Aromatization method without hydrogen for light hydrocarbon
An aromatization and non-hydrogenation technology, which is applied in the production of aromatics or clean gasoline components, as well as in the field of high-quality liquefied gas, can solve the problems of catalyst regeneration methods not given, and achieve easy control of reaction temperature, increased flexibility, and use long life effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0058] (1) Preparation of composite carrier
[0059] Get 67.6 kilograms of pseudo-boehmite powder (production of Sasol company, PURAL SB, the alumina content is 74% by mass), under stirring condition, join 300 kilograms concentration and be in the nitric acid aqueous solution of 1.1 mass %, after stirring for 2 hours peptization, add 55.0 kilograms of silica / alumina molar ratio is 60 HZSM- 5 Zeolite powder (zeolite content 91%), stirred at high speed for 3 hours. Drop the prepared slurry into an oily ammonia column containing 8% by mass of ammonia water, take out the wet bulb formed in the oily ammonia column, dry at 60°C for 10 hours, and roast at 550°C for 3 hours to obtain a composite carrier, which is a composite carrier containing HZSM- 5 zeolite 50% by mass alumina pellets.
[0060] (2) Preparation of catalyst
[0061] Get 50 kilograms of composite carriers, use 50 kilograms containing 4.7 mass % of zinc nitrate, 3.0 mass % of mixed rare earth chloride (wherein lanth...
example 2
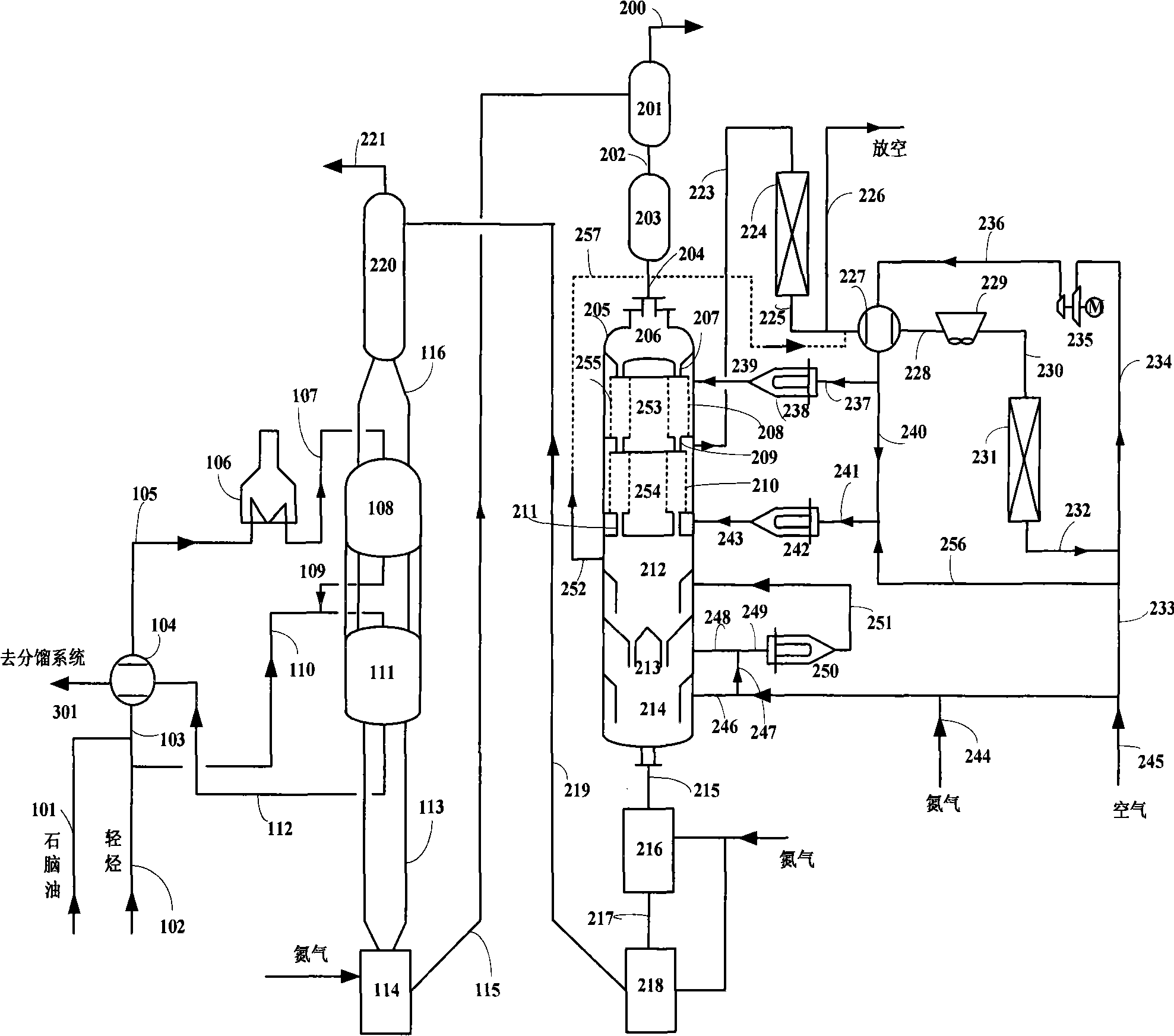
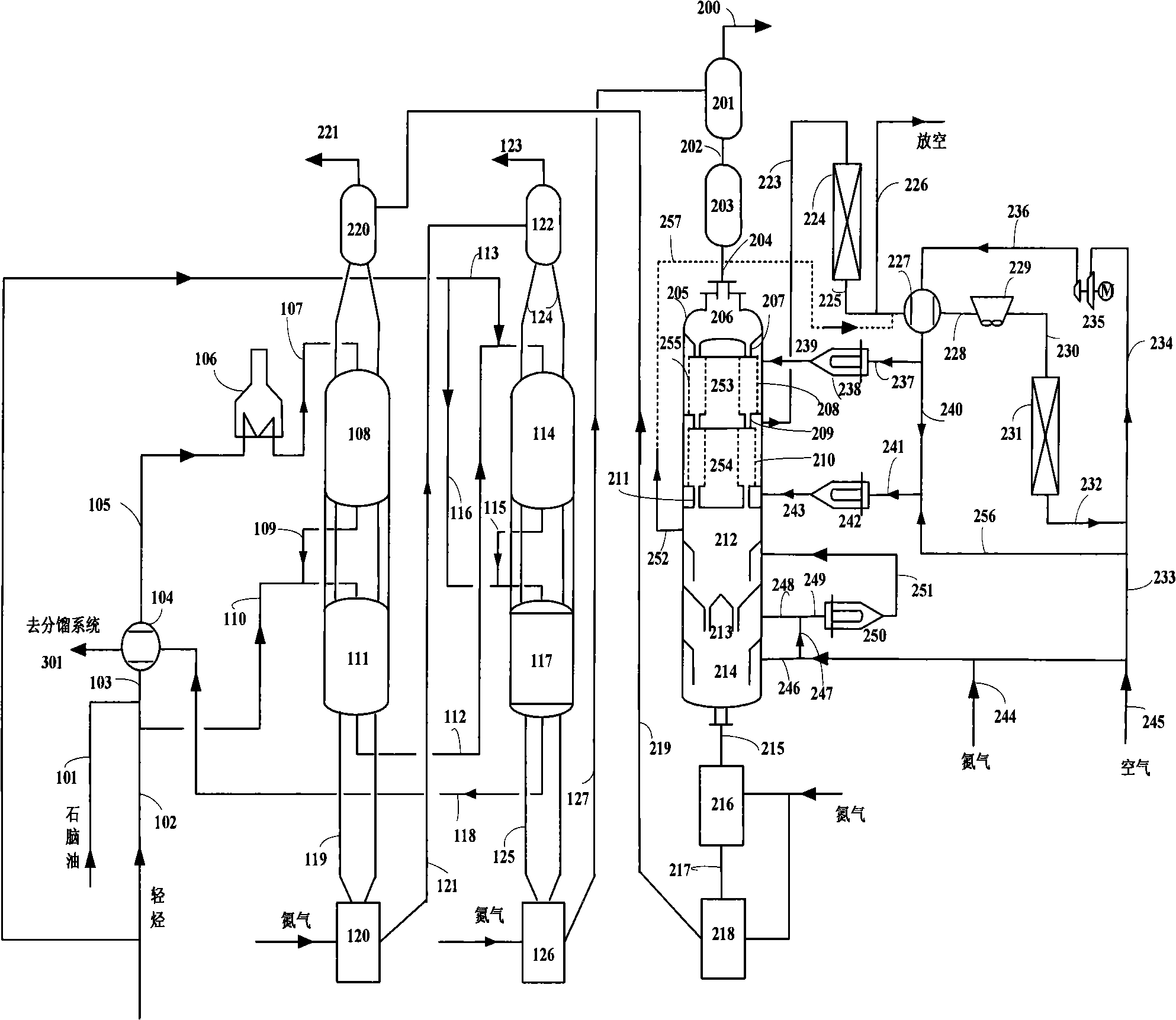
[0064] according to figure 1 Shown technological process, use the catalyst that example 1 makes, carry out aromatization reaction test with the straight-run naphtha shown in 60 mass % table 1 and the light hydrocarbon shown in 40 mass % table 2 as raw material, react in carried out under non-hydrogen conditions. Control the raw material inlet temperature of each reactor to be 400°C, the reaction pressure to be 0.5MPa, and the mass space velocity of raw material feed to be 0.5h -1 . Light hydrocarbons are equally divided into two streams, one stream is mixed with straight-run naphtha and enters the first reactor through a heating furnace, and the other stream of light hydrocarbons directly enters the second reactor 111 in the form of cold material. The pressure of the regenerator is 0.7MPa, the inlet temperature of regeneration gas in the first-stage coking zone is 470°C, and the oxygen content is 0.5% by volume; the inlet temperature of regeneration gas in the second-stage b...
example 3
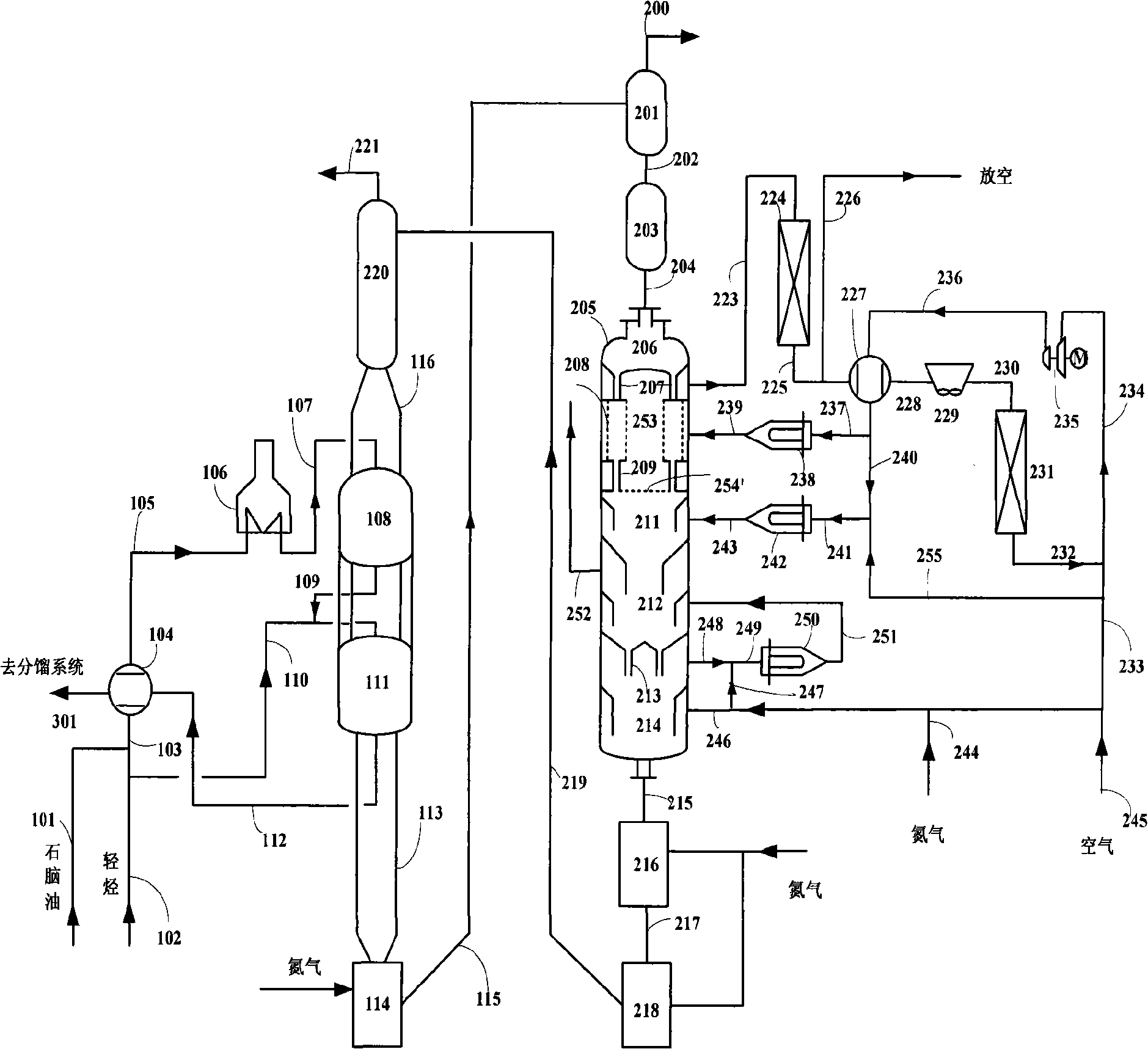
[0066] according to figure 2The technological process shown, uses catalyst A, carries out aromatization reaction test with the straight-run naphtha shown in 60 mass % table 1 and the light hydrocarbon shown in 40 mass % table 2 as raw material, reacts in non-hydrogenation under conditions. The operating conditions of the reaction part and the regenerator, the residence time of the ungenerated catalyst in the coking zone, the temperature of the drying zone and the cooling zone are all the same as in Example 2, the difference is that the regeneration gas enters the two-stage coking zone from the middle, and the test results are shown in table 3.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| research octane number | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com