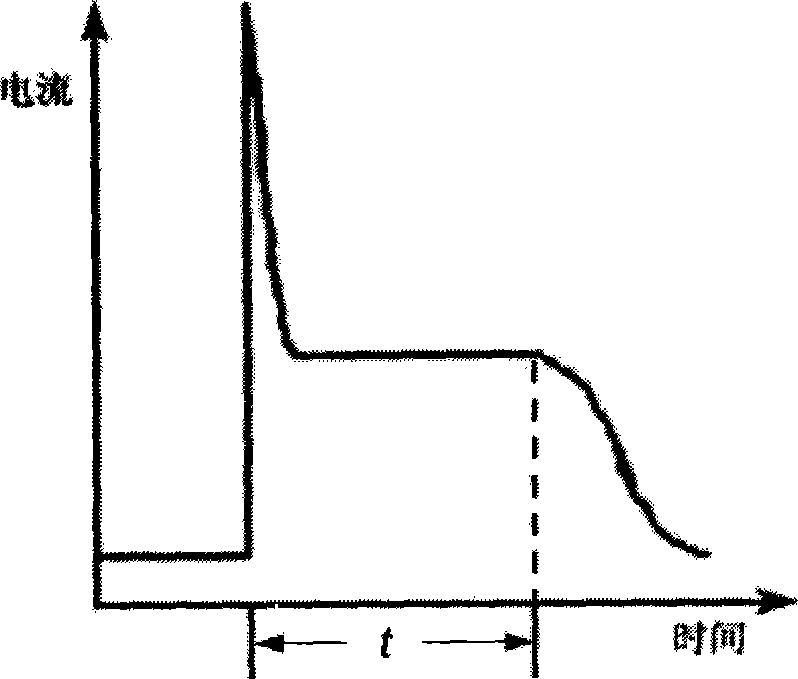
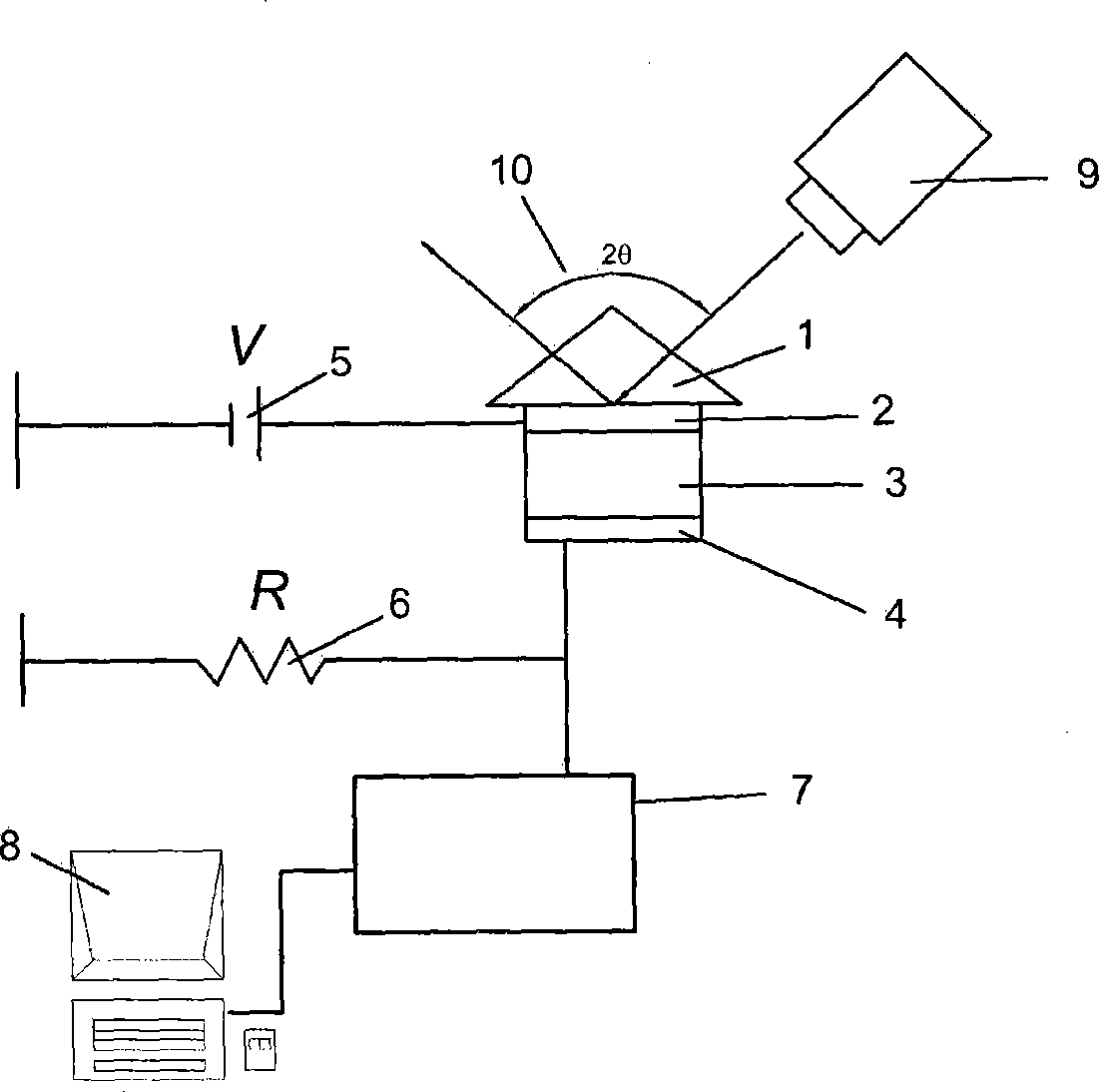
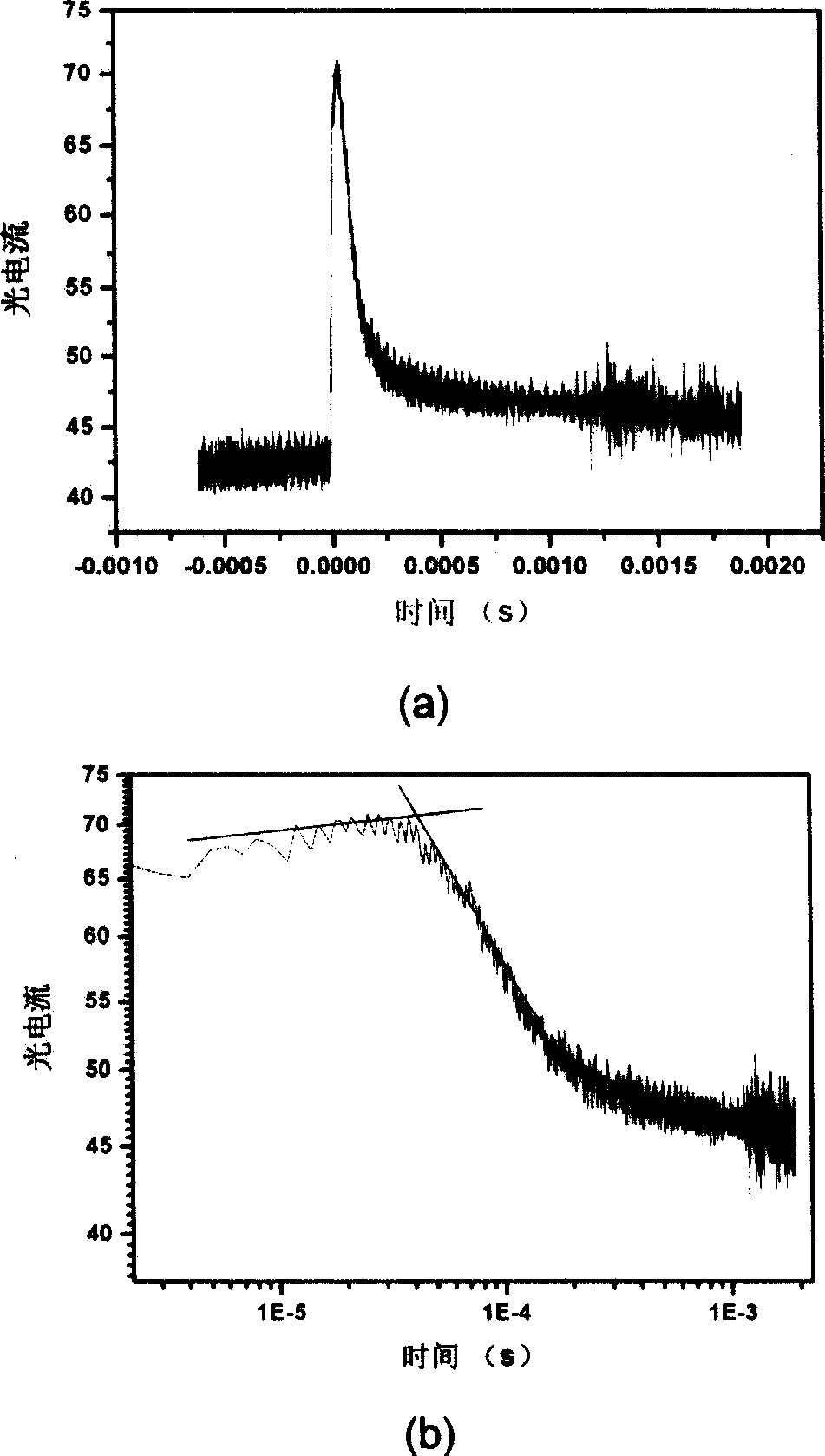
Method for measuring carrier mobility of organic semiconductor by using evanescent wave as excitation source
A carrier mobility, organic semiconductor technology, applied in the measurement of electricity, measurement devices, measurement of electrical variables, etc., can solve the problems of inaccuracy, difficulty in carrier mobility, and difficulty in measuring the thickness of photogenerated carrier thin layers. , to achieve the effect of improving accuracy and reducing measurement error
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0042] Firstly, according to the content of the invention, the instruments needed for the test system are selected. Among them, the Nd:YAG laser with a pulse width of 6 ns is selected as the light source (Contimuum Minilite II, the single pulse energy range of the excitation light is about 10uJ~5mJ, and the wavelength is 532nm); an adjustable optical goniometer (Rigakn, Japan) ; DC stabilized voltage, the output range is 0 ~ 200V; adjustable rheostat, the resistance range is 0 ~ 10 6 ohm; storage oscilloscope (Tektronix 4054), the frequency is 500MHz and microcomputer, etc., according to the attached figure 2 The composition of the carrier mobility measurement setup is shown.
[0043] The purpose of this example is to measure the hole mobility of a polyphenylene vinylene conjugated polymer (MEH-PPV) organic semiconductor film. Therefore, the MEH-PPV film was used as the active layer of the test sample.
[0044] First, 20 mg of MEH-PPV was dissolved in 1 ml of chloroform (C...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com