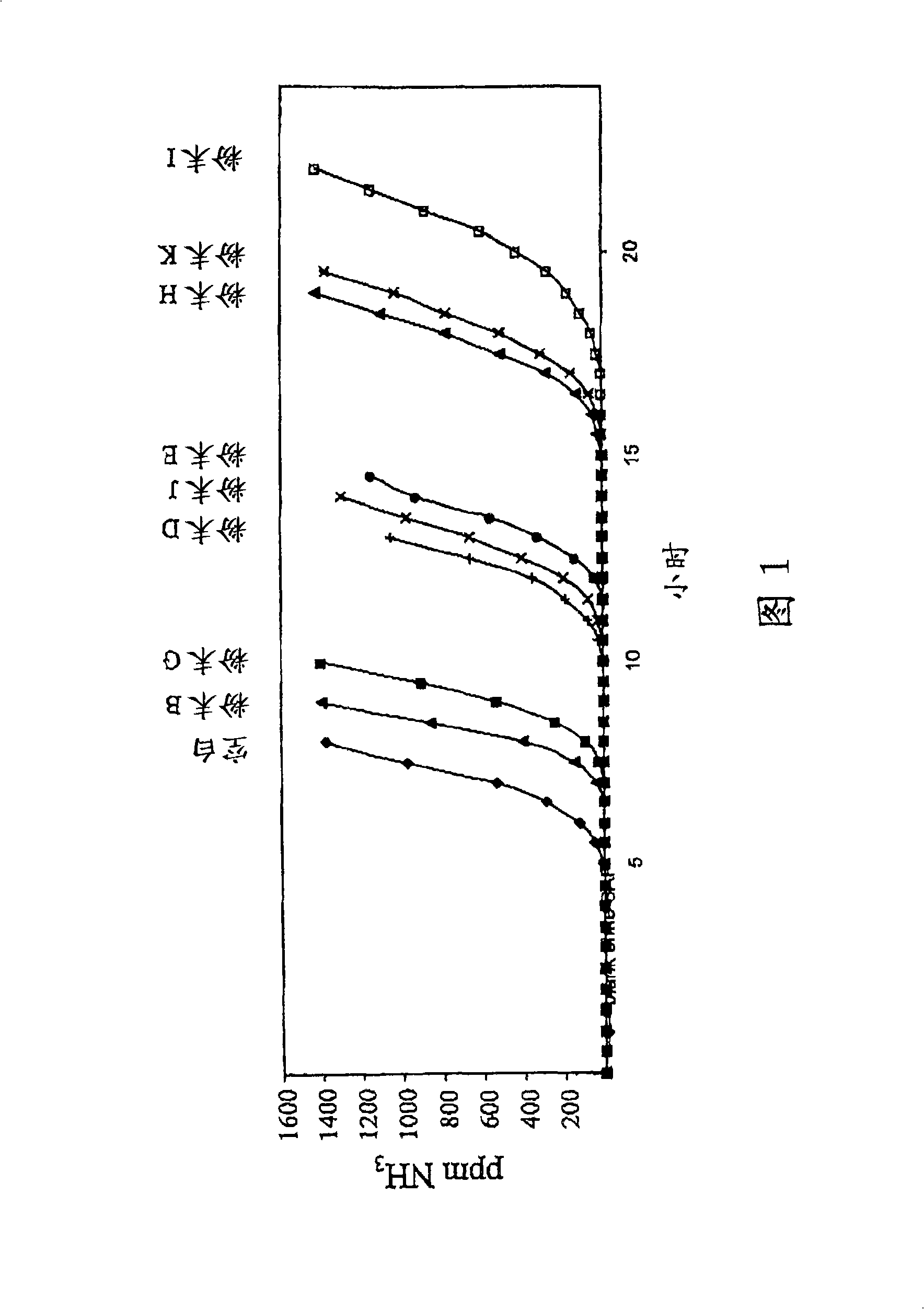
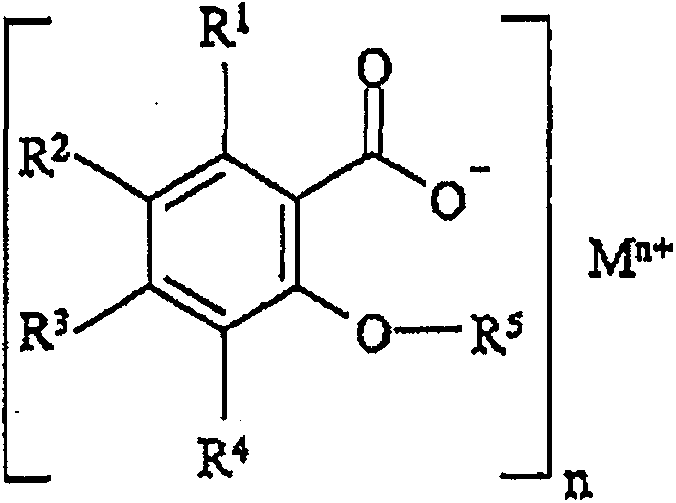
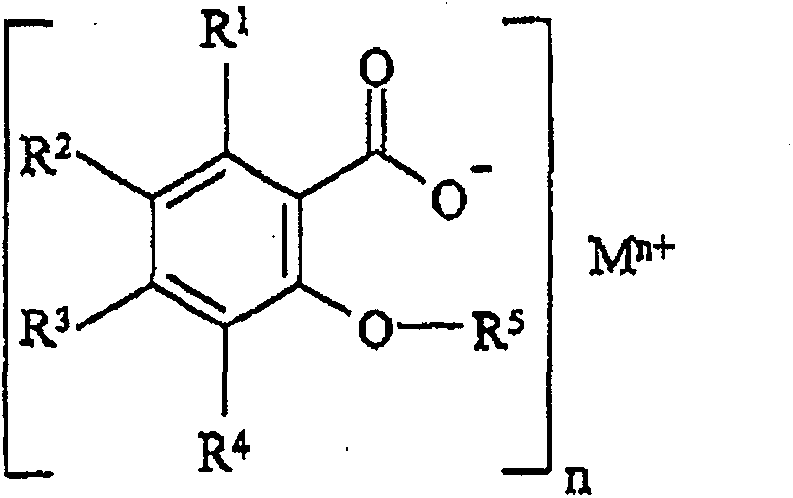
Water-absorbent composition containing water-absorbent polymer structures for smell control
A technology of water-absorbing polymers and compositions, applied in the direction of active ingredients of salicylic acid, absorbent pads, fertilizer mixtures, etc., which can solve the problems of imperfect application of superabsorbent particles and failure to provide odor-binding performance superabsorbents, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0085] Particular preference is given to using redox systems comprising hydrogen peroxide, sodium peroxodisulfate and ascorbic acid in the production of water-absorbing polymer structures.
[0086] The preparation of the polymer structure can also adopt inverse suspension / emulsion polymerization. According to these methods, partially neutralized aqueous solutions of monomers (α1) and (α2), optionally containing water-absorbing polymers and auxiliary substances, are dispersed in hydrophobic organic solvents by means of protective colloids and / or emulsifiers, and the polymerization reaction Initiated by free radical initiators. The crosslinker is either dissolved in the monomer solution and metered in together with it, or added separately, optionally during the polymerization. The water-absorbing polymer (α4) as graft base is optionally added via monomer solution or initially introduced directly into the oil phase. Water is then removed azeotropically from the mixture and the ...
Embodiment 1a
[0160] Example 1a Providing a water-absorbing polymer structure (step i))
[0161] A monomer solution containing 300 g of acrylic acid neutralized to 75 mol % with sodium hydroxide solution, 441 g of water, 0.9 g of polyethylene glycol 300 diacrylate and 1.35 g of allyloxy polyethylene glycol acrylate was blown through with nitrogen Dissolved oxygen was swept away and cooled to the starting temperature of 4°C. When the starting temperature is reached, add the initiator solution (10 g H 2 0.3 g sodium persulfate in O, 10 g H 2 0.07 g of 35% hydrogen peroxide solution in O and 2 g of H 2 0.015g ascorbic acid in O). When a final temperature of about 100°C was reached, the gel formed was cut to obtain particle particles of about 1-3 mm particle size. The water content is about 50%. These particles were dried at 150°C for 120 minutes. The dry polymer was coarsely crushed, ground, and sieved into a powder (powder A) with a particle size of 150-850 μm.
Embodiment 2a
[0162] Example 2a Surface postcrosslinking of water-absorbing polymer structures (step ii))
[0163] For post-crosslinking, 100 g of powder A obtained above was mixed with a solution of 1 g of 1,3-dioxolan-2-one and 3 g of water under vigorous stirring, and the mixture was then placed in an oven controlled at 180° C. Heat for 30 minutes. A surface postcrosslinked water-absorbing polymer structure (powder B) is thus obtained.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com