Method for extracting lithium from salt lake brine
A technology for extracting lithium from salt lake brine, applied in chemical instruments and methods, lithium compounds, alkali metal compounds, etc., can solve the problems of low extraction efficiency, serious environmental pollution, strong equipment corrosion, etc., to improve the utilization rate and improve the extraction rate. , the effect of eliminating environmental pollution problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
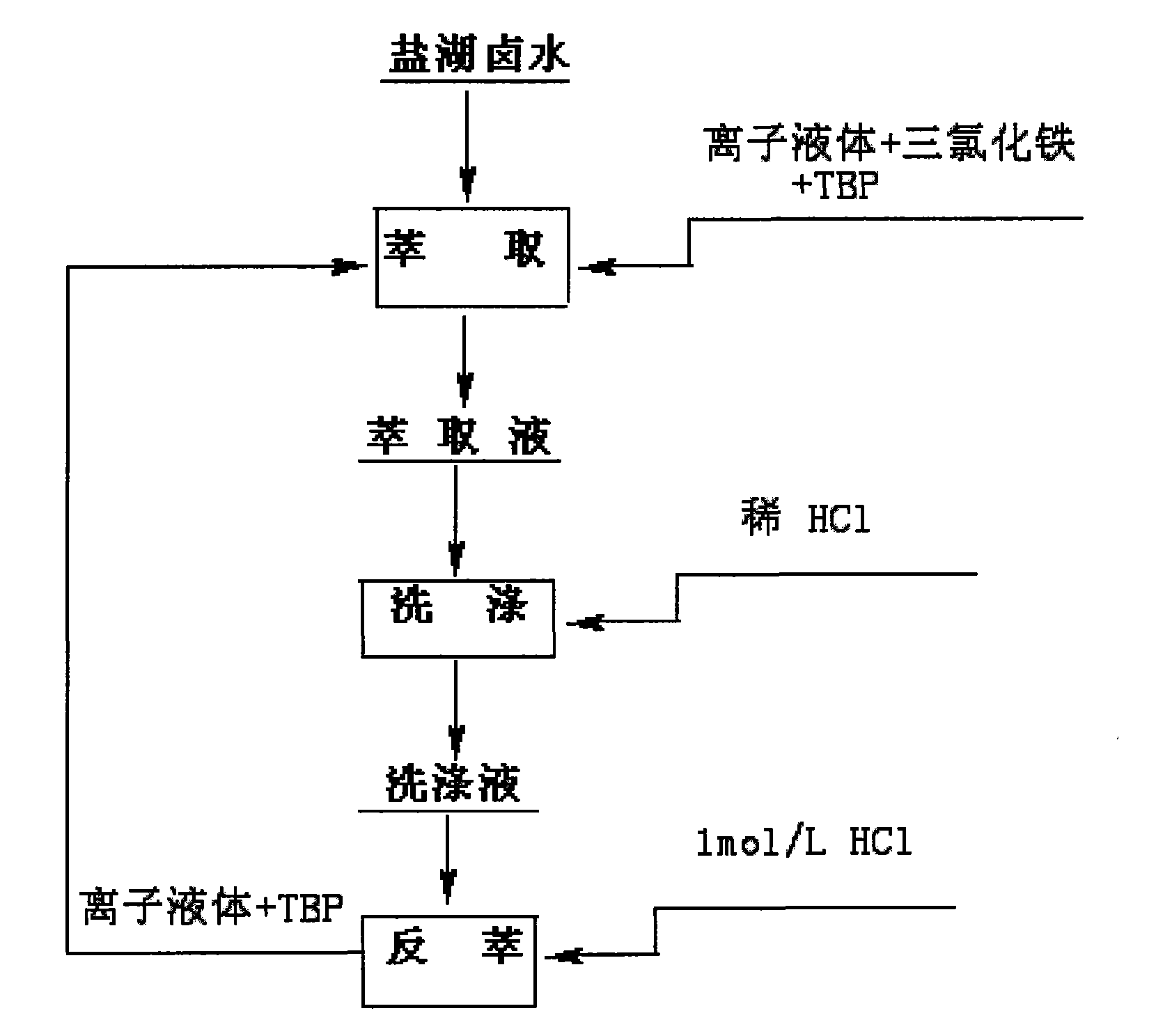
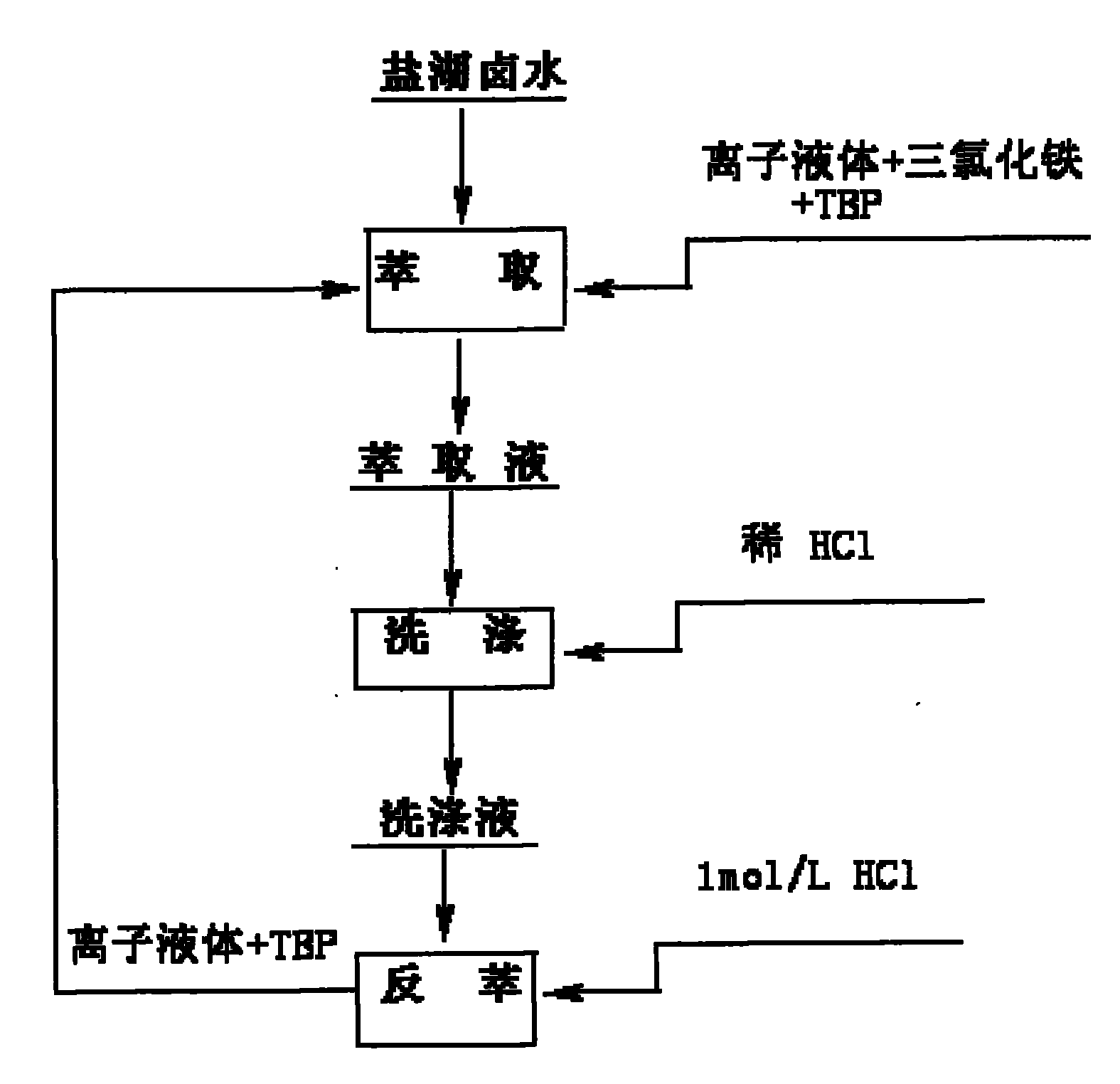
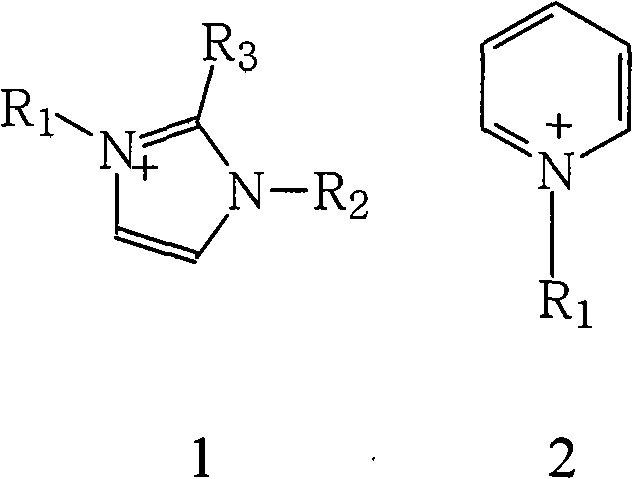
[0039] Take 20mL of salt lake brine containing 2mg / mL of lithium, add it to a 250mL volumetric flask, and add 12mL of 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate ionic liquid, 18mL of TBP, 2.1g of trichloro iron oxide, adjust the pH to 1.5, and shake for 10 minutes. The organic phase was separated by centrifugation, and the content of each element was measured by atomic absorption spectrophotometry, and the primary extraction rate of lithium was calculated to be 48%. Primary extraction rate of interfering ions: Na + 2.3%, Mg 2+ 2.1%, K + 2.7%, Ca 2+ 13%.
[0040] Take the organic phase and add 20 mL of salt lake brine and 2.1 g of ferric chloride to adjust the pH to 1.5. Shake for 10 minutes and perform a second extraction. The organic phase was separated by centrifugation, and the content of each element was determined by atomic absorption spectrophotometry. The secondary extraction rate of lithium is 82.4%, and the primary extraction rates of interfering ions are:...
Embodiment 2
[0043] Take 20 mL of salt lake brine containing 2 mg / ml lithium, add it to a 250 mL volumetric flask, and add 12 mL of 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)imide ionic liquid to it , 18mL TBP, 2.1g ferric chloride, adjust the pH to 1.5, and shake for 10 minutes. The organic phase was separated by centrifugation, and the content of each element was measured by atomic absorption spectrophotometry, and the primary extraction rate of lithium was calculated to be 48.6%. Primary extraction rate of interfering ions: Na + 2.4%, Mg 2+ 2.3%, K + 2.8%, Ca 2+ 13.7%.
[0044] The secondary extraction rate of lithium is 86.7%, and the primary extraction rates of interfering ions are: Na + 1.2%, Mg 2+ 1.4%, K + 1.2%, Ca 2+ 8.8%.
[0045] The third extraction rate of lithium is 97.8%, and the primary extraction rate of interfering ions is: Na + 0.1%, Mg 2+ 0.2%, K + 0.7%, Ca 2+ 3.2%.
Embodiment 3
[0047] Take 20mL of salt lake brine containing 2mg / mL lithium, add it to a 250mL volumetric flask, and add 12mL of 1-dodecyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate ionic liquid, 18mL TBP, 2.1g Ferric chloride, adjust the pH to 1.5, shake for 10 minutes. The organic phase was separated by centrifugation, and the content of each element was measured by atomic absorption spectrophotometry, and the primary extraction rate of lithium was calculated to be 60.1%. Primary extraction rate of interfering ions: N a+ 2.2%, Mg 2+ 2.3%, K + 2.8%, Ca 2+ 14.2%.
[0048] The secondary extraction rate of lithium is 81.7%, and the primary extraction rates of interfering ions are: Na + 1.0%, Mg 2+ 1.7%, K + 1.2%, Ca 2+ 1.8%.
[0049] The third extraction rate of lithium is 95.1%, and the primary extraction rate of interfering ions is: Na + 0.2%, Mg 2+ 0.3%, K + 0.5%, Ca 2+ 3.8%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com