Photoelectric position detector with high-sensitivity
A photoelectric position, high-sensitivity technology, used in circuits, electrical components, semiconductor devices, etc., can solve the problems that the sensitivity cannot meet the requirements of its application, the response band width, etc., and achieve the effect of convenient application, good linearity and simple structure.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
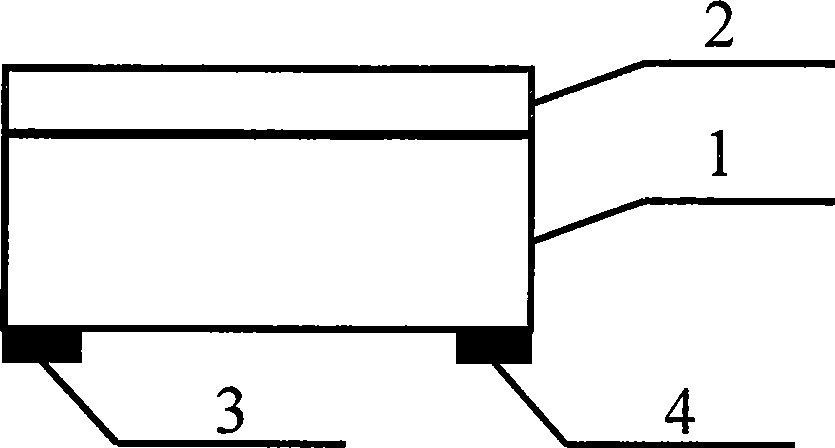
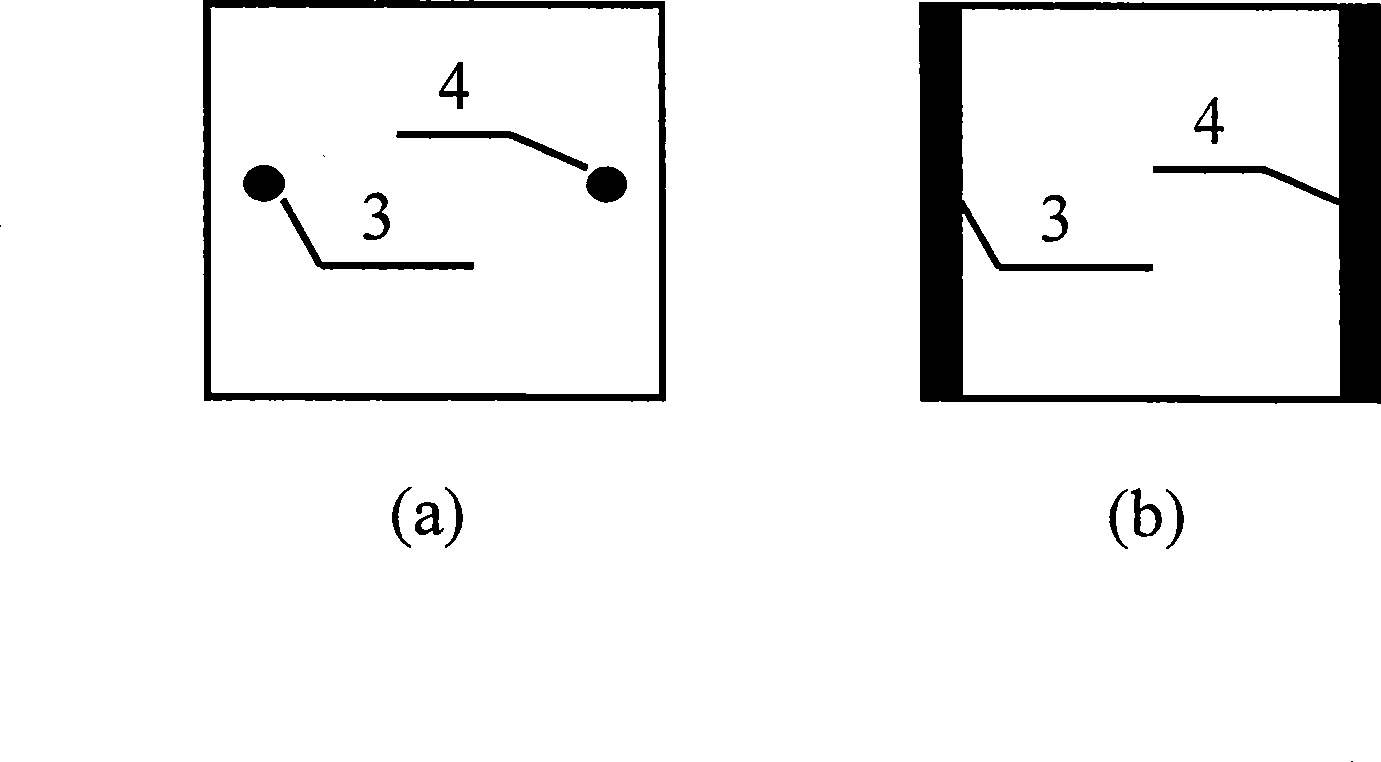
[0023] refer to figure 1 , in conventional laser molecular beam epitaxy equipment, laser molecular beam epitaxy technology is used to directly epitaxially grow a 100nm thick TiN thin film layer 2 on a 2-inch Si substrate 1 to form a TiN-Si two-layer heterojunction sample. A 2-inch TiN-Si sample was cut into a 10 mm x 10 mm square. On the outer surface of the Si substrate 1 of the TiN-Si two-layer heterojunction sample, with the center of the two sides, the first electrode 3 and the second electrode 4 (such as figure 2 As shown in a), the distance between the first electrode 3 and the second electrode is 8mm, that is, it is prepared as a photoelectric position detector whose working mode is voltage mode.
[0024] The measurement results are as follows:
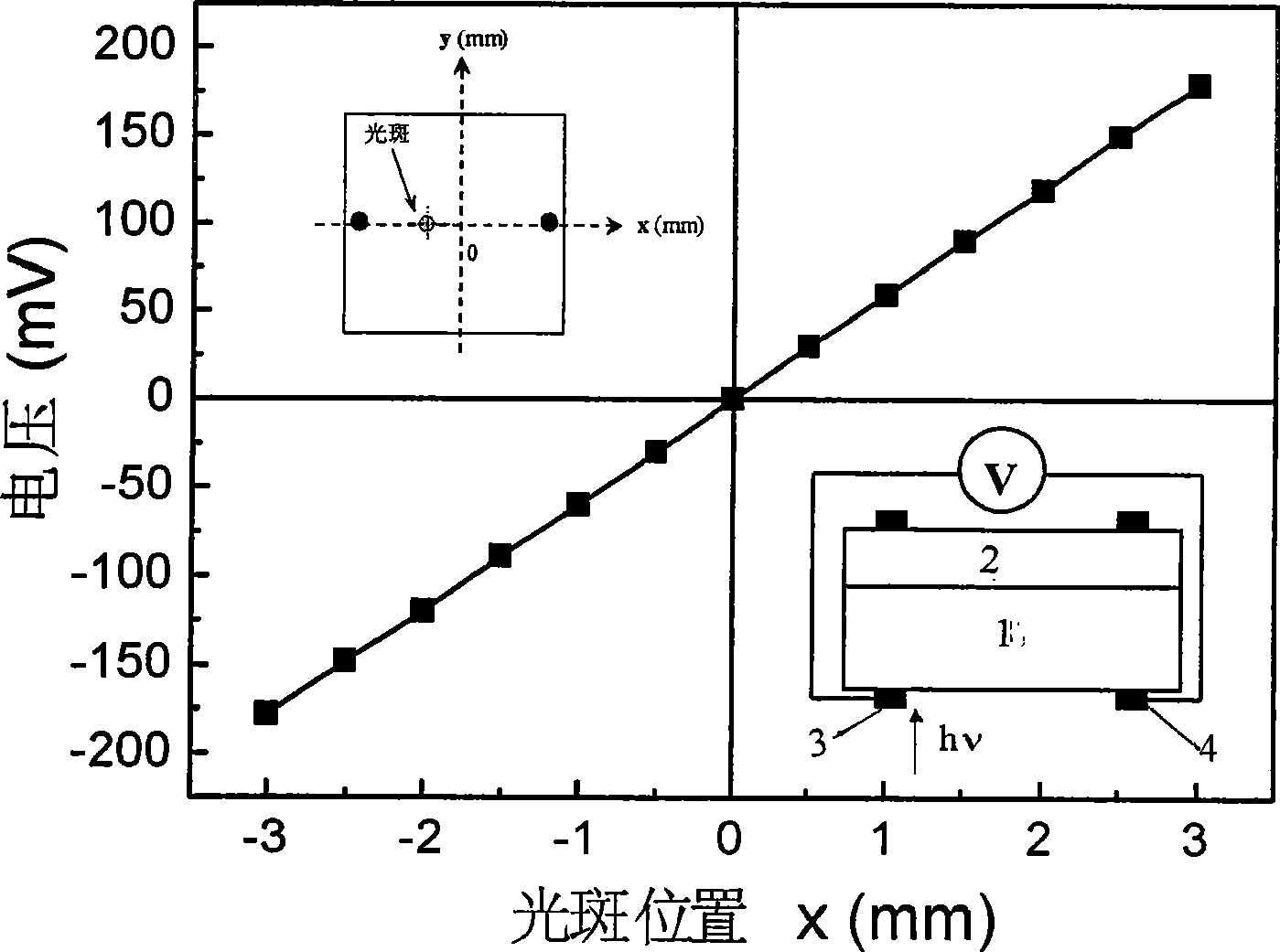
[0025] Use a 10mW HeNe laser (wavelength 632.8nm) as the light source, use a diaphragm with a diameter of 0.5mm to limit the spot area, and scan the spot between the first electrode 3 and the second electrode 4 on the Si sub...
Embodiment 2
[0027] Using the photoelectric position detector produced in Example 1, an excimer pulsed laser with a wavelength of 308 nm was used instead of HeNe laser as the light source for measurement. Figure 4 It is a TiN-Si heterojunction photoelectric position detector. When an excimer pulse laser with a wavelength of 308nm is used to scan in a straight line between two points on the Si surface electrode, the relationship between the output voltage between the first electrode 3 and the second electrode 4 and the position of the light point, The inset is a schematic diagram of the specific measurements.
Embodiment 3
[0029] Using laser molecular beam epitaxy technology, a 1nm-thick TiN film layer 2 is directly epitaxially grown on a 2-inch Si wafer 1 to form a TiN-Si two-layer heterojunction sample. A 2-inch TiN-Si sample was cut into a 10 mm x 10 mm square. At the center of the two sides of the Si substrate 1 square surface, prepare a gold first electrode 3 and a second electrode 4 with a diameter of about 0.5mm (such as figure 2 As shown in a), a photoelectric position detector prepared as a voltage mode.
[0030] When a light spot shines on the surface of the detector, measure the voltage between the first electrode 3 and the second electrode 4 with a voltmeter, or connect a voltage source between the first electrode 3 and TiN, so that TiN and Si form The Schottky diode works in the reverse bias state, and the current between the first electrode 3 and the second electrode 4 is measured, and the position of the light spot can be identified according to the measured voltage or current. ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com