Monophosphates as mutual prodrugs of anti-inflammatory signal transduction modulators (AISTM's) and ss-agonists for the treatment of pulmonary inflammation and bronchoconstriction
A technology for signal transduction and regulators, which can be used in drug combinations, pharmaceutical formulations, organic active ingredients, etc., and can solve problems such as systemic exposure
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0072] I. Preparation of compounds of the present invention
[0073] Compounds of the present invention can be prepared by the methods described in Reaction Schemes I-VI.
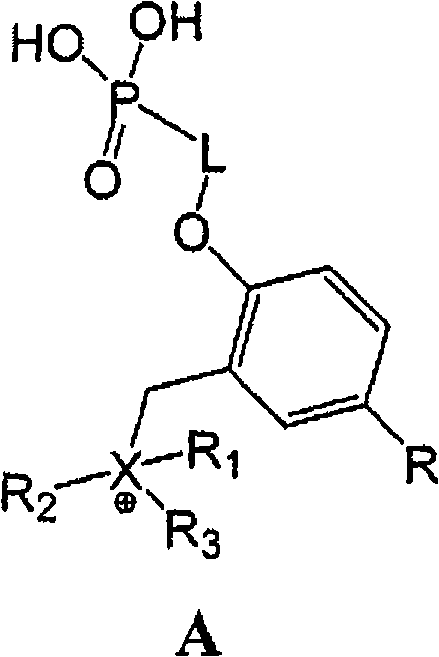
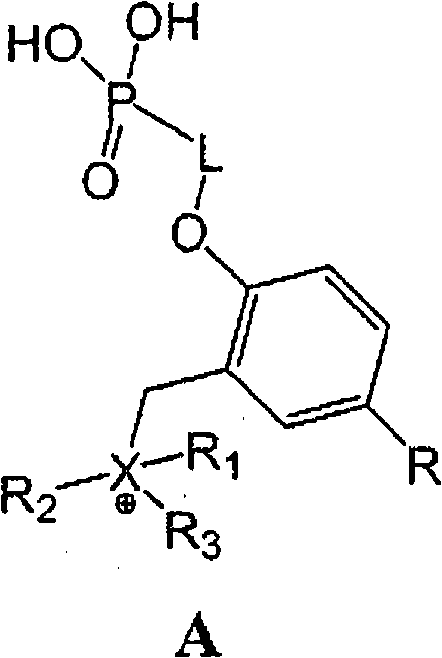
[0074] A comprehensive approach to compounds of formula A includes:
[0075] a) Synthesis of phosphorylated β-agonist derivatives activated towards alkylation (Schemes I-V); and
[0076] b) Quaternization (alkylation) of AISTM molecules carrying "quaternizable moieties" or their physiologically cleavable esters with activated β-agonist derivatives, followed by final deprotection (Scheme VI).
[0077] Reaction scheme I
[0078]
[0079] Reaction Scheme II
[0080]
[0081] Reaction Scheme III
[0082]
[0083] Reaction Scheme IV
[0084]
[0085] Reaction Scheme V
[0086]
[0087] Reaction Scheme VI
[0088]
[0089] The synthesis of phosphate-functionalized protected β-agonist derivatives is shown in Reaction Schemes I-V.
[0090] Commercially available racemic salmeterol xinafo...
Embodiment 1
[0114] Phosphorobromidic acid di-tert-butyl ester
[0115]
[0116] The title phosphorylating reagent was prepared according to conditions modified from those described by Gajda and Zwierzak (1976). By reducing the reaction temperature to 15°C and shortening the reaction time to 2.5 hours, we obtained the title compound with better purity than when using literature conditions (25°C, 4 hours). The title phosphobromidate was unstable and was therefore immediately used in the phosphorylation reaction (see Examples 4 and 10).
Embodiment 2
[0119] [2-Hydroxy-2-(4-hydroxy-3-hydroxymethyl-phenyl)-ethyl]-[6-(4-phenyl-butoxy)-hexyl-ammonia tert-butyl carbamate
[0120]
[0121] Suspend commercially available salmeterol xinafoate (6.04 g, 10 mmol) and potassium carbonate (1.39 g, 10 mmol) in a 1,4-dioxane / water mixture (1:1, 80 mL) with stirring )middle. Di-tert-butyl dicarbonate (2.40 g, 11 mmol) dissolved in 1,4-dioxane (10 mL) was then added dropwise at room temperature while stirring. TLC analysis after 30 minutes showed only a small amount of starting material. After 2 hours, 1,4-dioxane was evaporated off and the resulting suspension was diluted with water and extracted twice with chloroform (total 125 mL). Then, the organic layer was washed with saturated sodium bicarbonate, brine, and dried over anhydrous magnesium sulfate. The crude material obtained after decantation or evaporation was purified by chromatography on silica gel, eluting with an ethyl acetate / hexane mixture (1:1). The title compound ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com