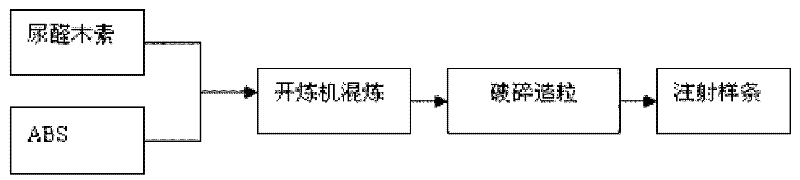
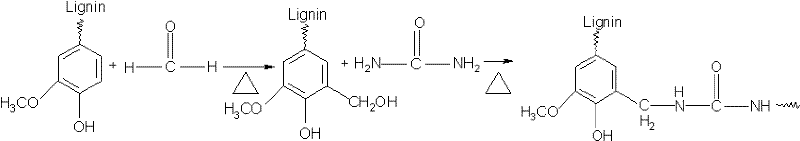
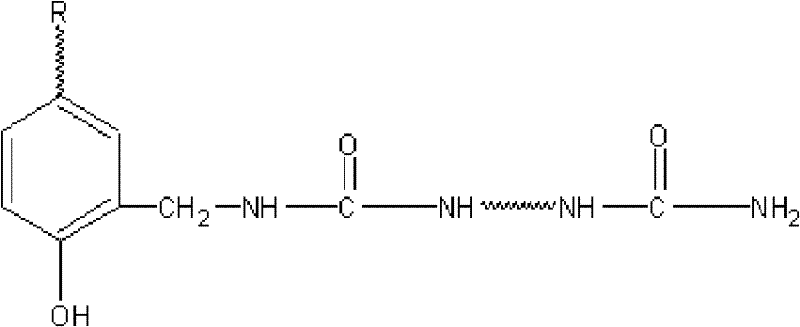
Preparation of macromolecular compatible additive, namely urea-formaldehyde modified lignin and application of macromolecular compatible additive
A technology of lignin and additives, which is applied in the field of preparation and application of urea-formaldehyde modified lignin polymer compatible additives, achieving the effects of high purity, high chemical activity and low manufacturing cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0033] The concrete steps of preparation method are:
[0034] 1) Add water with sodium hydroxide or potassium hydroxide to prepare a 2% by weight alkaline solution;
[0035] 2) Weigh and add the required amount of lignin or its derivatives and water according to the ratio, and adjust the solution to pH=10.0-12.0 with 2% alkaline solution;
[0036] 3) Weigh and add the required aldehyde according to the ratio, heat up to 75-95°C, and react for 0.5-2.0h;
[0037] 4) Add urea according to the required amount in the raw material ratio to the reactant in step 3), and continue the reaction for 1.0-1.5h;
[0038] 5) adding acid to adjust the pH value of the reactant in step 4) to 4.5-6.0, and polycondensation reaction at a temperature of 75-95°C for 15-80min;
[0039] 6) Discharging: Step 5) After the polycondensation reaction is completed, add acid to the reactant to adjust the pH=2.0-3.0, make it settle, suction filter, and dry to obtain urea-formaldehyde modified lignin, which i...
Embodiment 1
[0053] Weigh 15g of dried enzymatic lignin, put it into a 500ml three-necked bottle containing 225mL of 2% NaOH solution by weight, and stir for 15min to completely dissolve the enzymatic lignin in the NaOH solution; add 33mL, weight percent Formaldehyde solution with a concentration of 37% was heated in a water bath to 80°C, and after reflux and stirring for 1 hour, 24.3 g of urea was added and the reaction was continued for 1 hour; after the reaction was completed, a hydrochloric acid solution with a concentration of 12% by weight was slowly added to adjust the pH value to about 3. Let the precipitation stand, pour out the supernatant, centrifuge, wash the precipitate with deionized water three times, and then put the obtained product in a drying oven at 80°C to dry to a constant weight to obtain 40.5g of urea-formaldehyde modified enzymatic hydrolysis Lignin.
Embodiment 2
[0055] Preparation of lignin derivatives: Measure 21ml of epichlorohydrin, add it to a clean 250ml three-neck flask (in the container), weigh 5 grams of enzymatic lignin, pour it into the flask container, heat up to 50°C, stir for 30min, let Fully dissolve and mix lignin and epichlorohydrin, add 0.8ml of 30% NaOH solution by weight within 20 minutes, heat up to 5560°C, stir and reflux for 1 hour, heat up to 70°C, and add 2ml within 20 minutes NaOH solution with a concentration of 30% by weight, stirred and refluxed for 1 hour, and the excess epichlorohydrin was evaporated under reduced pressure to obtain 10ml of epichlorohydrin and a brown solid that is insoluble in water and has certain elasticity, washed with water and dried to obtain 10.85 grams of brittle brown solid enzymatic lignin epoxy resin.
[0056] Put 10.85 grams of brittle brown solid enzymatic lignin epoxy resin into a 500ml three-necked bottle filled with 210mL of 2% NaOH solution by weight, and stir for 25min t...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| ash containing ratio | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com