Compositions and methods for diagnosis and treatment of type 2 diabetes
A technology for type 2 diabetes and diabetes, applied in the direction of biochemical equipment and methods, drug combinations, metabolic diseases, etc., can solve the problems of rarely identifying and treating diabetes
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0189] The preparation method of the pharmaceutical composition containing the active ingredient is well known in the art, for example, by mixing, granulating or tableting processes. The active therapeutic ingredient is usually mixed with excipients that are pharmaceutically acceptable and compatible with the active ingredient. For oral administration, the active agent is mixed with additives commonly used for this purpose (e.g., solvents, stabilizers or inert diluents), and converted into a suitable administration form (e.g., tablets, coatings as detailed above) by conventional methods. Tablets, hard or soft gelatin capsules, aqueous, alcoholic or oily solutions, etc.).
[0190] For IV administration, glucuronic acid, L-lactic acid, acetic acid, citric acid or any pharmaceutically acceptable acid / conjugate matrix with reasonable buffer capacity and pH range acceptable for intravenous administration can be used as Buffer. It is also possible to use a sodium chloride solution whose...
Embodiment 1
[0194] Example 1: Identification of biomarkers in the Cohen rat model of type 2 diabetes
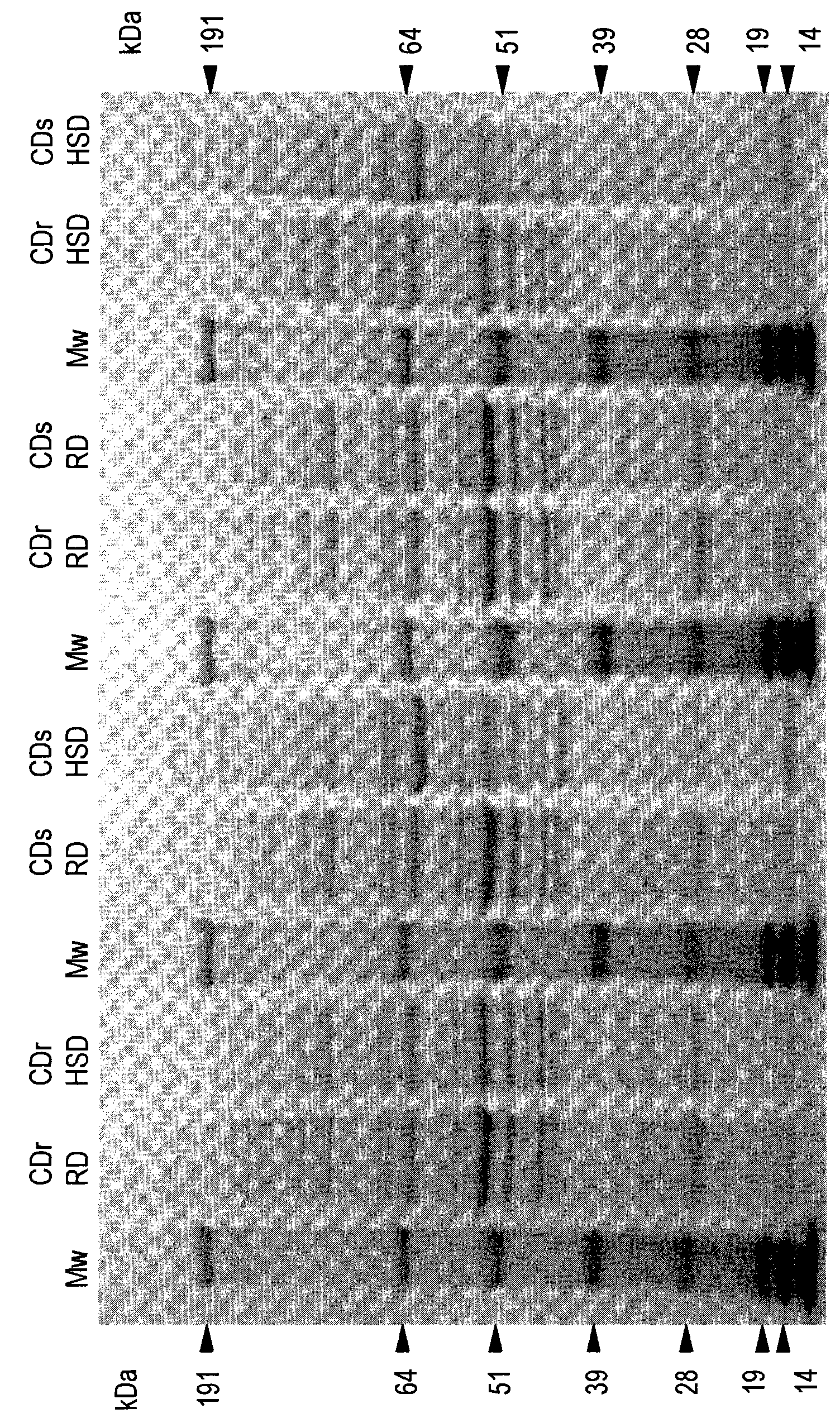
[0195] Cohen Diabetes (CD) rat is a well-known universal type 2 diabetes animal model, which is composed of two rodent strains that show many common features with human type 2 diabetes (T2D). When maintaining a high sucrose / low copper diet (HSD), sensitive strains (CDs) developed diabetes within 30 days, while resistant strains (CDr) maintained normal blood glucose levels. When the regular rodent diet (RD) is maintained for a long time, neither of these two strains will develop T2D symptoms.
[0196] Sample Preparation
[0197] Serum, urine and tissue samples (including spleen tissue, pancreatic tissue and liver tissue) were collected from CDr rats and CDs rats fed RD or HSD for 30 days. The samples were snap frozen and stored at -80°C.
[0198]A whole protein extract was prepared for each of the 4 experimental conditions, and 10 organs were used in each group. A mechanical shearing device...
Embodiment 2
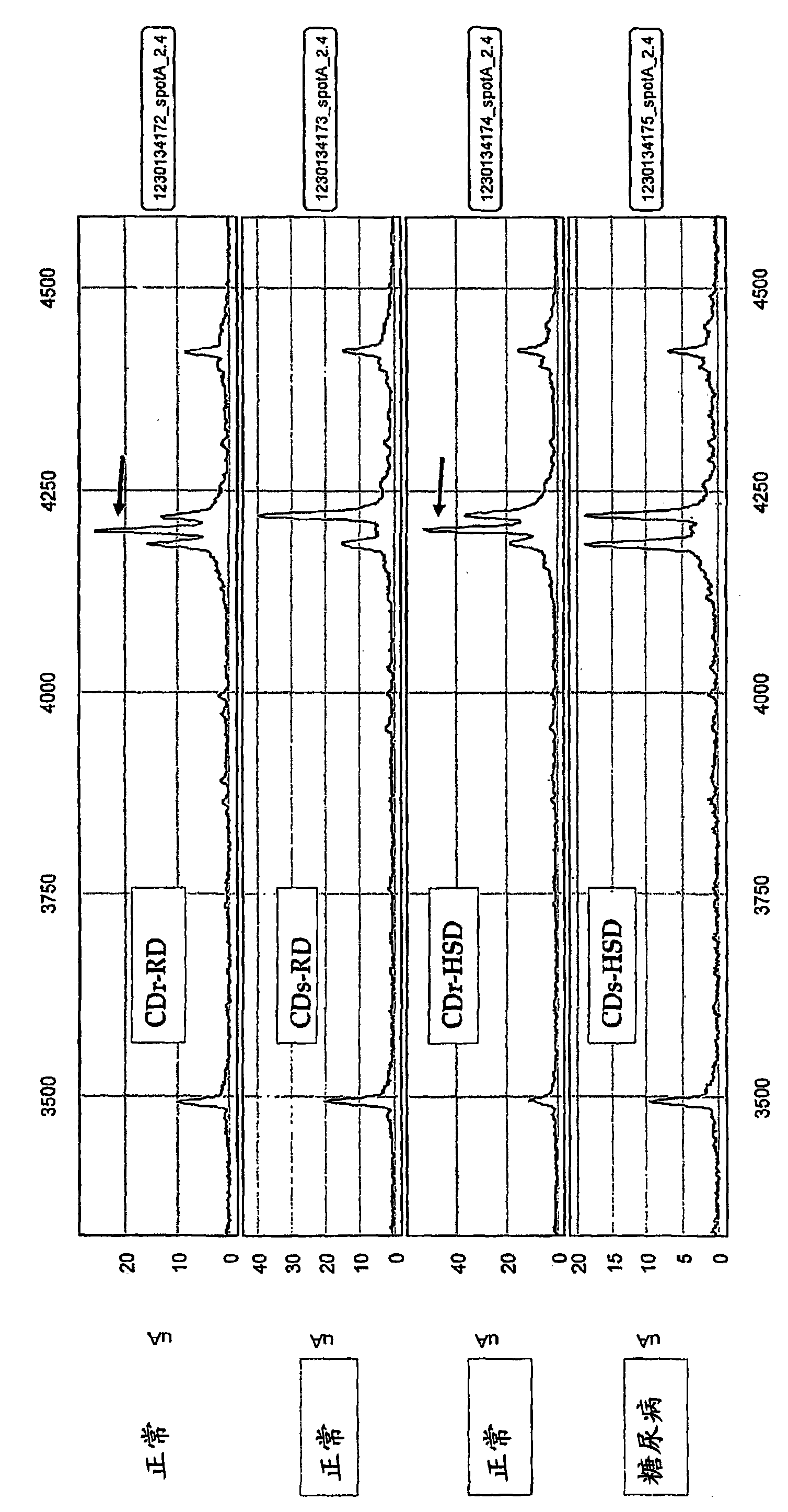
[0230] Example 2: Identification of biomarkers in human serum
[0231] With D3 hyperimmune serum (rabbit; Picture 11 ) The human serum was analyzed. The first antibody used is a rabbit polyclonal antibody produced after immunization with D3 peptide. Compared with patients with type 2 diabetes, the expression intensity of proteins with a molecular weight of 20kD (between 14kD and 28kD markers) in the serum of normal individuals (human) is higher. In both (normal and diabetic) samples, a pair of proteins with a molecular weight of 60-80 kD appeared to be present. Interestingly, the protein intensities in the two seem to be transformable; observations were made with monoclonal antibodies from CDr-HSD pancreas and CDs-HSD pancreas from subtractive immunoassay. Figure 12A with Figure 12B Represents a preparative gel containing 100 μg CDr-HSD or CDs-HSD pancreatic extract. The positive control was stained with 20 μg of anti-actin antibody, and the subcloning lane was stained with 6...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com