Chlorinated phenol photocatalysis degradation method in water using Fe0/TiO2
A photocatalytic and chlorinated phenol technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, physical/chemical process catalysts, metal/metal oxide/metal hydroxide catalysts, etc., can solve problems such as low photocatalytic activity and reduced reactivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] TiO 2 Preparation: every 21mL Ti(O-Bu) 4 Add 80mL pure ethanol to the Ti(O-Bu) 4 -The ethanol solution was stirred in an ice bath, and then 2 mL of water and 0.2 mL of 50% nitric acid were added to 80 mL of ethanol to make an ethanol-water-nitric acid solution. Stir and cool the ethanol-water-nitric acid solution in an ice bath and slowly inject it into Ti(O-Bu) 4 -In the ethanol solution, a sol is gradually formed until the gel is formed. The gel is placed at room temperature for 24 hours, and then dried at 70°C under vacuum, and then placed. The obtained powder is calcined in a muffle furnace for use, first calcining at 100°C for two hours, then at 500°C for two hours, and grinding and storing.
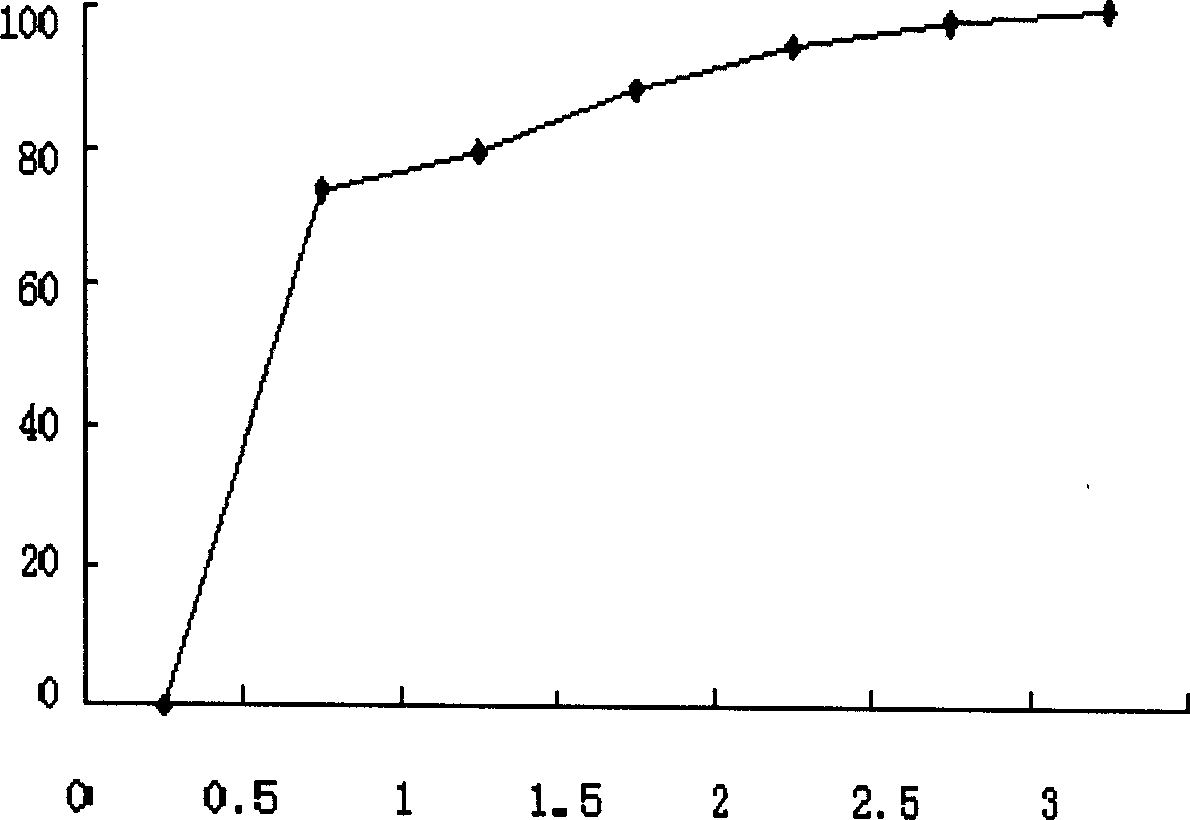
[0023] Fe 0 / TiO 2 Preparation: Weigh 1.00g of titanium dioxide prepared by sol-gel method, add a certain amount of ferrous sulfate heptahydrate, add deionized water to make the volume up to 50mL, ultrasonically disperse for 20 minutes, bubbling with nitrogen for 30 minutes, add s...
Embodiment 2
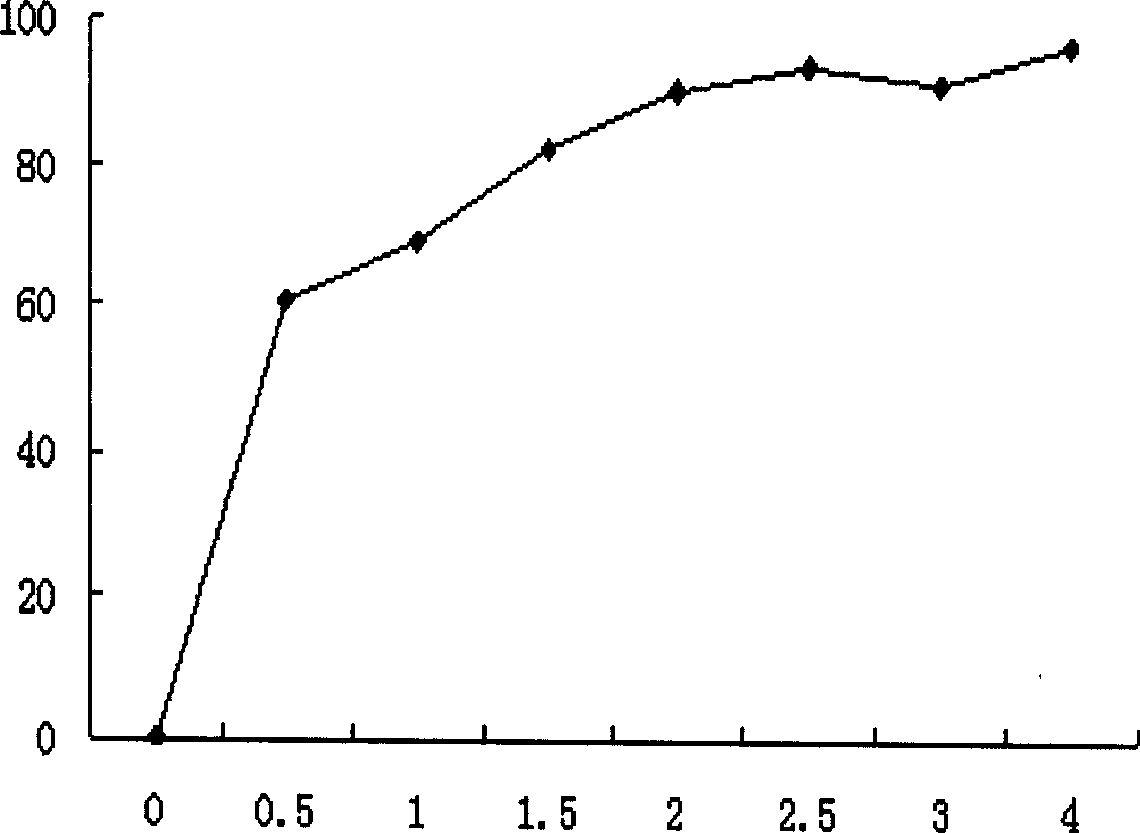
[0028] The nano-zero-valent iron composite titanium dioxide catalyst prepared by the same method as in Example 1 was used for the photocatalytic oxidation and degradation of 2,4-dichlorophenol. The doping amount of iron is 5wt% TiO 2 , The catalyst concentration is 1gL -1 , The photocatalytic degradation concentration is 10mgL -1 2,4 Dichlorophenol, under the same ultraviolet light irradiation as in Example 1, at pH 4, with the light and the progress of the reaction, the removal rate of 2,4 Dichlorophenol changes as figure 2 Shown. The removal rate of 2,4-dichlorophenol reached 70% after 0.5h of light, 90% after 2h, and more than 96% after 4h. The final product contains almost no phenols.
[0029] Analysis shows that TOC removal rate is also faster and higher.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com