Method for separating electrochemical activity bacterial strain and detecting electrochemical activity
A separation method and electrochemical technology, applied in the field of microbial separation and inspection, can solve the problems of cumbersome inspection operation of electrochemically active strains, unfavorable growth of electrochemically active strains, difficulty in obtaining high-efficiency electricity-producing bacteria, etc., so as to shorten the screening period. , The effect of rich composition, saving time and effort
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
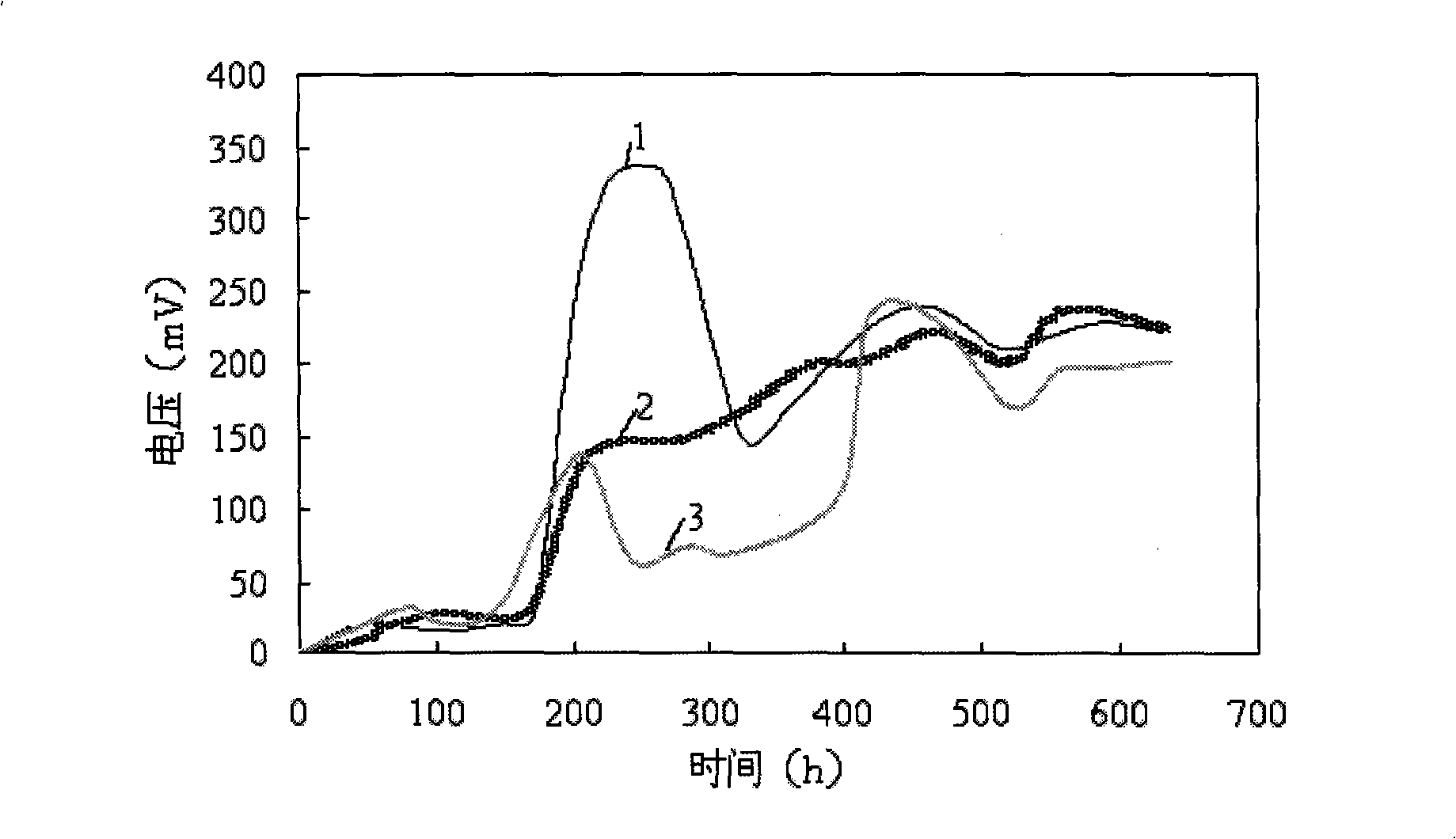
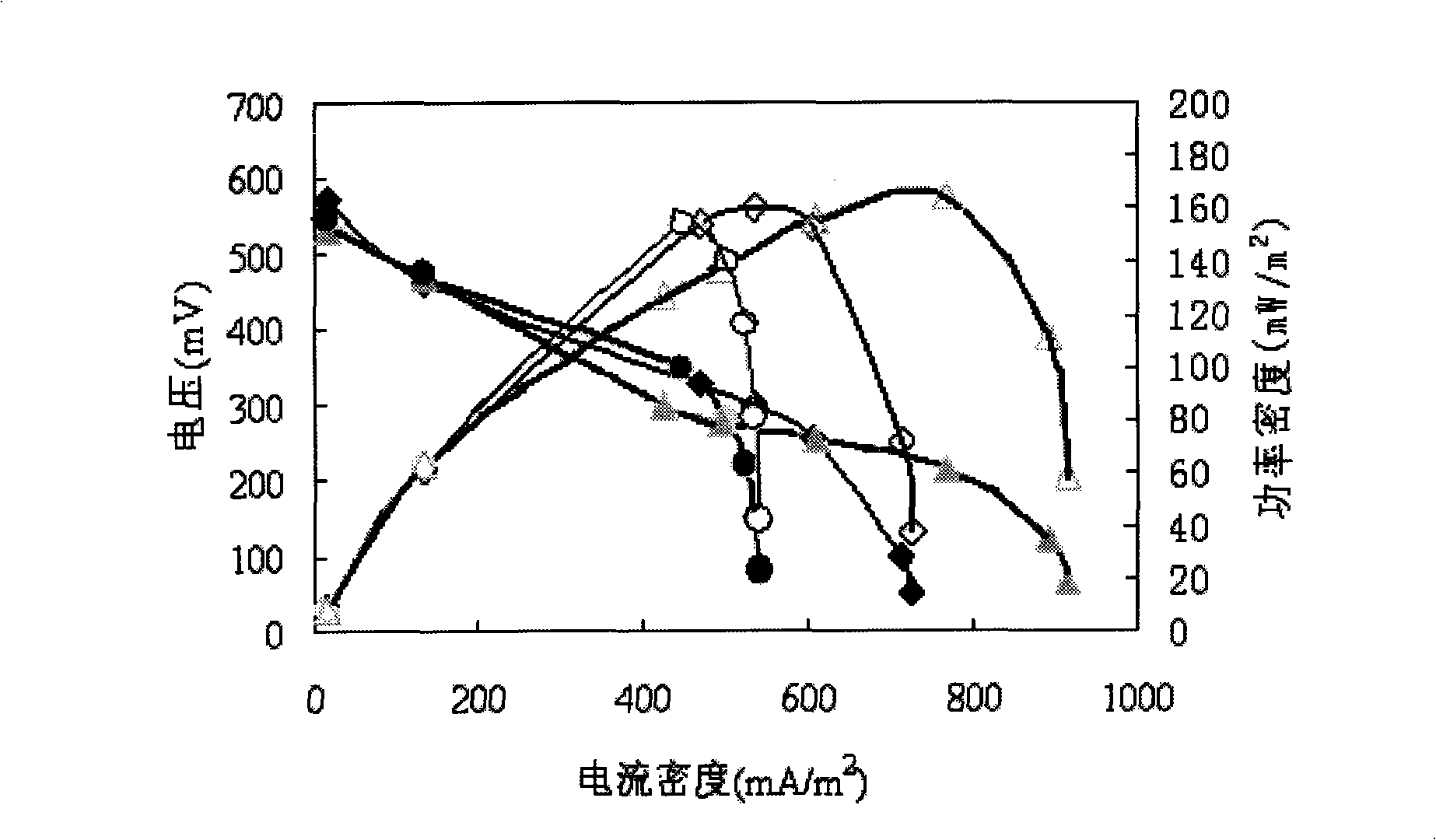
[0013] Specific embodiment one: the separation of the electrochemically active bacterial strain of this embodiment is carried out according to the following steps: one, under aseptic condition, cut off the anode of the microbial fuel cell, then drop into the bottle containing the liquid culture medium of sterilization, seal and place Cultivate for 2 to 4 days at 25-32°C; 2. Take 1 mL of the bacterial solution obtained in Step 1 for doubling dilution; The bacterial liquid is evenly distributed on the entire solid medium, and then cultivated at 28-31°C for 5-10 days; 4. Pick a single colony in the Henggate rolling tube in step 3 and inoculate it in the liquid medium, and inoculate it at 25-31°C. Cultivate at 32°C for 2 to 4 days, and the obtained bacterial solution is an electrochemically active strain; wherein every 1000 mL of liquid medium in step 1 contains 10 to 20 g of glucose, 2 to 4 g of tryptone, and 2 to 4 g of Beef extract, 1-1.5g of yeast, 3-6g of NaCl, 1-2g of K 2 H...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0015] Specific embodiment 2: The difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment 1 is that in step 1, under aseptic conditions, cut off 2-5mm 2 Anode of the microbial fuel cell. Other steps and parameters are the same as those in Embodiment 1.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0016] Specific embodiment three: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one is that the multiple dilution ratio in step two is 10 3 ~10 7 times. Other steps and parameters are the same as those in Embodiment 1.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com