Degerming method for recycling somatic cells from amino acid zymotic fluid/extraction waste liquid
A technology for bacterial cells and fermentation broth, applied in the field of fermented food industry, can solve the problems of inability to remove water-soluble proteins in fermentation broth, reduced protein content in filter residues, low bacterial cell removal rate, etc., and achieves low power consumption and reduced addition amount. , the effect of improving the filtration efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
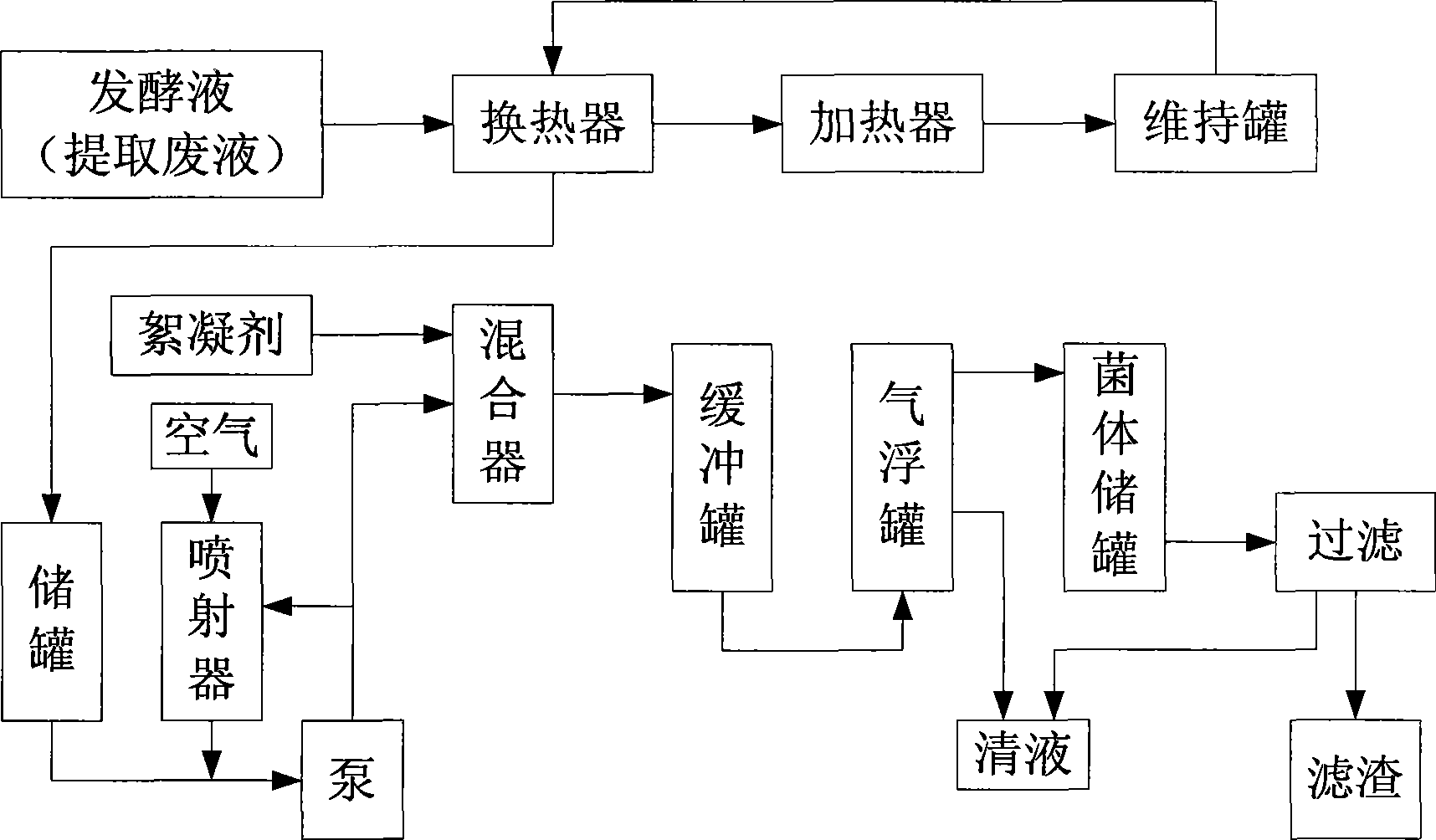
[0031] Embodiment 1: A method for removing bacteria from the amino acid fermentation liquid / extraction waste liquid, adopting the following process steps:
[0032] 1. Glutamic acid fermentation broth, glutamic acid concentration 12%, temperature 32°C, continuously sent to the tube side of the heat exchanger, the tube side of the heat exchanger is the glutamic acid from the maintenance tank at a temperature of 100 °C in step 3 For sour fermentation broth, the two materials exchange heat on the inner wall of the heat exchanger. After the heat exchange, the original 32°C fermentation broth is heated to 76°C, while the original 100°C fermentation broth is cooled to 50°C;
[0033] 2. The fermented liquid heated to 76°C flows into the heater, heated to 100°C with steam at a pressure of 0.3Mpa, then enters the maintenance tank, and stays in the maintenance tank for 30 minutes;
[0034] 3. Return the fermented liquid in the tank at 100°C to the tube side of the heat exchanger describe...
Embodiment 2
[0040] Embodiment 2: A method for removing bacteria from the amino acid fermentation liquid / extraction waste liquid, adopting the following process steps:
[0041] 1. Glutamic acid extraction waste liquid, glutamic acid concentration 2%, temperature 15 ℃, continuously sent to the shell side of the heat exchanger, the tube side of the heat exchanger is the valley of the temperature 80 ℃ from the maintenance tank in step 3 Acid extraction waste liquid, the two materials exchange heat in the heat exchanger, after the heat exchange, the original 15°C extraction waste liquid is heated to 45°C, while the original 80°C extraction waste liquid is cooled to 48°C;
[0042] 2. The extraction waste liquid heated to 45°C flows into the heater, heated to 80°C with steam at a pressure of 0.2Mpa, then enters the maintenance tank, and stays in the maintenance tank for 20 minutes;
[0043] 3. The extraction waste liquid in the maintenance tank at 80°C is refluxed to the tube side of the heat ex...
Embodiment 3
[0049] Embodiment 3: A method for removing bacteria from the amino acid fermentation liquid / extraction waste liquid, adopting the following process steps:
[0050] 1. Lysine fermentation broth, lysine concentration 16%, temperature 30°C, continuously sent to the shell side of the heat exchanger, the tube side of the heat exchanger is lysine from the maintenance tank at a temperature of 80°C in step 3 For acid fermentation broth, the two materials exchange heat in the heat exchanger. After the heat exchange, the extraction waste liquid at 30°C is heated to 50°C, while the lysine fermentation liquid at 80°C is cooled to 53°C;
[0051] 2. The lysine fermentation broth heated to 50°C flows into the heater, heated to 80°C with steam at a pressure of 0.3Mpa, then enters the maintenance tank, and stays in the maintenance tank for 25 minutes;
[0052] 3. The lysine fermentation liquid in the maintenance tank at 80°C is returned to the tube side of the heat exchanger described in step ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com