Comprehensive treatment method of vinegar residues
A technology of comprehensive treatment and vinegar residues, applied in fertilizer mixtures, fertilizers made from biological waste, applications, etc., can solve the problems of small treatment capacity, waste of resources, long treatment time, etc. short time effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
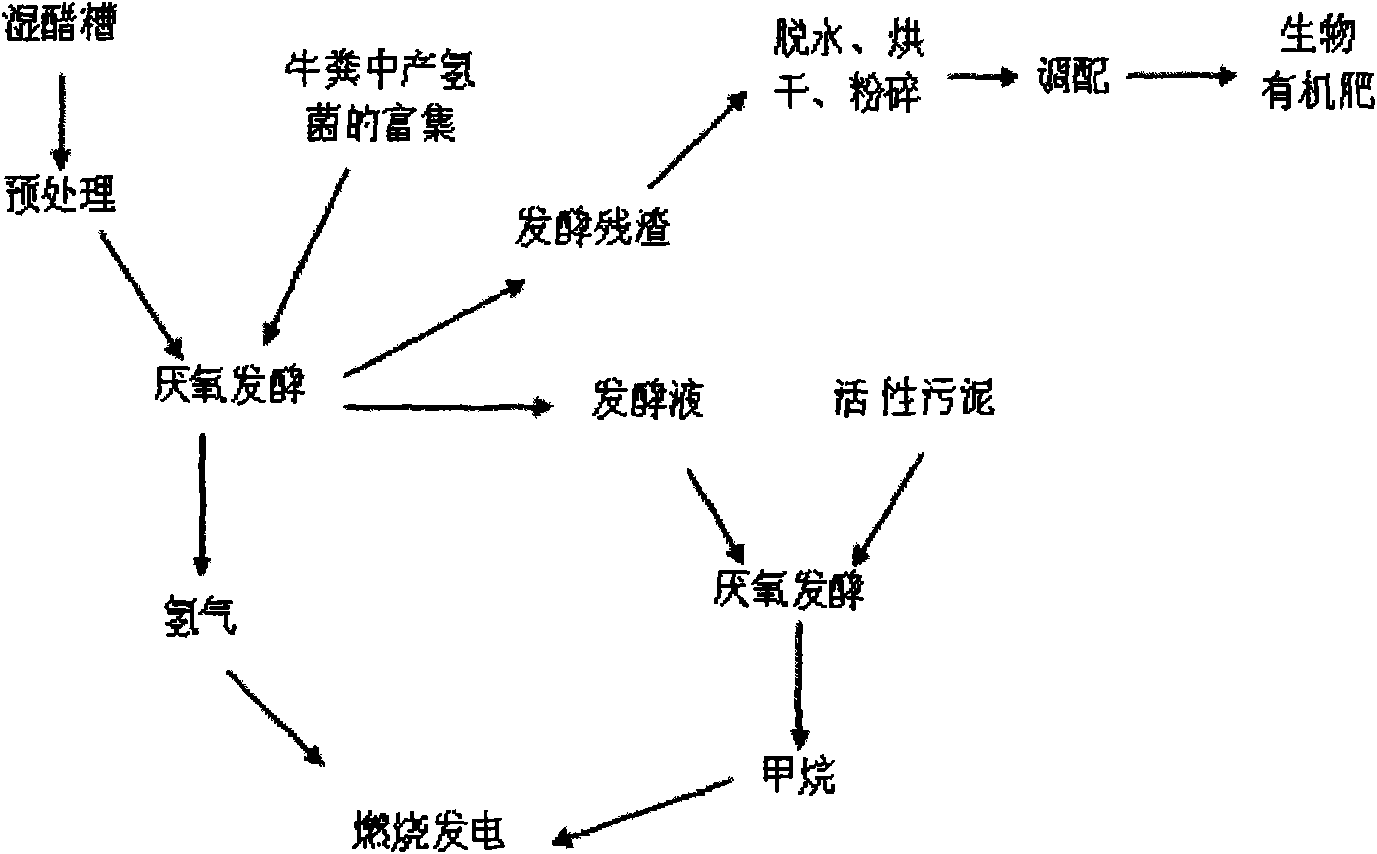
[0018] a. Pretreat the collected wet vinegar grains: add 2187.5 g of hydrochloric acid solution with a mass concentration of 1.0% to 875 g of vinegar grains at a solid-to-liquid ratio of 2:5, and let stand at room temperature for 24 hours.
[0019] b. Enrichment of hydrogen-producing bacteria in cow dung: add 500 ml of NaOH solution with a concentration of 0.5 mol / L to 300 g of cow dung according to a solid-to-liquid ratio of 3:5, and process for 1.5 hours at a temperature of 100°C.
[0020] c. Add the pretreated vinegar grains to the anaerobic fermentation device, inoculate 750 g of enriched hydrogen-producing bacteria, dilute to 5 L with brewery sewage (or tap water), and adjust the pH to 6.5 with hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide solution Around, 25 ℃ fermentation, stirring. Under these conditions, the cumulative hydrogen production of vinegar grains fermented for 48h was 39.12ml / gTS.
[0021] d. After the fermented liquid after anaerobic fermentation hydrogen product...
Embodiment 2
[0024] a. Pretreat the collected wet vinegar grains: add 1250 g of hydrochloric acid with a mass concentration of 0.5% to 500 g of vinegar grains at a solid-to-liquid ratio of 2:5, and let stand at room temperature for 24 hours.
[0025] b. Enrichment of hydrogen-producing bacteria in cow dung: add 1000 ml of NaOH solution with a concentration of 0.3 mol / L to 600 g of cow dung according to the solid-to-liquid ratio of 3:5, the treatment time is 2 hours, and the temperature is 100°C.
[0026] c. Add the pretreated vinegar grains to the anaerobic fermentation device, inoculate 500 g of enriched hydrogen-producing bacteria, dilute to 5 L with brewery sewage (or tap water), and adjust the pH to 6.5 with hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide solution Around, 55 ℃ fermentation, stirring. Under these conditions, the cumulative hydrogen production of vinegar grains fermented for 48h was 43.41ml / gTS. .
[0027] d. After the fermented liquid after anaerobic fermentation hydrogen prod...
Embodiment 3
[0030] a. Pretreat the collected wet vinegar grains: add 3215 g of hydrochloric acid with a mass concentration of 3% to 1250 g of vinegar grains at a solid-to-liquid ratio of 2:5, and let stand at room temperature for 24 hours.
[0031] b. Enrichment of hydrogen-producing bacteria in cow dung: add 500 ml of NaOH solution with a concentration of 1.0 mol / L to 300 g of cow dung according to a solid-to-liquid ratio of 3:5, and treat for 1 hour at a temperature of 100°C.
[0032] c. Add the pretreated vinegar grains to the anaerobic fermentation device, inoculate 1000 g of enriched hydrogen-producing bacteria, dilute to 5 L with brewery sewage (or tap water), and adjust the pH to 6.5 with hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide solution Around, 55 ℃ fermentation, stirring. Under these conditions, the cumulative hydrogen production of vinegar grains fermented for 48h was 34.62ml / gTS. .
[0033] d. After the fermented liquid after anaerobic fermentation hydrogen production is centri...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com