Method for screening and identifying adhesion proteins
An adhesion protein and protein technology, which is applied in the field of screening and identification of proteins, can solve the problems of high false positive rate of adhesion proteins, no adhesion function, complex intestinal environment, etc., and achieves the effect of low cost and improved efficiency.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
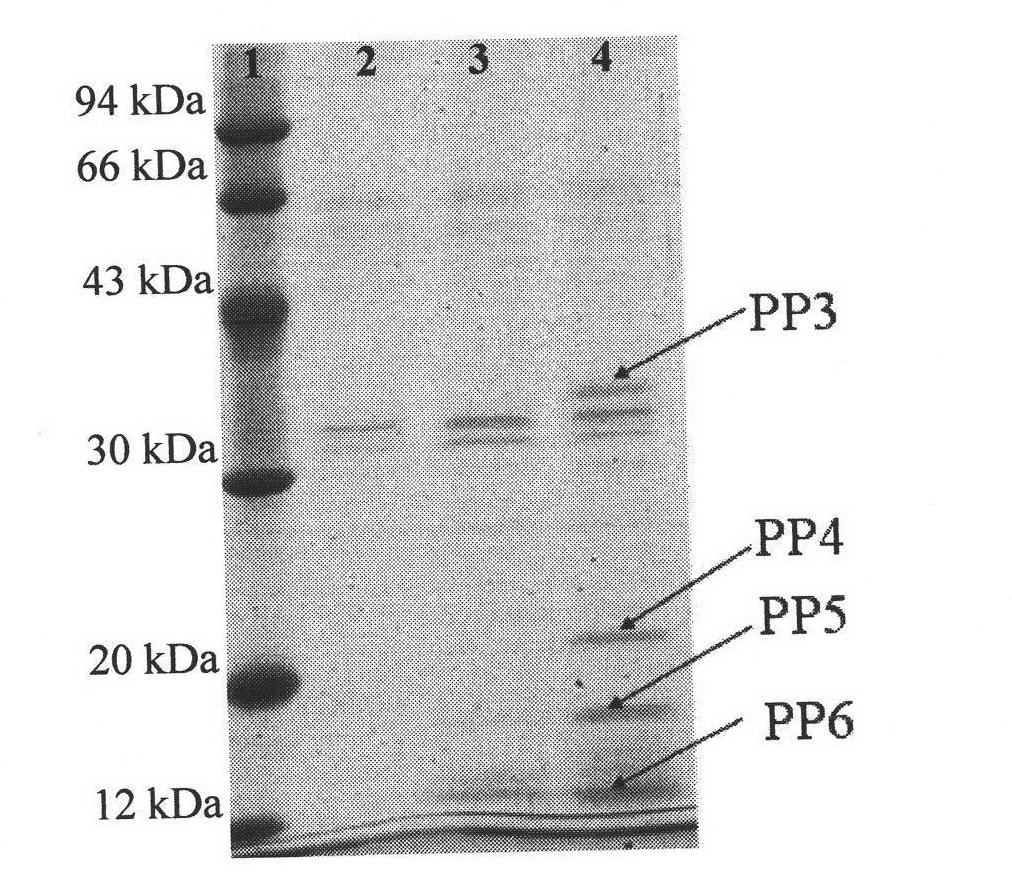
[0016] Example 1: Screening of Bifidobacterium longum adhesion proteins by magnetic bead method
[0017] 1. Activation of magnetic beads: Wash 30 mg of carboxylated magnetic beads with 6 mL of sodium phosphate buffer (0.2 M, pH 4.5) for 3 times, resuspend in 1.5 mL of sodium phosphate buffer, add 2.25 mg of carbodiimide and 1.5 mg thiohydroxysuccinimide, react at room temperature for 40min.
[0018] 2. Adjust the pH of the above reaction system to 7.8, add 1500 mg of intestinal epithelial cell HT-29 cell fragments, react at room temperature for 3 hours, and overnight at 4°C.
[0019] 3. Adsorb the magnetic beads on the magnetic stand to remove the solution, wash the magnetic beads 3 times with PBS to wash away the unbound intestinal epithelial cell fragments, add 1.5mL 3% BSA solution to seal the magnetic beads for 1h, adsorb the magnetic beads on the magnetic stand to remove the solution, wash with PBS Wash the magnetic beads 3 times.
[0020] 4. Divide the magnetic beads i...
Embodiment 2
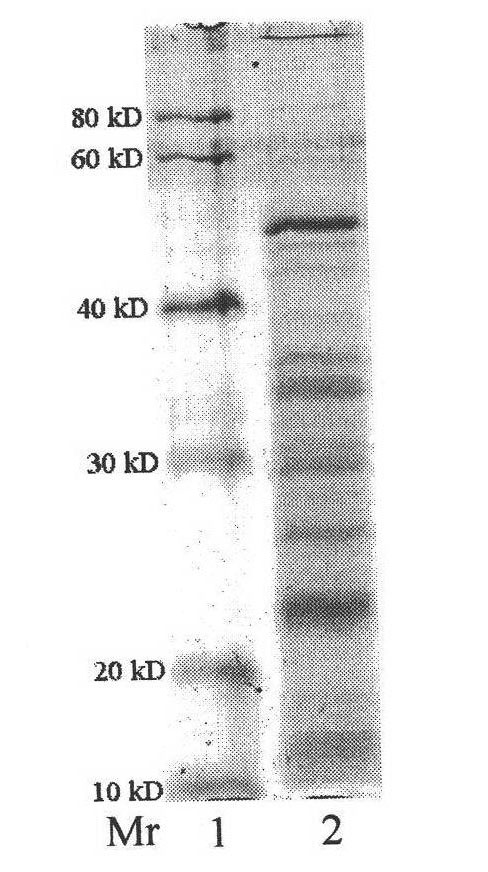
[0023] Example 2: Screening of Adhesive Proteins of Bifidobacterium adolescentis by Magnetic Beads Method
[0024] 1. Activation of magnetic beads: wash 10 mg of carboxylated magnetic beads with 2 mL of sodium phosphate buffer (0.2 M, pH 4.5) for 3 times, resuspend in 0.5 mL of sodium phosphate buffer, add 0.75 mg of carbodiimide and 0.5 mg thiohydroxysuccinimide, react at room temperature for 40min.
[0025] 2. Adjust the pH of the above reaction system to 7.8, add 500 mg of intestinal epithelial cell HT-29 cell fragments, react at room temperature for 3 hours, and overnight at 4°C.
[0026] 3. Adsorb the magnetic beads on the magnetic stand to remove the solution, wash the magnetic beads 3 times with PBS to wash away the unbound intestinal epithelial cell fragments, add 1.5mL 3% BSA solution to seal the magnetic beads for 1h, adsorb the magnetic beads on the magnetic stand to remove the solution, wash with PBS Wash the magnetic beads 3 times.
[0027] 4. Add 0.2mL 2.5mg / mL...
Embodiment 3
[0030] Example 3: Magnetic bead method for screening Lactobacillus plantarum adhesion proteins
[0031] 1. Activation of magnetic beads: wash 10 mg of carboxylated magnetic beads with 2 mL of sodium phosphate buffer (0.2 M, pH 4.5) for 3 times, resuspend in 0.5 mL of sodium phosphate buffer, add 0.75 mg of carbodiimide and 0.5 mg thiohydroxysuccinimide, react at room temperature for 40min.
[0032] 2. Adjust the pH of the above reaction system to 7.8, add 500 mg of intestinal epithelial cell HT-29 cell fragments, react at room temperature for 3 hours, and overnight at 4°C.
[0033] 3. Adsorb the magnetic beads on the magnetic stand to remove the solution, wash the magnetic beads 3 times with PBS to wash away the unbound intestinal epithelial cell fragments, add 1.5mL 3% BSA solution to seal the magnetic beads for 1h, adsorb the magnetic beads on the magnetic stand to remove the solution, wash with PBS Wash the magnetic beads 3 times.
[0034] 4. Add 0.2 mL of Lactobacillus pla...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com