Viscous microstructure preparation method
A manufacturing method and microstructure technology, applied in microstructure technology, microstructure devices, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve problems such as failure to meet mass production requirements, changes in fiber structure characteristics, and inability to reuse
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0034] In order to describe in detail the technical characteristics of the present invention, the following two preferred embodiments are given and are described as follows in conjunction with the accompanying drawings, wherein:
[0035] Such as Figure 1 to Figure 5 As shown, the manufacturing method of a viscous microstructure provided by the first preferred embodiment of the present invention mainly has the following steps:
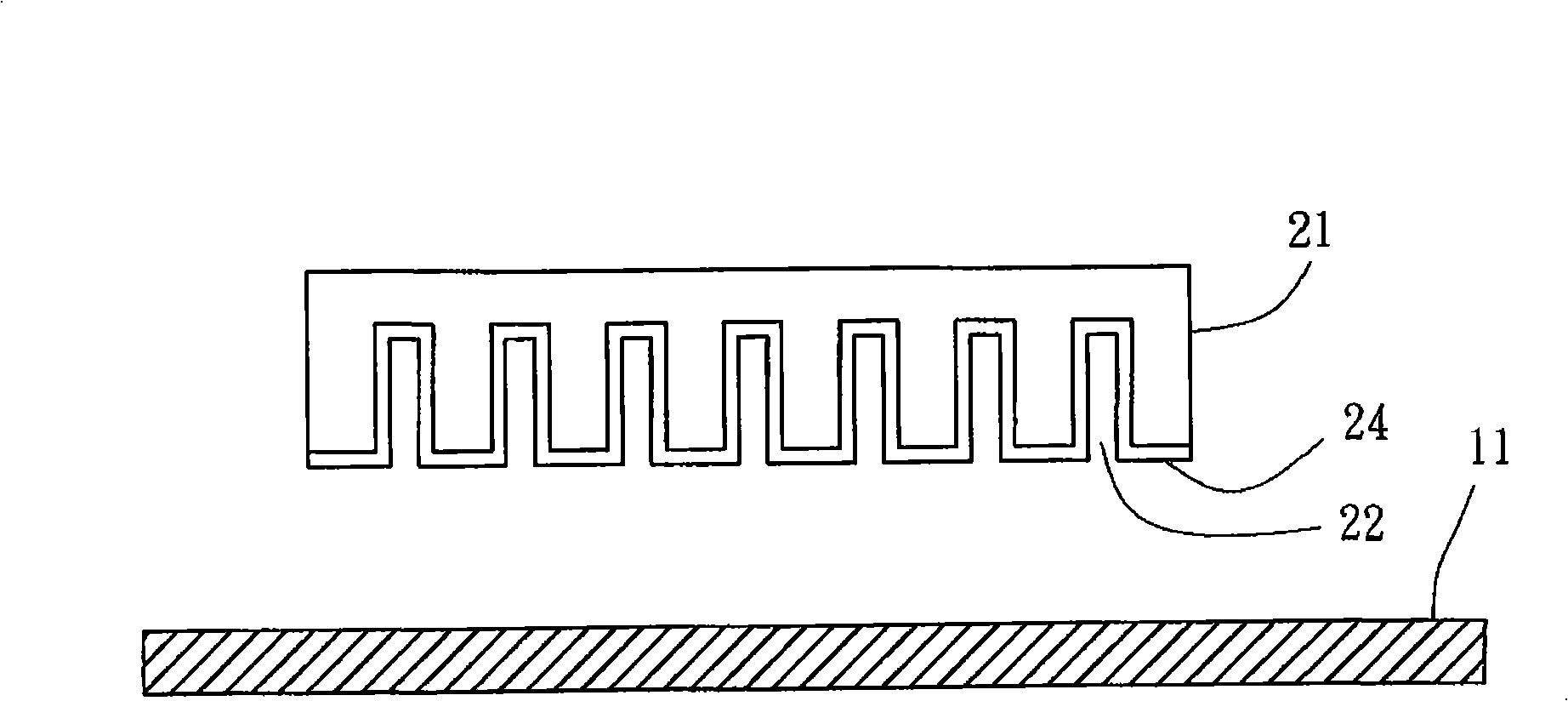
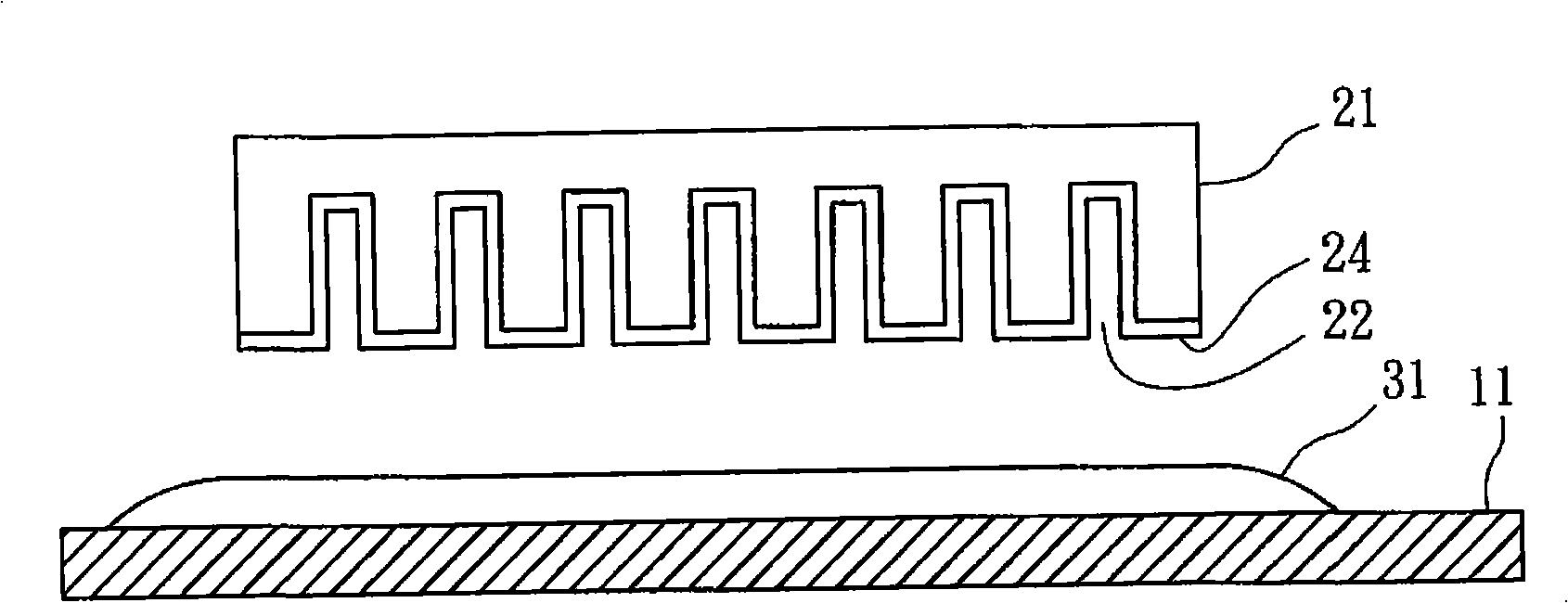
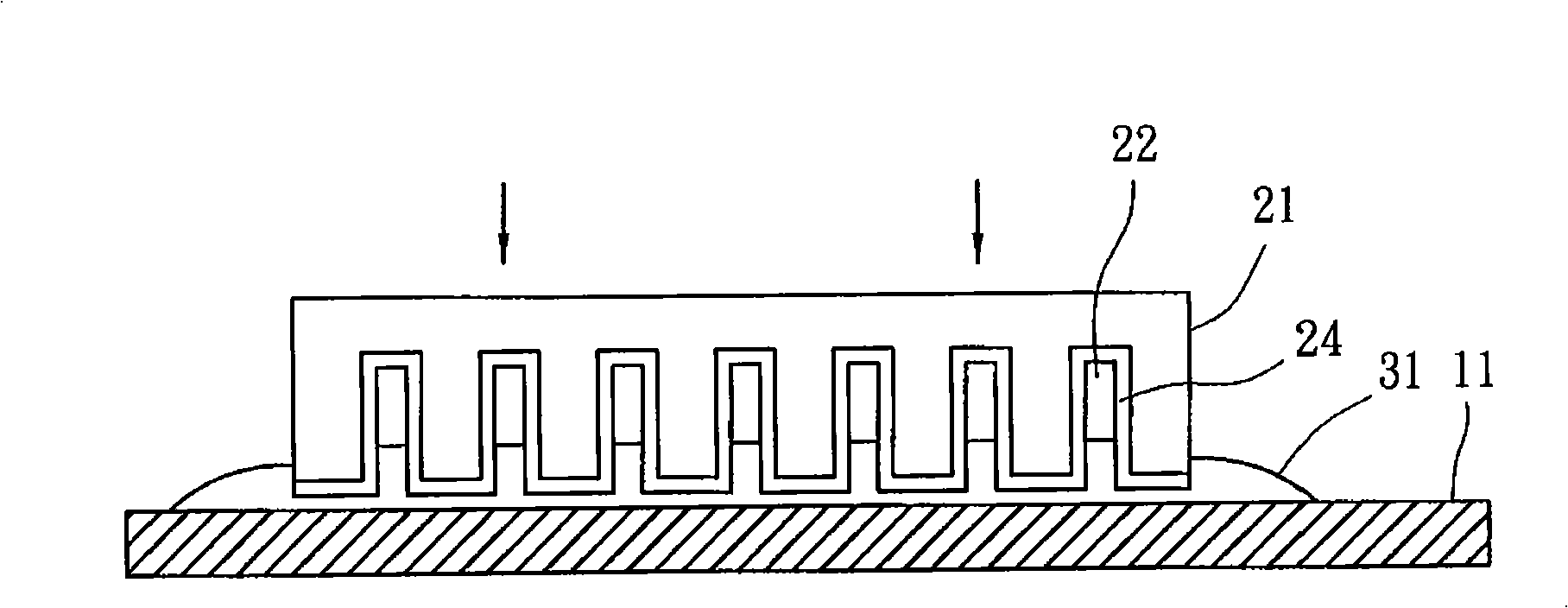
[0036] a) Prepare a substrate 11 and a mold 21: as figure 1 As shown, the bottom surface of the mold 21 has a plurality of nano-scale grooves 22, each of which has a predetermined depth, and the diameter of each of the grooves 22 is between 0.01 and 5 microns. The bottom surface of the mold 21 is provided with a layer of release agent 24 , and the release agent 24 covers the bottom surface of the mold 21 and the groove walls of the grooves 22 . The mold release agent 24 helps to pull out the mold, allowing the finished product to break away from the ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| height | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com