Sulfonic acid compound-containing and tin compound-containing polylactic acid composition and preparation method thereof
A technology of sulfonic acid compound and tin compound, applied in the field of preparing polylactic acid, can solve the problems of poor heat resistance and hydrolysis resistance of polylactic acid
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
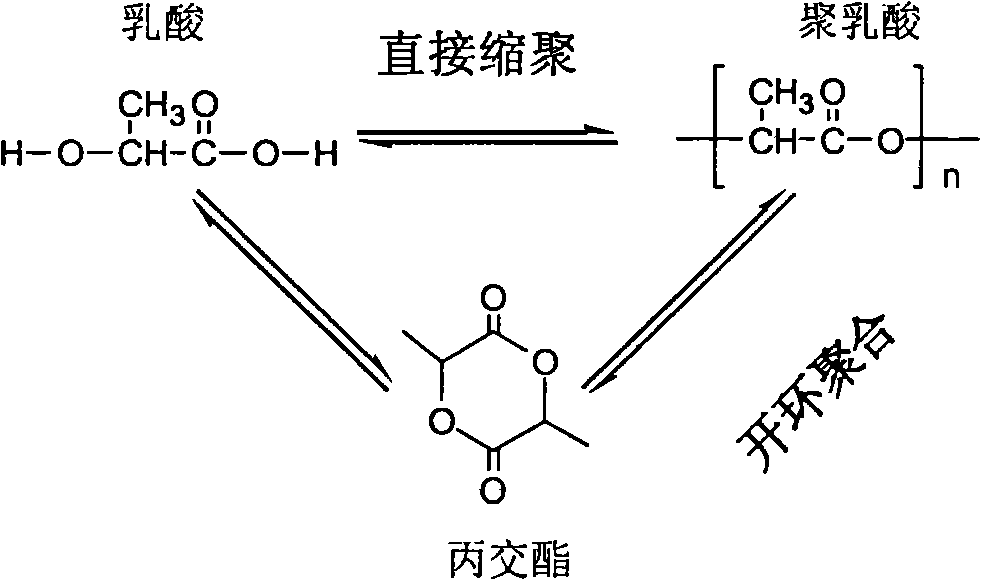
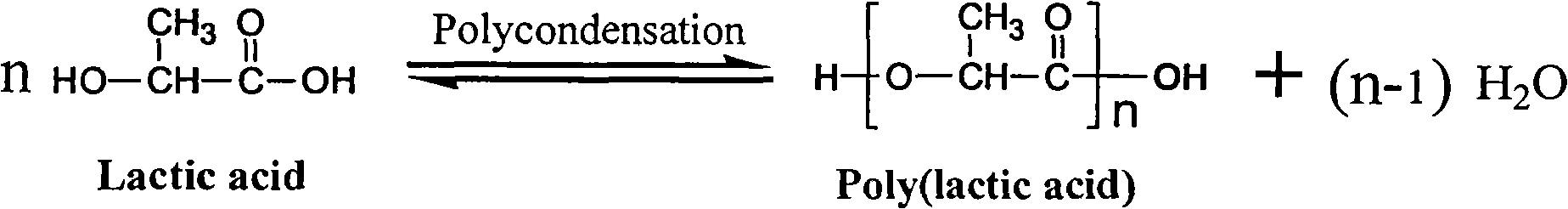
[0114] After pouring 200 g of 90 wt % L-lactic acid aqueous solution into a 500 mL four-necked flask, the flask was placed in an oil bath. Install a stirrer on the four-neck flask, insert a thermocouple thermometer, connect the vacuum pipeline and the nitrogen pipeline and replace with nitrogen for 3 times, then raise the temperature of the oil bath to 120°C for dehydration. The system pressure gradually decreased from normal pressure to 5KPa within 60 minutes from the start of dehydration; then continued dehydration at 5KPa for 1.5 hours (total dehydration 2.5 hours); at this time, after returning the system pressure to normal pressure with nitrogen, add 4952mg of tin (the addition amount is 27513ppm relative to the mass of lactic acid in terms of metal elements, the same below), 3964mg of methanedisulfonic acid (the addition amount is based on sulfonate-SO 3 The sulfur element mass in H is 8000ppm relative to the lactic acid mass, the same below). Then the temperature of th...
Embodiment 2
[0117] After pouring 200 g of 90 wt % L-lactic acid aqueous solution into a 500 mL four-necked flask, the flask was placed in an oil bath. Install a stirrer on the four-neck flask, insert a thermocouple thermometer, connect the vacuum pipeline and the nitrogen pipeline and replace with nitrogen for 3 times, then raise the temperature of the oil bath to 120°C for dehydration. The system pressure gradually decreased from normal pressure to 5KPa within 60 minutes from the start of dehydration; then continued dehydration at 5KPa for 1.5 hours (total dehydration 2.5 hours); at this time, after returning the system pressure to normal pressure with nitrogen, add Stannous acetate 9mg (25ppm), ethanedisulfonic acid 338mg (632ppm). Then the temperature of the system was raised to 160°C, the pressure was gradually reduced from normal pressure to 0.3KPa within 2 hours, and the pressure was kept at 0.3KPa for 4 hours (6 hours in total) after melt polymerization, poured out, and cooled to o...
Embodiment 3
[0120] After pouring 200 g of 90 wt % L-lactic acid aqueous solution into a 500 mL four-necked flask, the flask was placed in an oil bath. Install a stirrer on the four-neck flask, insert a thermocouple thermometer, connect the vacuum pipeline and the nitrogen pipeline and replace with nitrogen for 3 times, then raise the temperature of the oil bath to 120°C for dehydration. The system pressure gradually decreased from normal pressure to 5KPa within 60 minutes from the start of dehydration; then continued dehydration at 5KPa for 1.5 hours (total dehydration 2.5 hours); at this time, after returning the system pressure to normal pressure with nitrogen, add Stannous acetate 107.7mg (300ppm), propanedisulfonic acid 765mg (1333ppm). Then the temperature of the system was raised to 160°C, the pressure was gradually reduced from normal pressure to 0.3KPa within 2 hours, and the pressure was kept at 0.3KPa for 4 hours (6 hours in total) after melt polymerization, poured out, and cool...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com