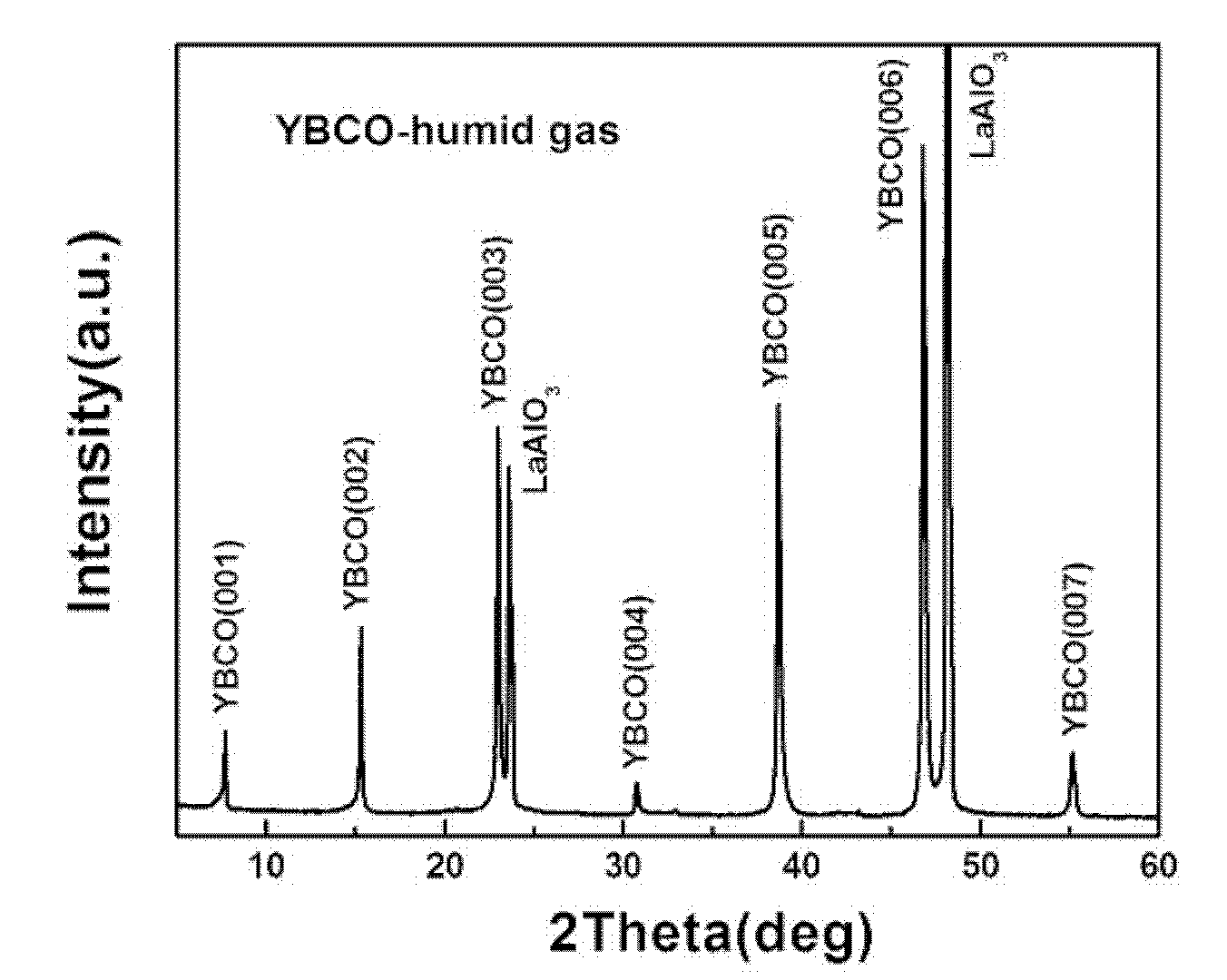
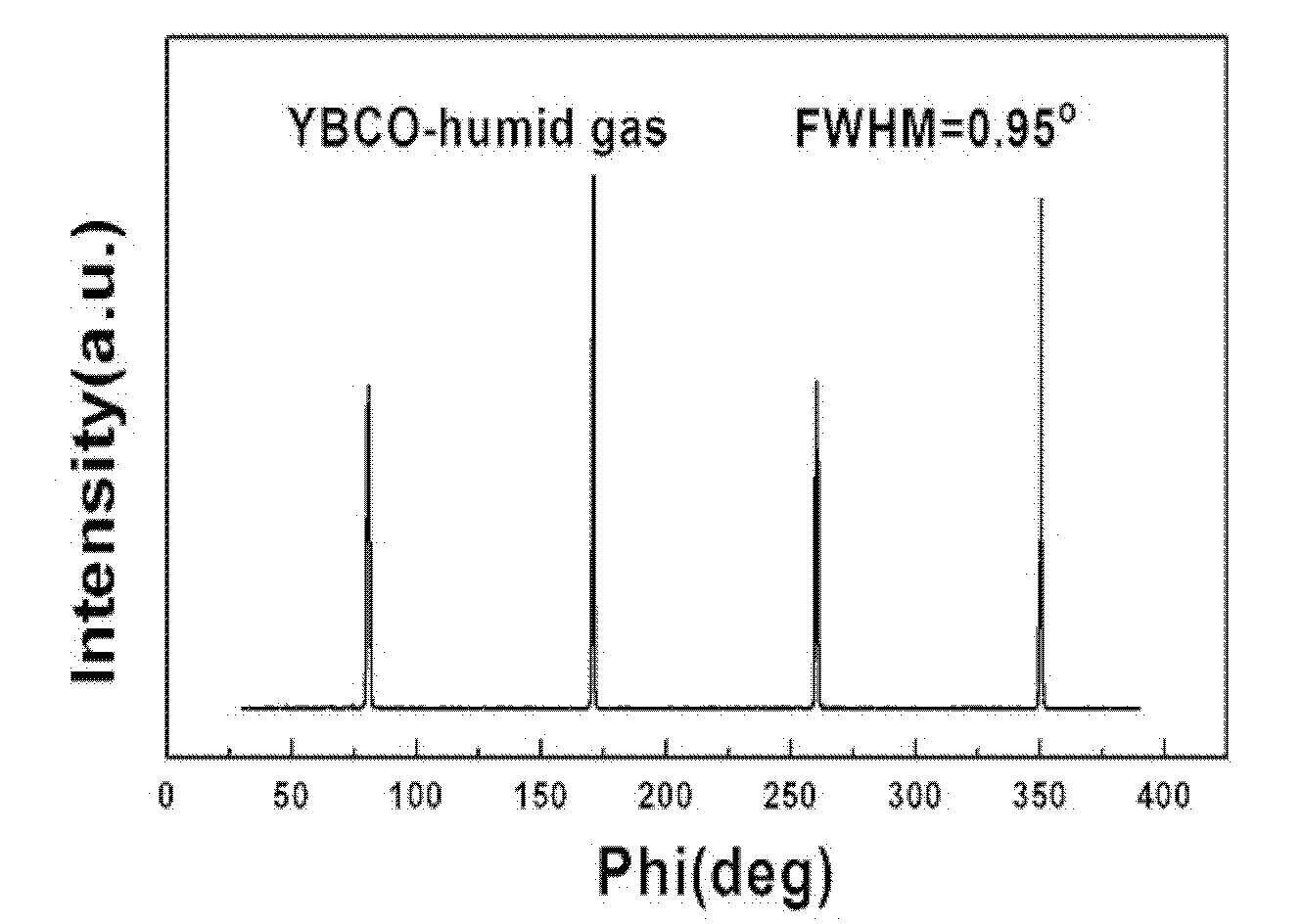
Method for preparing superconducting layer of high-temperature superconducting coated conductor by depositing fluorine-free chemical solution
A solution deposition and high-temperature superconducting technology, which is applied in the usage of superconducting elements, superconducting/high-conducting conductors, superconducting devices, etc., can solve the problem of hindering the transmission of superconducting current, the limitation of the application of fluorine-free method, and reducing the superconducting layer Current-carrying performance and other issues to achieve the effect of ensuring purity, good superconducting performance, and suppressing volatilization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach
[0039] A specific embodiment of the present invention is: a method for preparing a high-temperature superconducting coating conductor superconducting layer by deposition of a fluorine-free chemical solution. The method is as follows:
[0040] a. Preparation of precursor solution: dissolving yttrium acetate, barium acetate, and copper acetate in propionic acid according to the stoichiometric ratio of yttrium:barium:copper: 1:2:3, to obtain a precursor solution.
[0041] b. Preparation of coating colloid: In the precursor solution, add 3 parts of polyvinyl butyral (PVB) macromolecular additives and stir well to obtain a uniform and transparent coating colloid with a certain viscosity.
[0042] c. Coating and drying: Spin coating is used for coating, that is, the colloid is dropped on the substrate and rotated with a coater to obtain a uniform coating film, and then dried at 100°C for 20 minutes.
[0043] d. Wet decomposition heat treatment: In an argon atmosphere, the temperatur...
Embodiment 2
[0050] This example is basically the same as Example 1, the difference is:
[0051] In the preparation of the precursor solution in step a, the rare earth acetate is dysprosium acetate.
[0052] In the d-step decomposition heat treatment process, the temperature is raised from room temperature to 135°C at a rate of 3°C / min in a dry argon atmosphere, and then a mixture of water vapor and argon with a dew point of 18°C is introduced into the furnace to form moist argon At this time, the temperature was raised to 480°C at a rate of 1°C / min, and the temperature was kept for 0.75 hours.
[0053] In the phase-forming heat treatment of step e, argon gas is introduced into the tube furnace of the upward step to form an argon protective atmosphere, and the furnace temperature is rapidly raised to 810 °C at 25 °C / min, and kept for 5 minutes; then at 7 °C / min Lower the temperature to 775°C, keep it warm for 1 hour, and finally lower it to 450°C in dry argon, then change the atmosphere...
Embodiment 3
[0059] This example is basically the same as Example 1, the difference is:
[0060] In the preparation of the precursor solution in step a, the rare earth acetate is gadolinium acetate.
[0061] In the preparation of the coating colloid in step b, 5 parts of polyvinyl butyral are added to the precursor solution as a polymer material additive.
[0062] The drying in step c is 150° C. for 15 minutes.
[0063] During the decomposition heat treatment in step d, the temperature is raised from room temperature to 125°C at a rate of 2°C / min in a dry argon atmosphere, and then a mixture of water vapor and argon with a dew point of 15°C is introduced into the furnace to form moist argon Protective atmosphere. At this time, the temperature was raised to 470° C. at a rate of 0.25° C. / min and kept for 1 hour.
[0064] In the phase-forming heat treatment of step e, argon gas is introduced into the tube furnace of step d to form an argon protective atmosphere, and the furnace temperature ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com