New cartilaginous affinity polypeptide sequence, screening method and application thereof
A sequence and cartilage technology, applied in the application field of targeted PEI nanocarriers, can solve the problems of low gene transfection efficiency and the inability of polypeptide sequences to take into account tissue specificity and cell affinity, so as to improve tissue specificity. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0101] Example 1 Screening of cartilage-affinity polypeptide sequences by phage display technology
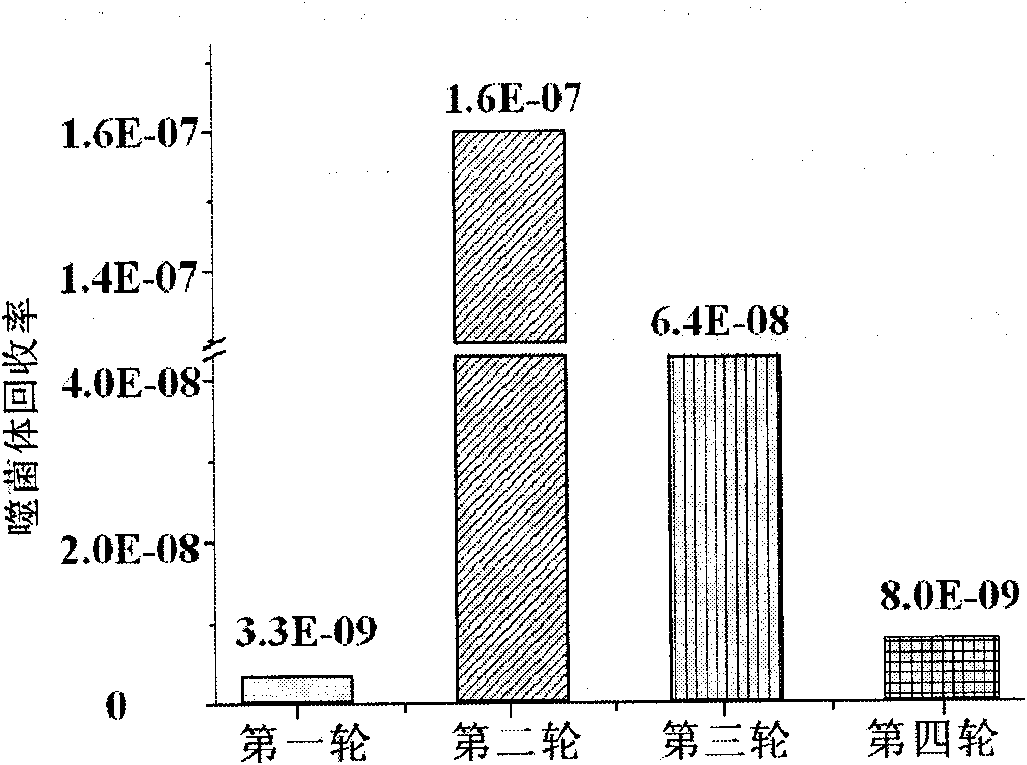
[0102] 1. The first round of screening
[0103] (1) Rabbit synovium and cartilage sample preparation:
[0104] Select 4-week-old healthy rabbits, male or female, and overdose with 100 mg / Kg pentobarbital sodium to anesthetize them to death. The double knee joints of rabbits were separated under aseptic conditions, and the muscles and ligaments around the joints were removed. Under a microscope, the synovial tissue on the surface of the articular cartilage was scraped off with a sharp blade, and the articular cartilage and synovial tissue were cut. PBS (Na 2 HPO 4 10mM, KH 2 PO 4 2mM, NaCl 137mM, KCl 2.7mM, pH 7.4, DecentBio) fully washed 3 times.
[0105] Positive screening dish: Cut rabbit articular cartilage into cartilage slices with a diameter of about 5-10mm and a thickness of 2-3mm, about 20-30 slices, and place them in a 60mm culture dish;
[0106] Negative scre...
Embodiment 2
[0149] Example 2 Modification of polyethylenimine cationic polymers with articular cartilage tissue-specific and chondrocyte-high affinity polypeptides
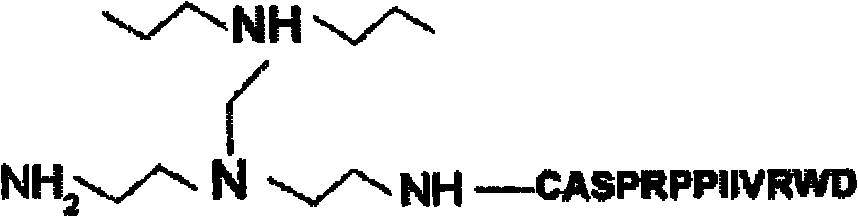
[0150] 1. Polypeptide synthesis: Synthesize and screen the obtained cartilage-friendly polypeptide, and connect a cysteine (C) at its 3'C end to obtain the corresponding cartilage-friendly polypeptide DWRVIIPPRPSAC (synthesized by Scilight-peptide Inc, China), using FITC (fluorescein isothiocyanate, Fanbo, China) fluorescent dye was used to label the polypeptide. A cysteine residue (C) is linked at the 3' end of the polypeptide in order to covalently modify PEI (25KDa) so that it can be combined with the imino group (-NH 2 ) covalently bound.
[0151] 2. Activation of PEI and coupling of peptides:
[0152] (1) Under a dry nitrogen atmosphere, dissolve 5 mg PEI in 500 μl DMSO (dimethylsulfoxide, Dimethylsulfoxide, sigma) to form a 10 mg / ml solution;
[0153] (2) Add 1 mg of MBS (Maleiimido-benzoic acid Nhydroxysuccinimide...
Embodiment 3
[0157] Example 3 Identification of cartilage-affinity polypeptides for the affinity of rabbit-derived chondrocytes
[0158] In this example, cartilage-affinity phages containing DWRVIIPPRPSA polypeptide fragments were used to detect their affinity to rabbit-derived chondrocytes.
[0159] 1. Rabbit-derived chondrocyte culture:
[0160] (1) Cut out the full-thickness cartilage slices of the rabbit knee joint under aseptic conditions, wash them three times with PBS containing 0.1% (W / V) ampicillin, and cut off non-cartilage tissues such as synovial tissue or fibrous connective tissue;
[0161] (2) Transfer the cleaned cartilage into a 60mm petri dish, add 6ml of 0.2% trypsin (Gibco, USA), digest it in a 37°C incubator for 60min (preferably in a state of stirring), and remove the synovium on the surface of the cartilage and fibroblasts, discard the trypsin, wash 3 times with PBS (pH 7.4) containing 0.1% (W / V) ampicillin;
[0162] (3) Resuspend the cartilage slices with 1ml PBS, ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com