Amphiploid histidine auxotroph saccharomyces cerevisiae and constructing method thereof
An auxotrophic, Saccharomyces cerevisiae technology, applied in the field of diploid histidine auxotrophic Saccharomyces cerevisiae and its construction, can solve problems such as characteristic change, achieve simple construction method, easy identification and protection, and maintain original characteristics constant effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
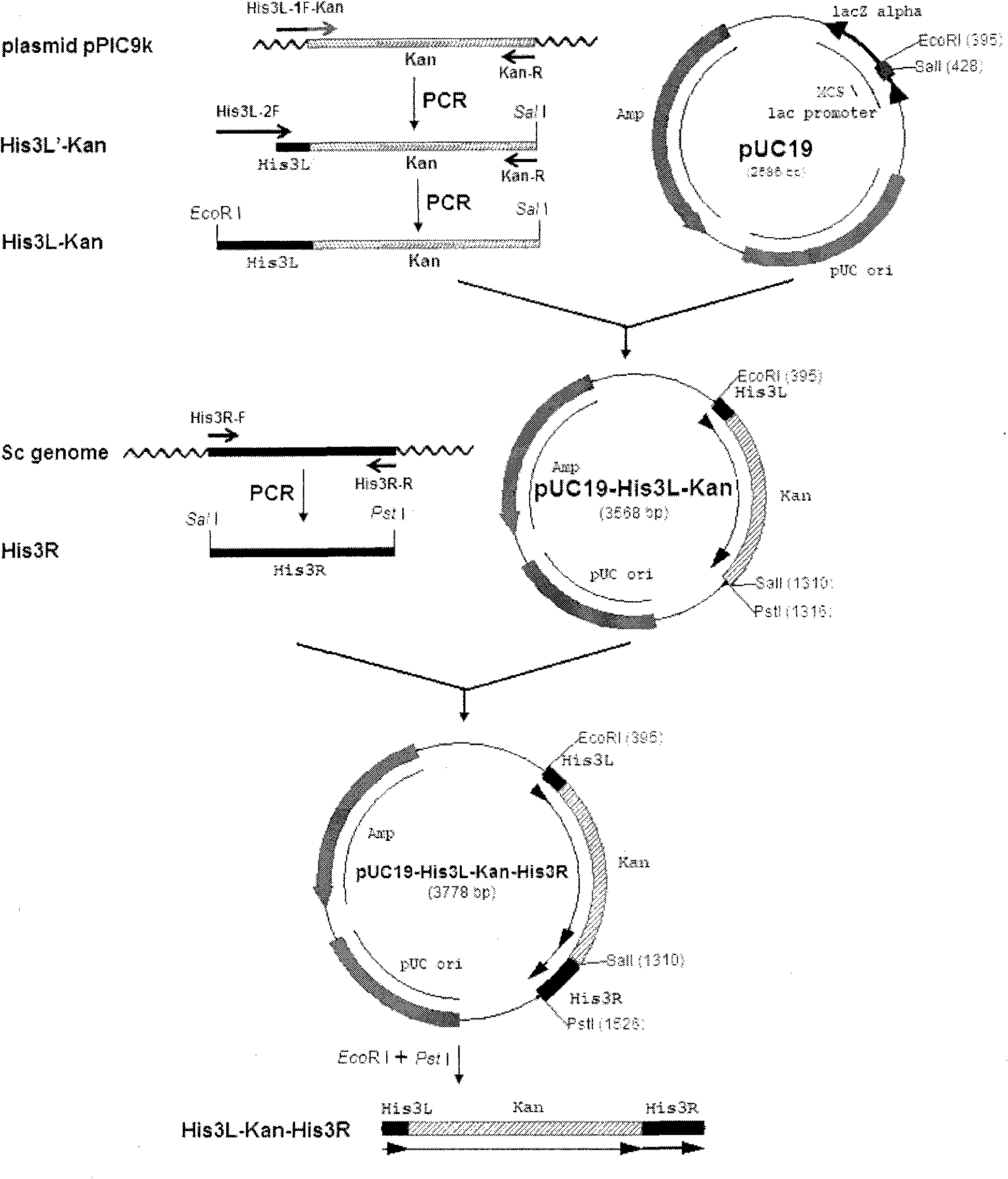
[0052] Example 1 Construction of Homologous Recombination Fragment His3L-Kan-His3R
[0053] 1.1 Construction of pUC19-His3L-Kan plasmid containing homologous recombination left arm and g418 resistance gene
[0054] 1.1.1 Amplify the His3L-Kan fragment (926bp) containing homologous recombination left arm and g418 resistance
[0055] According to the sequence data of S.cerevisiae His3 gene reported in Genebank (Accession No. NC001147) and the sequence data of pPIC9K plasmid (Invitrogen, Cat. No. V175-20), PCR primers were designed using Primer Premier 5 software.
[0056] Upstream primer His3L-1F-Kan
[0057] 5'-GATTGCGATCTCTTTAAAGGGTGGTCCCCTAGCGATAGAGATGAGCCATATTCAACGGG-3' (SEQ ID No. 1)
[0058] Upstream primer His3L-2F
[0059] 5'-GGAATTCATGACAGAGCAGAAAGCCCTAGTAAAGCGTATTACAAATGAAACCAAGATTCAGATTGCGATCTCTTTAAAG-3' (SEQ ID No. 2)
[0060] Downstream primer Kan-R
[0061] 5'-ACGCGTCGACTTAGAAAAACTCATCGAGCATC-3' (SEQ ID No.3)
[0062] 1) Use the pPIC9K plasmid as a template, ...
Embodiment 2
[0154] Example 2 Obtaining of single chromosome exchange Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain
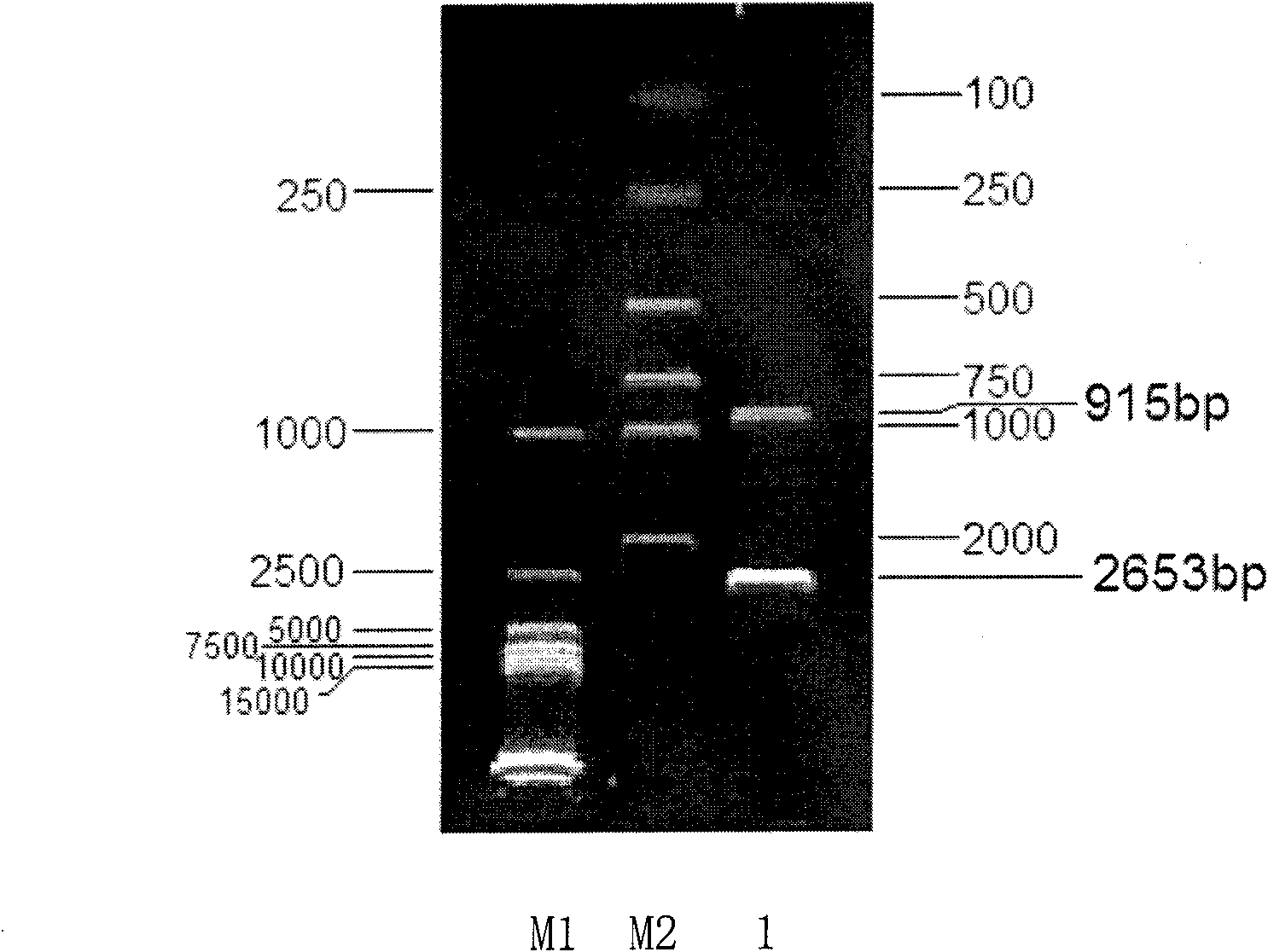
[0155] The 1135bp His3L-Kan-His3R fragment obtained in 1.3 of Example 1 was used to transform S. cerevisiae TSH-Sc-001 (CGMCC NO.1949) competent cells by electroporation. The electroporator used was Gene Pulser Xcell TM Electroporation System (Bio-Rad Company), the preparation method of S.cerevisiae competent cells refers to the instrument manual.
[0156] For each electroporated sample, prepare a small test tube containing 1ml of 1M sorbitol YPD liquid medium and place it on ice to cool, and prepare a 2mm electroporation cup and place it on ice to cool.
[0157] Cool the His3L-Kan-His3R fragment (100ng / 5μl) to be transformed on ice, add 40μl of competent cells to the DNA sample, mix gently, and place on ice for about 5 minutes.
[0158] The electroporator was prepared, and the Saccharomyces cerevisiae cells were transformed according to the preset program. The parameters of the elect...
Embodiment 3
[0179] Example 3 Obtaining of Double Chromosome Exchange Saccharomyces cerevisiae Strains
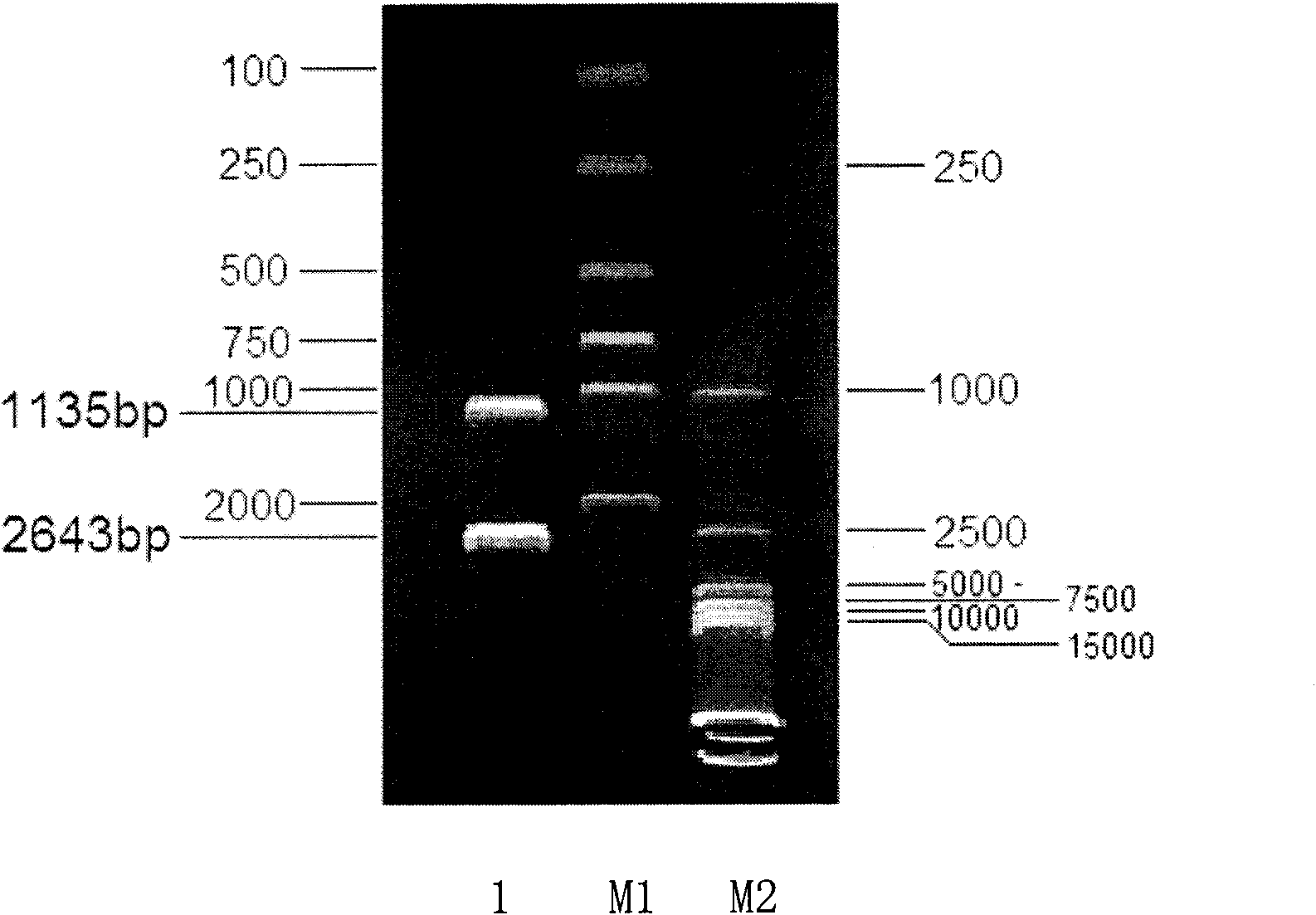
[0180] TSH-Sc-001 (His3) obtained with embodiment 2 + / - ) strain to prepare competent cells, the transformation method is the same as in Example 2. The transformed cells were spread on YPD plate medium containing 1M sorbitol and 0.5g / L g418, and cultured upside down at 30°C for 3 days. The culture method of monoclonal colony, genomic DNA extraction method and PCR identification method are the same as embodiment 2.
[0181] The results of agarose gel electrophoresis of PCR products showed (see Figure 6 ), the monoclonal colony that can grow on the YPD medium containing 0.5g / L g418 obtained through twice electrotransformation, only primer His3-F and Kan-ID can amplify the PCR product (SEQ ID No. 14), primers His3-F and His-ID failed to amplify the PCR product, which proved that homologous recombination had occurred in both chromosomes, and obtained Saccharomyces cerevisiae (S.cerevisi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com