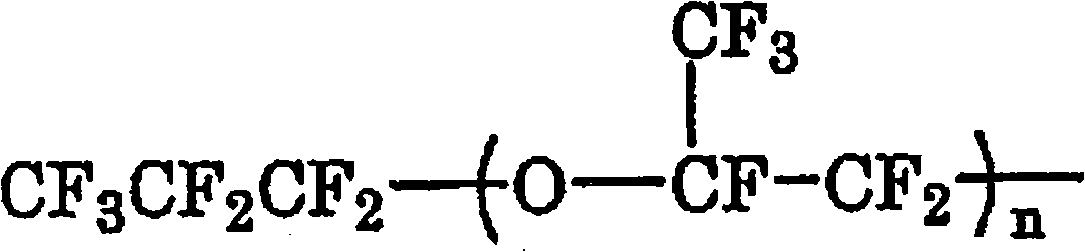Aqueous dispersion of low molecular weight polytetrafluorethylene and preparation method thereof
A technology of water-based dispersion liquid and polytetrafluoroethylene, which is applied in the direction of pharmaceutical formulations, toiletry preparations, cosmetic preparations, etc., can solve the problems of lack of practicability, unrecorded implying addition of chain transfer agent, polymer emulsified particle size and molecular weight Data and other issues to achieve the effect of low manufacturing cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
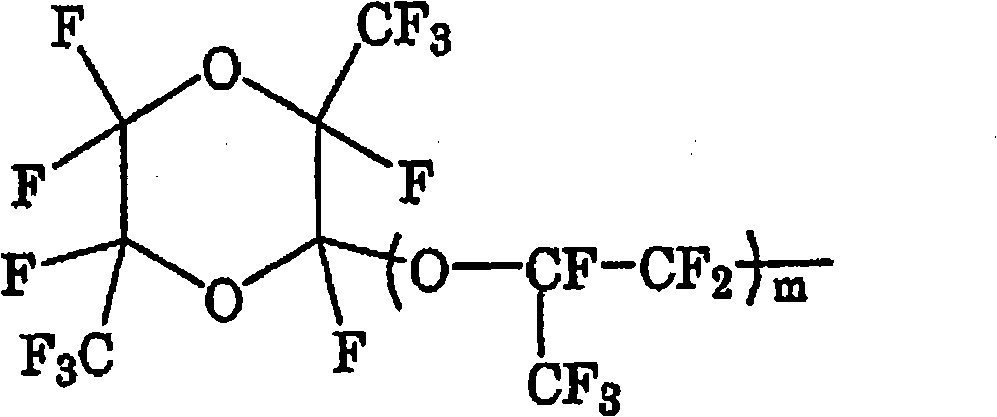
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
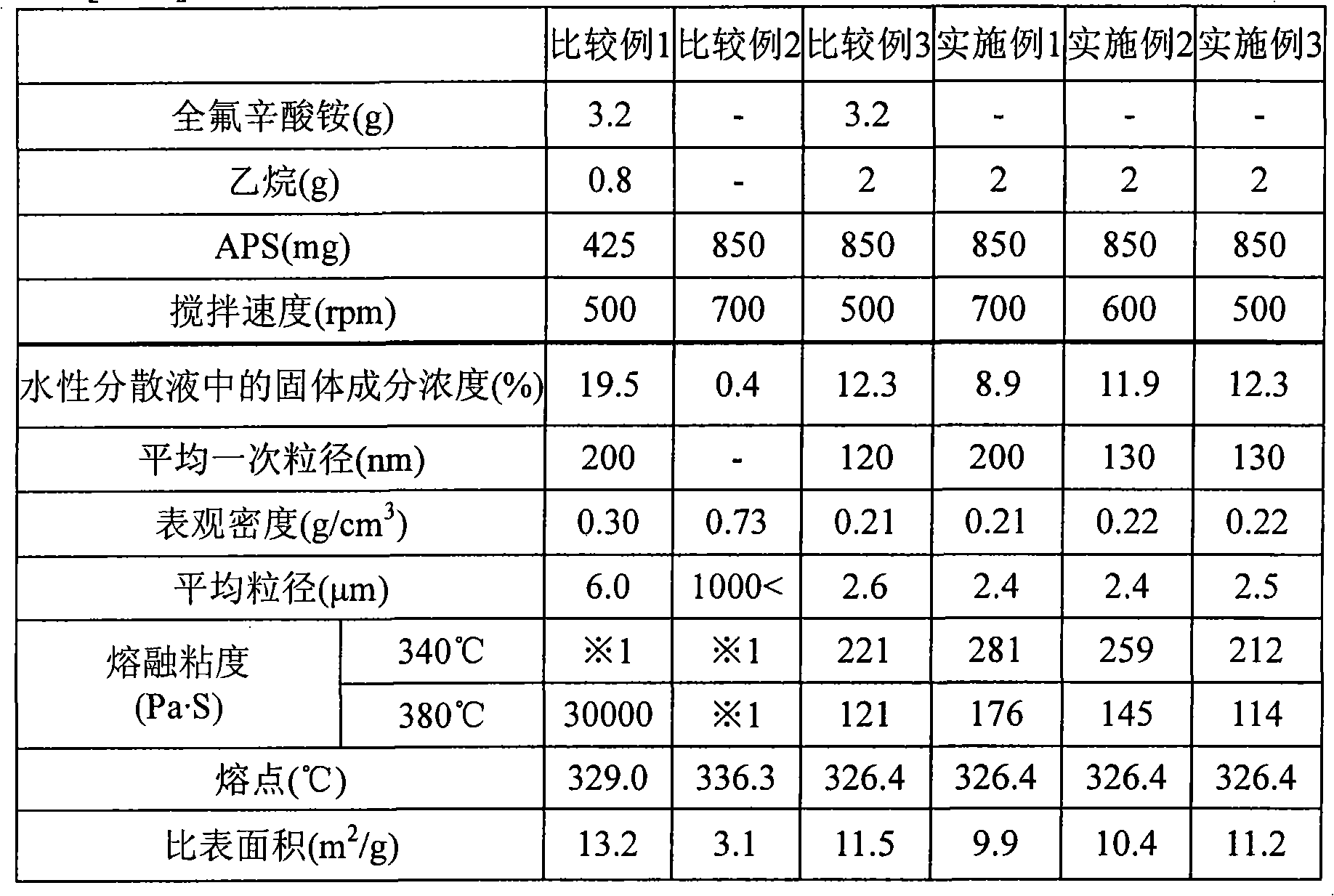
[0148] APFO is not added to the system, and the polymerization initiator and the chain transfer agent are the amounts shown in Table 1, and the stirring speed in the reaction is controlled to 700rpm, except that, in the same manner as in Comparative Example 1, an aqueous solution of low molecular weight PTFE was obtained. Dispersions. In the resulting aqueous dispersion, polymer particles hardly appeared on the air-liquid interface.
[0149] Coagulation, washing, and drying steps were performed on the above-mentioned aqueous dispersion in the same manner as in Comparative Example 1 to obtain the target low-molecular-weight PTFE powder.
[0150] Add TDS-80C (Daiichi Kogyo Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.) at 6.0% by mass relative to the mass of low-molecular-weight PTFE as a nonionic surfactant to the above-mentioned aqueous dispersion, adjust the pH to 9.0 with aqueous ammonia, and place the mixture under normal pressure. By standing still at a temperature of 65° C., water was evapor...
Embodiment 2
[0152] An aqueous dispersion of low-molecular-weight PTFE was obtained in the same manner as in Example 1, except that the stirring speed during the reaction was controlled to 600 rpm. In the resulting aqueous dispersion, polymer particles hardly appeared on the air-liquid interface.
[0153] Coagulation, washing, and drying steps were performed on the aqueous dispersion in the same manner as in Example 1 to obtain the desired low-molecular-weight PTFE powder.
Embodiment 3
[0155] An aqueous dispersion of low-molecular-weight PTFE was obtained in the same manner as in Example 1, except that the stirring speed during the reaction was controlled to 500 rpm. In the resulting aqueous dispersion, polymer particles hardly appeared on the air-liquid interface. Coagulation, washing, and drying steps were performed on the aqueous dispersion in the same manner as in Example 1 to obtain a low-molecular-weight PTFE powder as the target object.
[0156] The aqueous dispersion of low-molecular-weight PTFE obtained in each embodiment and comparative example 1 was subjected to the physical property evaluations of the following (1) to (2), and the powder obtained in each embodiment and each comparative example was subjected to the following (3) )~(7) physical performance evaluation.
[0157] (1) Solid content concentration (P%) in aqueous dispersion
[0158] The aqueous dispersion (Xg) was heated at 150° C. for 3 hours, and the solid content concentration (P%) ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com