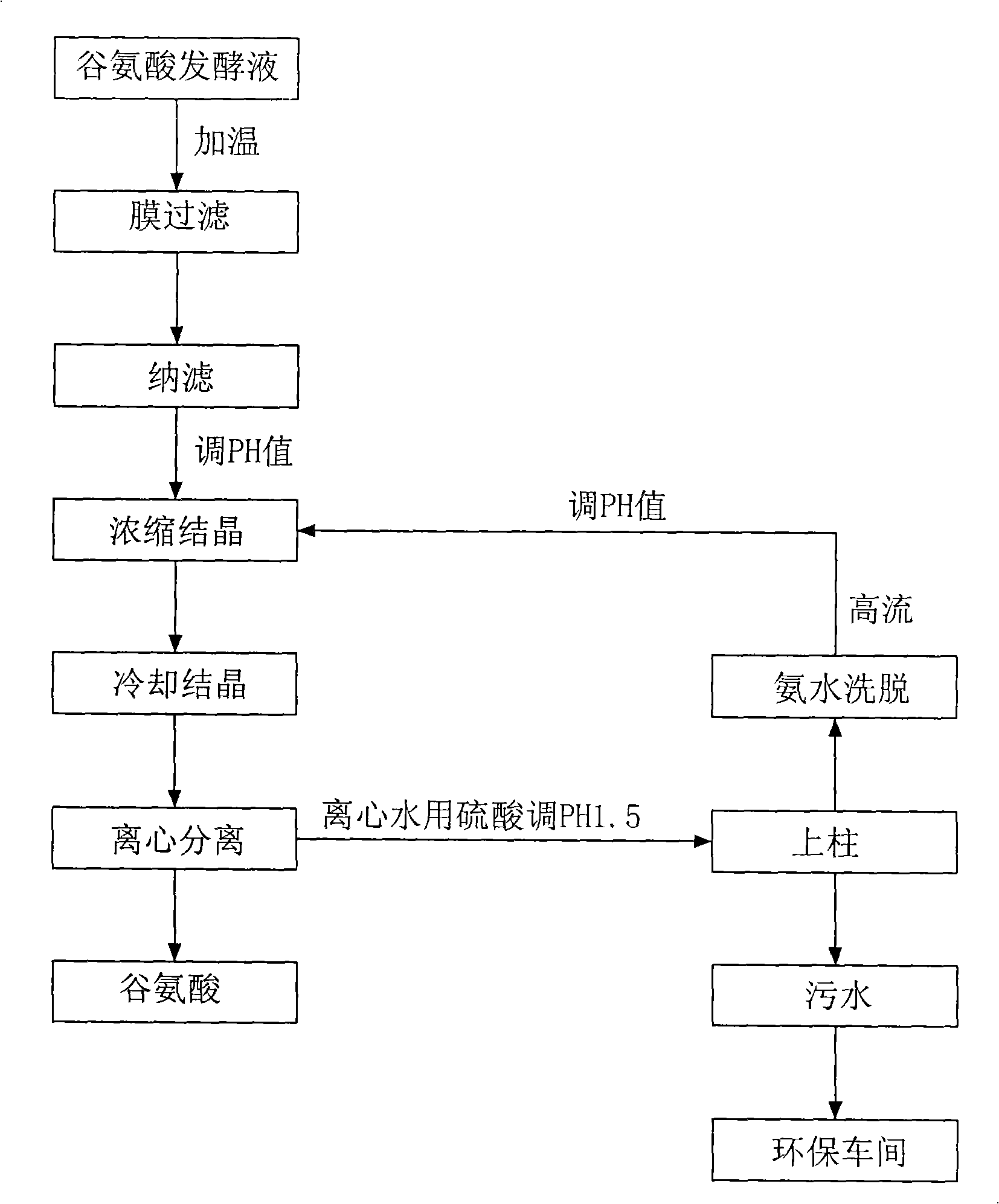
[0031] 1. Heat the glutamic acid fermentation broth (containing 12% glutamic acid) with steam to 95°C for ultrafiltration (membrane molecular weight cut-off is 30,000 molecular weight, the same below), and remove bacteria and macromolecular proteins in the fermentation broth;
[0032] 2. Filter the fermented liquid after ultrafiltration with a nanofiltration system (membrane filtration with a molecular weight cut-off of 600) to remove small molecular proteins and pigments in the fermented liquid;
[0033] 3. Take 800 ml of glutamic acid fermentation broth (containing 11.6% glutamic acid) after ultrafiltration and nanofiltration, heat it to 95°C, add sulfuric acid to adjust the pH of the fermentation broth to 4.0, and then add it to the crystallization pot of the rotary evaporator , while adding 2g of glutamic acid as a seed crystal for evaporation and concentration, the temperature is controlled at 90-95°C during concentration;
[0034] 4. Concentrate until about 200ml of liqu...
Embodiment 2
[0039] 1. Heat 800 liters of glutamic acid fermentation broth (containing 10.2% glutamic acid) to 60°C, adjust the pH to 4.8 and perform ultrafiltration to remove bacteria and macromolecular proteins in the fermentation broth;
[0040] 2. Filter the fermented liquid after ultrafiltration with a nanofiltration system (membrane filtration system with a molecular weight cut-off of 1000) to remove small molecular proteins and pigments in the fermented liquid;
[0041] 3. Heat the fermented liquid after nanofiltration to 75°C, add sulfuric acid to adjust the pH of the fermented liquid to 3.0, then enter the crystallization pot, and add 2kg of glutamic acid as a seed crystal for evaporation and concentration, and control the temperature at 80-85°C during concentration;
[0042] 4. Concentrate until there are about 200 liters of liquid left in the evaporator, then evaporate about 75% of the water, discharge to the crystallization tank, slowly cool down to 40°C, and centrifuge to separ...
Embodiment 3
[0047] 1. Heat 800 liters of glutamic acid fermentation broth (containing 10.2% glutamic acid) to 80°C, adjust the pH to 4.8 and perform ultrafiltration to remove bacteria and macromolecular proteins in the fermentation broth;
[0048] 2. Filter the fermented liquid after ultrafiltration with a nanofiltration system (membrane filtration system with a molecular weight cut-off of 800) to remove small molecular proteins and pigments in the fermented liquid;
[0049]3. Heat the fermented liquid after nanofiltration to 85°C, add sulfuric acid to adjust the pH of the fermented liquid to 3.5, then enter the crystallization pot, add 2kg of glutamic acid as a seed crystal for evaporation and concentration, and control the temperature at 80-85°C during concentration;
[0050] 4. Concentrate until there are about 200 liters of liquid left in the evaporator, then evaporate about 75% of the water, discharge to the crystallization tank, slowly cool down to 40°C, and centrifuge to separate gl...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com