Process for the production of palladium supported catalysts for catalyzing heck, suzuki-miyaura sonogashira coupling and buchwald-hartwig reactions
A technology for chemical reactions and heterogeneous catalysts, applied in catalytic reactions, carbon compound catalysts, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve the problems of low yield, insufficient stability of coordination compounds and high leakage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0044] Embodiment 1: catalyst preparation
[0045] Will IRA 900 (chloride form) (Acros, BE) was packed into a column and treated repeatedly with 0.5% sodium formate solution until a negative response to chloride ions was observed. The resin was then washed with water until it exhibited a low conductivity response and dried under vacuum. Palladium acetate (20 mg, 0.089 mmol) was added to a suspension of ARF (2 g) in DMF (4 ml), and the 2 The mixture was stirred at room temperature for 1 hour and then at 50°C for 3 hours. Orange or dark orange solutions become completely colorless, while ARF beads turn black. In a control experiment, using IRA 900 (chloride form) and Pd(OAc) 2 or Na 2 PdCl 4 This color change was not observed, suggesting that in the presence of counterions (formate as a reducing source), Pd (II) is reduced to Pd (0) and is adsorbed on the resin surface. At this point, the gray beads turned black and the dark orange supernatant became completely col...
Embodiment 2
[0046] Example 2: From Na 2 PdCl 4 Start to prepare the catalyst
[0047] Repeat the method of embodiment 1, just use the Na of equimolar amount 2 PdCl 4 Replacement of Pd(OAc) 2 . get similar results.
[0048] Will IRA 900 (chloride form) (Acros, BE) was packed into a column and treated repeatedly with 0.5% sodium formate solution until a negative response to chloride ions was observed. The resin was then washed with water until it exhibited a low conductivity response and dried under vacuum. Then, the dried resin (2 g) was placed in methanol and allowed to stand for 2 hours. Excess methanol was removed and palladium acetate (20 mg, 0.089 mmol) diluted in DMF (15 ml) was added under N 2 The mixture was stirred at room temperature for 1 hour and then at 50°C for 3 hours. Orange or dark orange solutions become completely colorless, while ARF beads turn black. In a control experiment, using IRA 900 (chloride form) and Pd(OAc) 2 or Na 2 PdCl 4 This color ch...
Embodiment 3
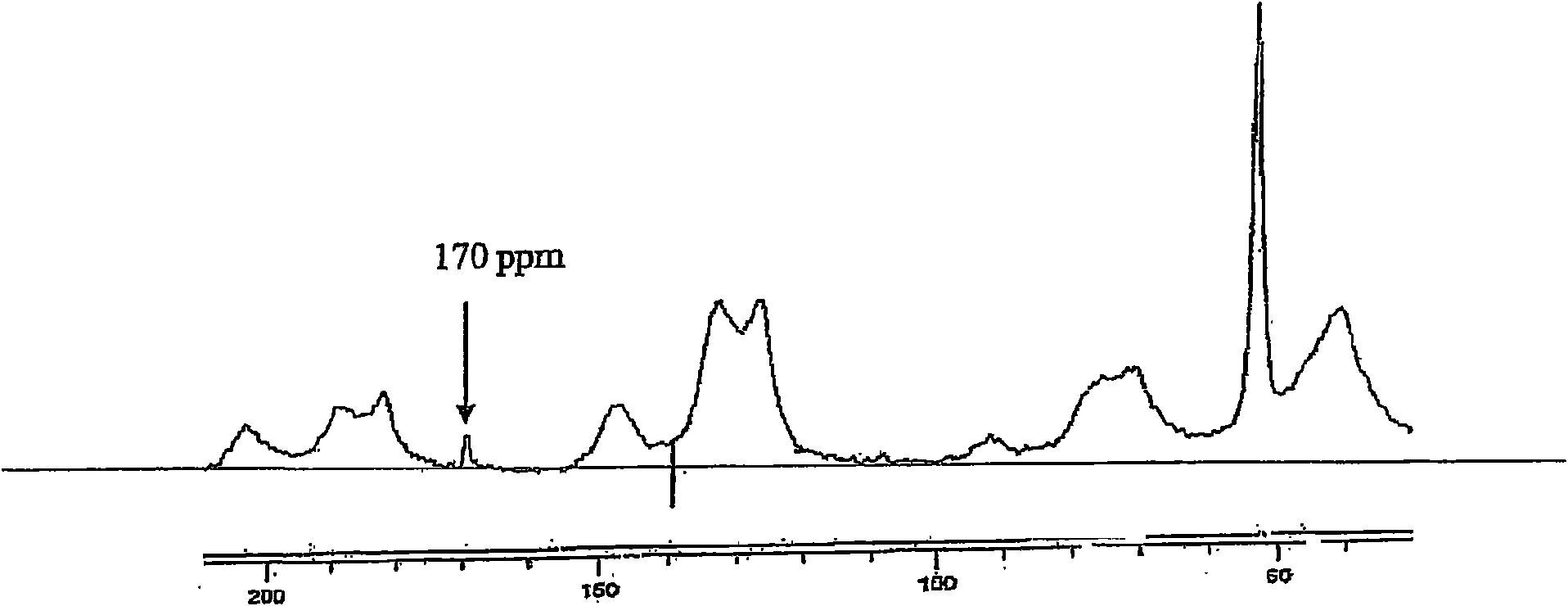
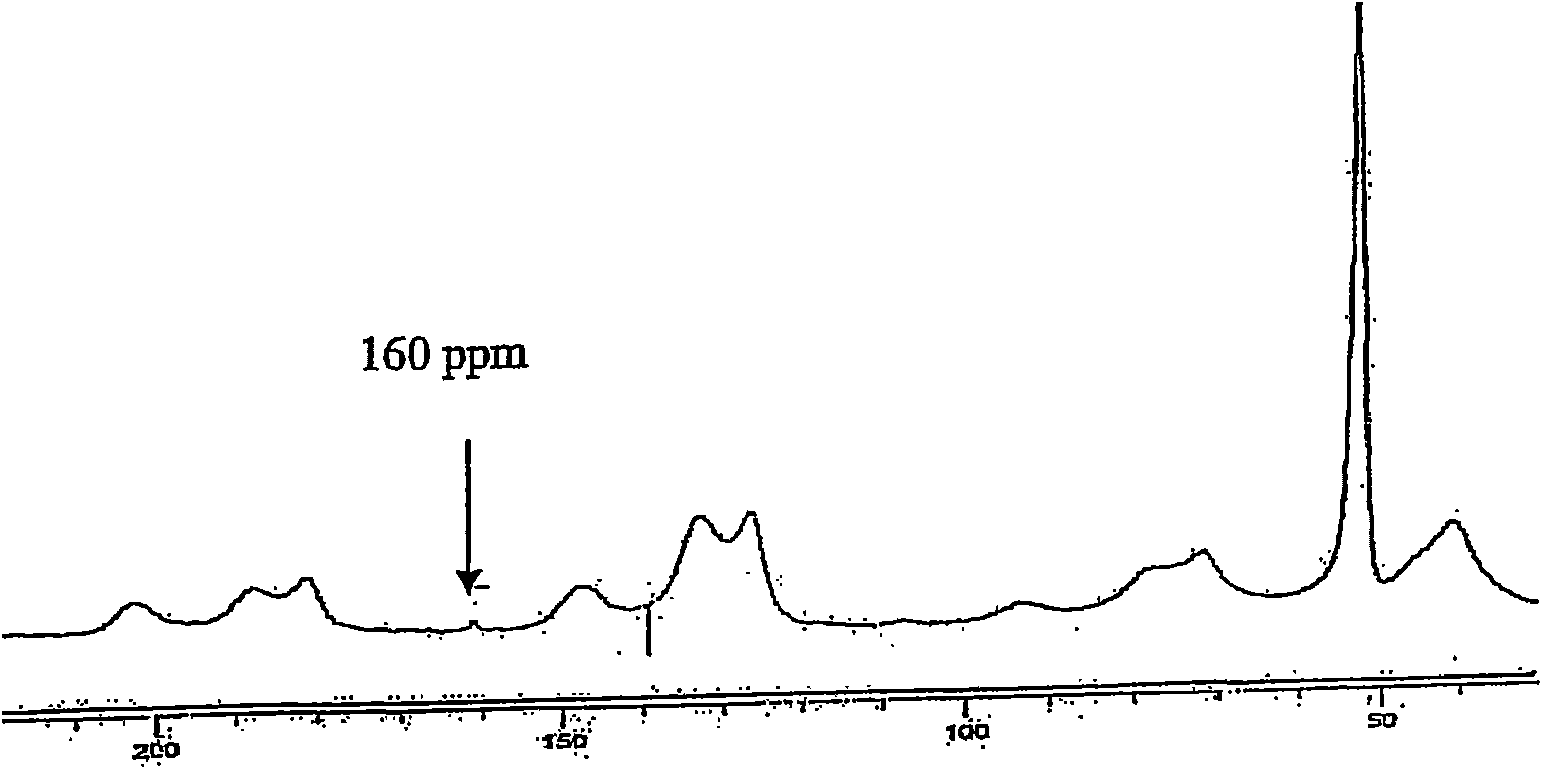
[0050] Example 3: FT-IR Spectrum of New Pd Catalyst
[0051] The new Pd catalyst was first characterized by IR spectroscopy. Carboxylate consists of two identical The bond is precisely represented by the resonance-stabilized carboxylate anion, thus giving antisymmetric and symmetric stretch absorption. In Table 1 the FT-IR spectral data for different formate, ARF and new Pd catalysts are given. The new Pd catalyst and ammonium formate (HCOONH 4 ), potassium formate (HCOOK) and ARF for comparison. 1595-1593cm observed -1 range due to HCOONH 4 , HCOOK, and ARF's carboxylate anions caused by antisymmetric stretching, while the new Pd catalyst absorbs at 1653 cm -1 . Similar observations were noted in the case of symmetric stretching of carboxylate anions. v of the new Pd catalyst max A significant increase in α indicates possible palladium metal deposition and possible bonding of palladium metal to the formate carbonyl.
[0052] Table 1: Carboxylate anion FT-IR data ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| porosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com