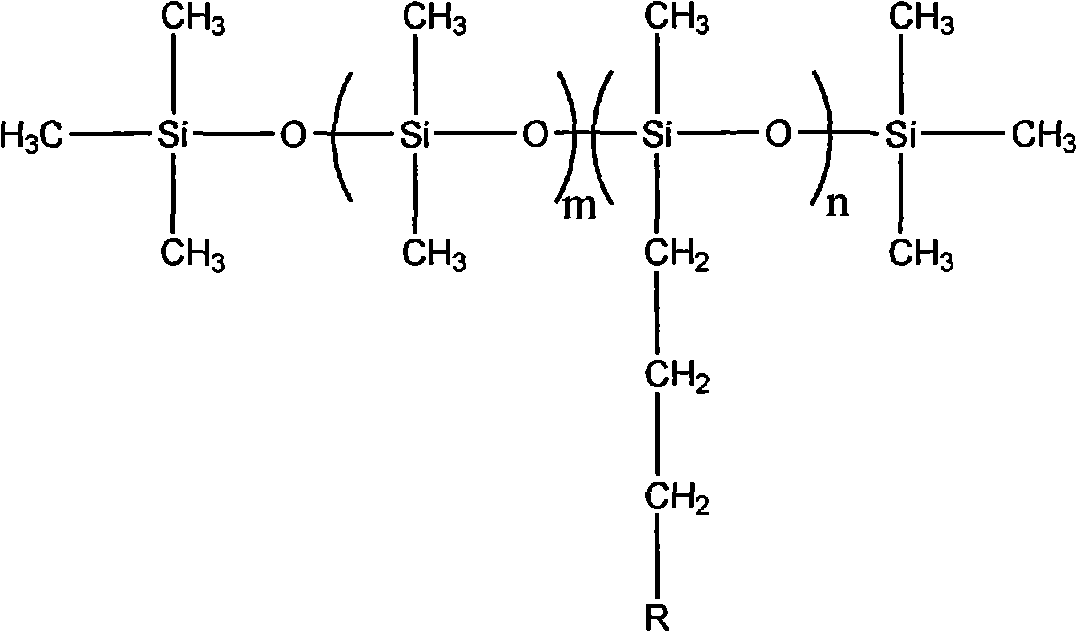
Method for preparing glycosyl amide modified polysiloxane
An aminopolysiloxane and polysiloxane technology, which is applied to non-active ingredients in medical preparations, pharmaceutical formulations, etc., can solve the problems of high toxicity of allylamine, expensive catalyst chloroplatinic acid, and lengthy reaction process. and other problems, to achieve the effect of being conducive to industrialization, cheap catalysts, and reducing the reaction process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0020] Add 5.93kg of octamethylcyclotetrasiloxane, 6.18kg of aminoethylaminopropyldimethoxymethylsilane, 1.62kg of hexamethyldisiloxane, and 10.9g of tetramethylammonium hydroxide into the reaction kettle , heated to dissolve, the temperature was controlled at 30°C, and after 5 hours of reaction, the temperature was raised to 135°C to deactivate the catalyst. Aminoethylaminopropyl polysiloxane was obtained after vacuum distillation, and the primary ammonia value was measured by potentiometric titration. Add equimolar gluconolactone according to the number of moles of the primary ammonia value, use methanol as a solvent, and react at a temperature of 70° C. for 6 hours. The solvent methanol was evaporated, and the product glucamide-modified aminoethylaminopropyl polysiloxane was obtained after vacuum drying. The minimum surface tension of its aqueous solution measured with a K12 surface tensiometer is 23mN / m, and the critical micelle concentration is 35mg / L.
Embodiment 2
[0022] Add 2.97kg of octamethylcyclotetrasiloxane, 5.74kg of aminopropyldiethoxymethylsilane, 1.62kg of hexamethyldisiloxane, and 112g of potassium hydroxide in the reaction kettle, heat and dissolve, and control the temperature at After reacting at 220°C for 7 hours, add acetic acid to neutralize the catalyst, deactivate it and filter it out. Aminopropyl polysiloxane was obtained after rectification under reduced pressure, and the ammonia value was measured by potentiometric titration. According to the number of moles of the ammonia value, three times the moles of gluconolactone were added, and ethanol was used as a solvent, and the reaction was carried out at a temperature of 30° C. for 5 hours. The solvent ethanol was evaporated, and the product glucamide-modified aminopropyl polysiloxane was obtained after vacuum drying. The lowest surface tension of its aqueous solution measured with a K12 surface tensiometer is 24mN / m, and the critical micelle concentration is 23mg / L. ...
Embodiment 3
[0024] Add 1.12kg of hexamethylcyclotrisiloxane, 2.45kg of aminopropyldimethoxymethylsilane, 0.81kg of hexamethyldisiloxane, and 104.5g of tetrabutylphosphonium hydroxide in the reaction kettle, and heat to dissolve. The temperature is controlled at 80°C, and after 8 hours of reaction, the temperature is raised to 110°C to deactivate the catalyst. Aminopropyl polysiloxane was obtained by rectification under reduced pressure, and the ammonia value was measured by potentiometric titration. According to the number of moles of ammonia value, add twice moles of lactobionic acid, use isopropanol as a solvent, and react at a temperature of 90° C. for 10 hours. The solvent isopropanol was distilled off, and the product lactosamide-modified aminopropyl polysiloxane was obtained after vacuum drying. The minimum surface tension of its aqueous solution measured with a K12 surface tensiometer is 26mN / m, and the critical micelle concentration is 74mg / L.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Surface tension | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Surface tension | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Critical micelle concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com