Nutrient medium and application for soilless culture
A nutrient matrix and soilless cultivation technology, applied in the field of agriculture, can solve the problems of not easy to fix the root system, poor water and fertilizer retention, and few sources of raw materials, and achieve the effect of meeting the physiological needs of different plants, low price, and significant economic benefits
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] Embodiment 1: (the optimum formula of screening nutrient solution with Chinese rose as material)
[0038] (1) configure the nutrient solution, the content of the compound in every liter of water is calculated in mg / L, and its composition and proportioning ratio are shown in Table 1 below;
[0039] Table 1: Components and contents of five nutrient solutions
[0040]
[0041]
[0042] Note: No. 1 is the Dutch rock wool drip irrigation formula
[0043] (2) Perlite-peat composite matrix is configured, and perlite and peat are mixed in a volume ratio of 1:1;
[0044] (3) Irrigation of the upper pot of the plant and the nutrient solution. First move the cutting seedlings of the annual 'Taohong Heping' rose into the cultivation container, then water the seedlings slowly for 7 days, and then water every 7 days, with 400mL per pot. See Table 2 for the implementation effect.
[0045] Table 2: Effects of different formulations of nutrient solutions on rose growth
[00...
Embodiment 2
[0047] Embodiment 2: (take Chinese rose as the optimal volume ratio of material screening matrix)
[0048] (1) Prepare the nutrient solution, the content of the compound in every liter of water is calculated in mg / L, and its composition and proportion are as follows:
[0049] Macronutrients
[0050] Calcium nitrate tetrahydrate (Ca(NO 3 ) 2 4H 2 O) 1370mg / L;
[0051] Potassium nitrate (KNO 3 ) 690mg / L;
[0052] Ammonium nitrate (NH 4 NO 3 ) 53mg / L;
[0053] Potassium dihydrogen phosphate (KH 2 PO 4 ) 1320mg / L;
[0054] Magnesium Sulfate Heptahydrate (MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O) 415mg / L;
[0055] trace elements
[0056] Disodium EDTA (Na 2 Fe-EDTA) 30mg / L;
[0057] Boric acid (H 3 BO 3 ) 2.86mg / L;
[0058] Manganese sulfate tetrahydrate (MnSO 4 4H 2 O) 2.13mg / L;
[0059] Zinc sulfate heptahydrate (ZnSO 4 ·7H 2 O) 0.22mg / L;
[0060] Copper sulfate pentahydrate (CuSO 4 ·5H 2 O) 0.08mg / L;
[0061] Ammonium molybdate tetrahydrate ((NH 4 ) 6 Mo 7 o 24 4H 2 O) 0.0...
Embodiment 3
[0070] Embodiment 3: (taking Chinese rose as the contrast of material optimal matrix and other media)
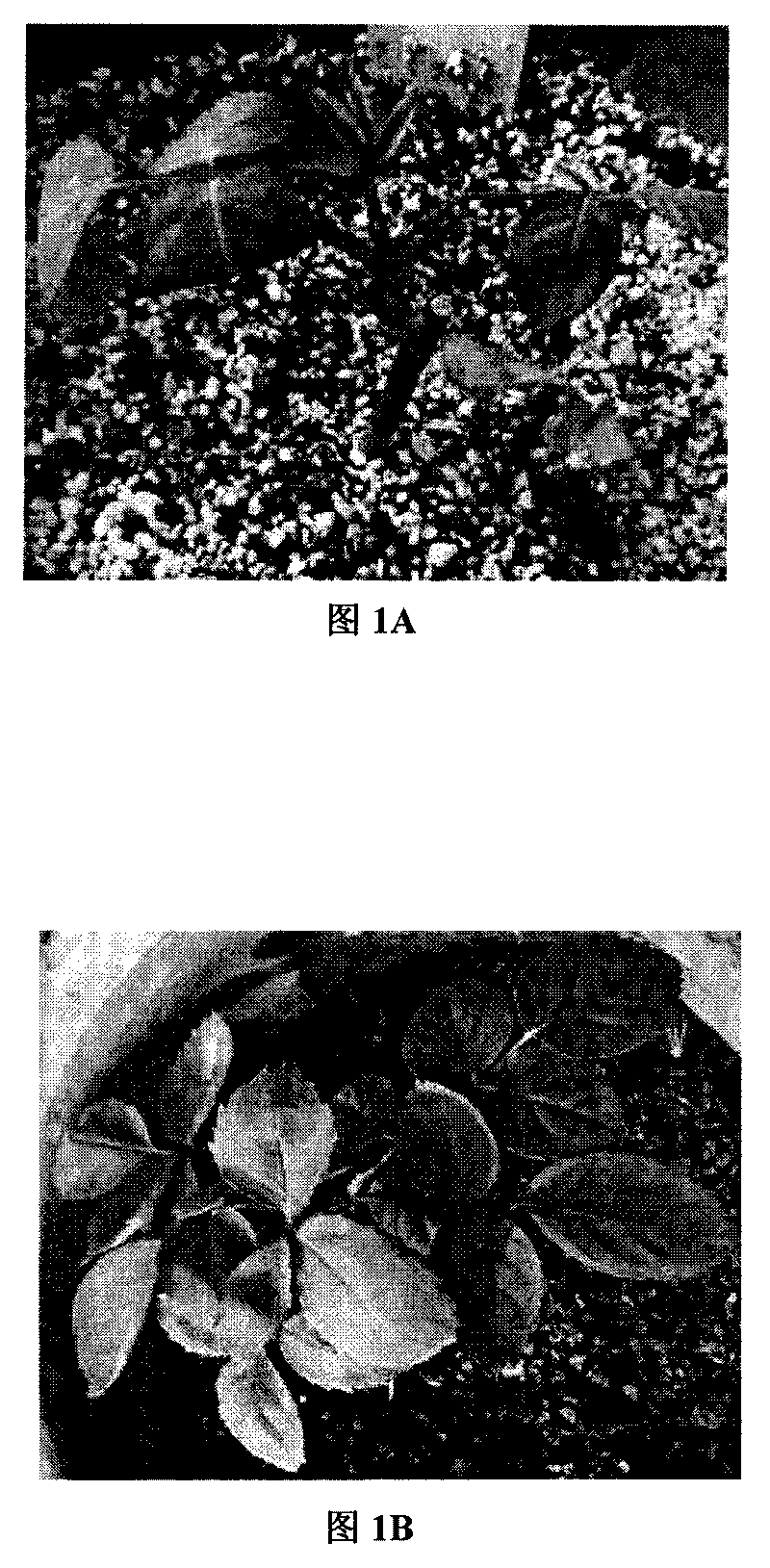
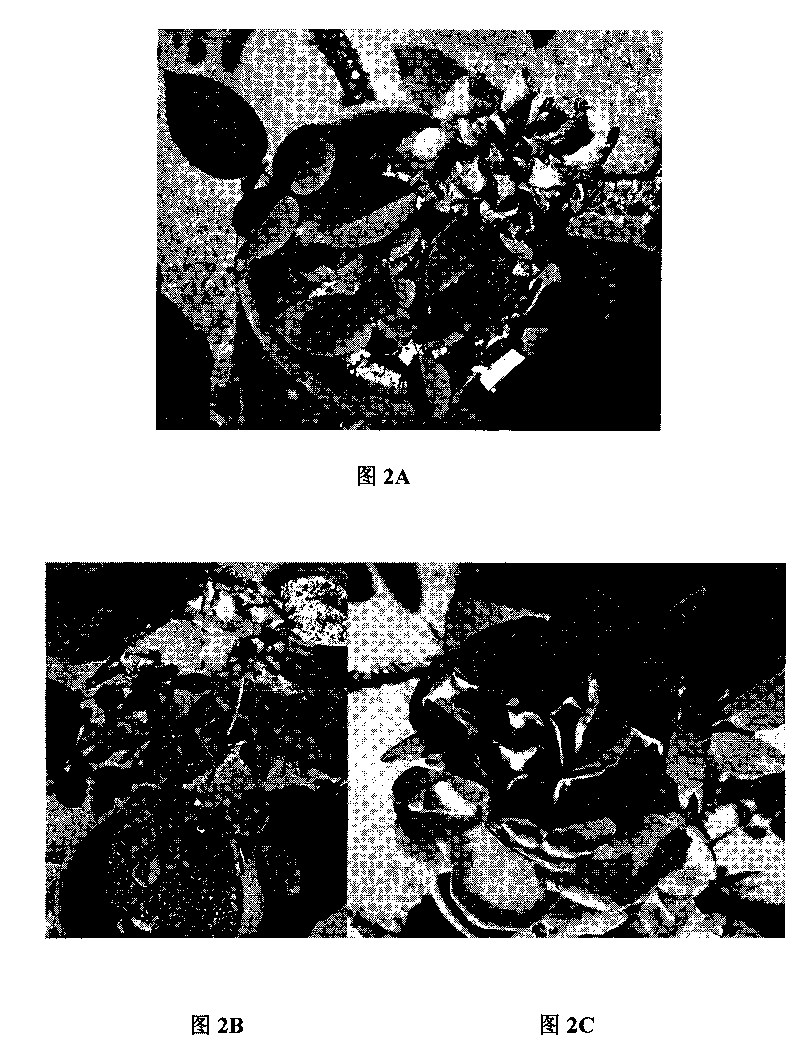
[0071] A kind of nutrient matrix (cotton seed hulls: coal cinder=9: 1) of soilless culture in embodiment 2 is applied to the cultivation of annual ' peach red and peace' rose cutting seedlings (see Figure 1A ), with a perlite-peat composite matrix (perlite:peat=1:1; see Figure 1B ), soil as a contrast, under the same management conditions, rose cultivation is carried out, and the application effects of the three substrates are shown in Table 4, and the flower viewing characteristics are shown in Figure 2.
[0072] Table 4: Effects of different soilless culture substrates on rose growth
[0073]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com