Method for etching class-III nitride by using photo-assisted oxidation wet method
A wet etching and nitride technology, which is applied in the fields of electrical components, semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, circuits, etc., can solve the problems of high ion energy and difficulty in obtaining etching mesa
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] In conjunction with accompanying drawing 1 (a), Fig. 1 (b), Fig. 1 (c), Fig. 1 (d) and figure 2 , the first embodiment of a method for wet etching Group III nitrides using photo-assisted oxidation of the present invention is described in detail as follows.
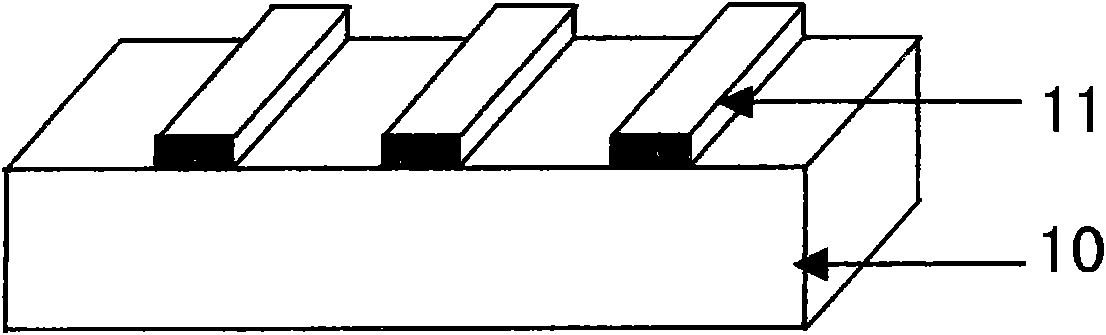
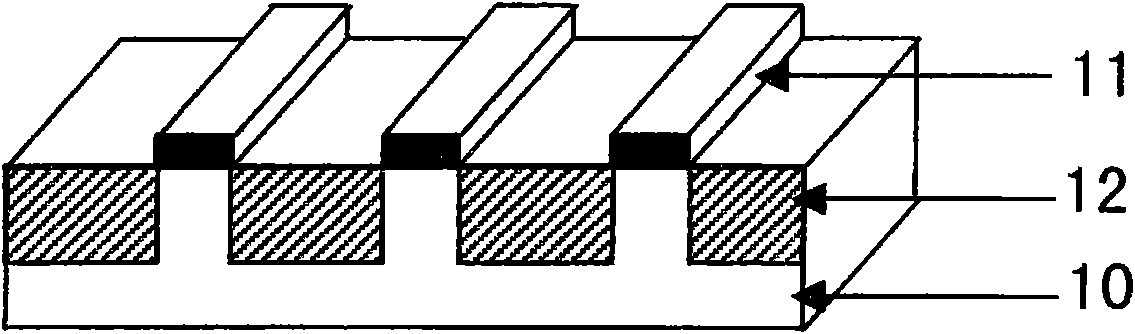
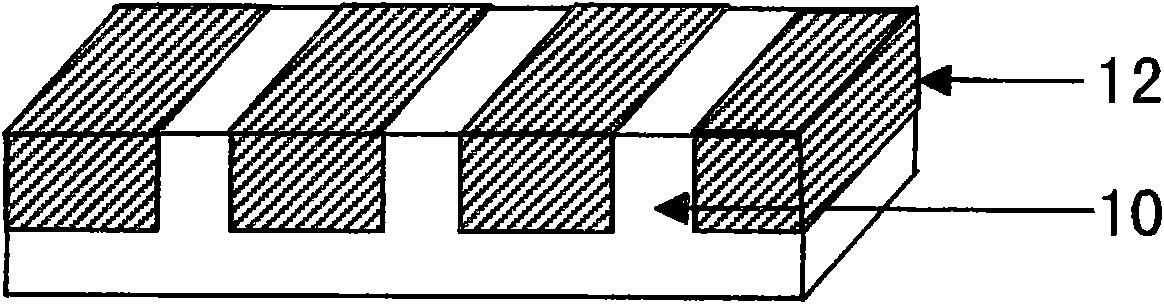
[0034] Step 1: Using a standard photolithography process, fabricate an ultraviolet light masking layer 11 with a certain pattern on the surface of the III-nitride sample 10 to be etched. The process includes baking the sample, cleaning the photoresist, coating the photoresist, baking the photoresist, exposing, developing, low-temperature coating, and stripping to form a pattern. The details are as follows: First, bake the III-nitride sample 10 at 120°C for 30 minutes, and then use a coater to evenly coat a layer of photoresist on its surface after it cools down, and then bake it at 90°C for 20 minutes. The photoresist has a certain hardness, and the photoresist is exposed by pattern exposure equipment, that is, a p...
Embodiment 2
[0040] In conjunction with accompanying drawing 1 (a), Fig. 1 (b), Fig. 1 (c), Fig. 1 (d) and image 3 , the second embodiment of a method for wet etching Group III nitrides using photo-assisted oxidation of the present invention is described in detail as follows.
[0041] Step 1, placing III-nitride sample 10 under a focused ultraviolet laser 34 for exposure (refer to image 3 ), the optical path is adjusted through the optical element group 35, the stepper motor 31 is precisely controlled by the computer control system 30 to move the sample, and the ultraviolet light switch 33 is used to realize the scanning exposure of the area to be exposed. The stepper motor can also be installed on the ultraviolet laser 34 to move the ultraviolet laser 34 or on the optical element group 35 to move the optical path, so as to realize the scanning exposure of the area to be exposed. The ultraviolet laser 34 may be a He—Cd laser or a frequency-doubled Ar+ laser or the like. The exposed are...
Embodiment 3
[0045] In conjunction with accompanying drawing 1 (a), Fig. 1 (b), Fig. 1 (c), Fig. 1 (d) and Figure 4 , the third embodiment of a method for wet etching Group III nitrides using photo-assisted oxidation of the present invention is described in detail as follows.
[0046] Step 1, at first adjust optical path, the light that makes ultraviolet laser 34 send is divided into two beams of coherent light beams after reflecting mirror 42 and half mirror 41 (referring to Figure 4 ). The two beams of coherent beams interfere on the surface of the III-nitride sample 10 after passing through two mirrors 40 respectively, forming alternate light and dark fringes. The ultraviolet laser 34 may be a He—Cd laser or a frequency-doubled Ar+ laser or the like.
[0047] Step 2. The group III nitride sample 10 is exposed under the light and dark ultraviolet light interference fringes. The ultraviolet light is strengthened, that is, the bright stripe area is oxidized under the assistance of ultr...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com