Method for reducing calcined magnesite by using calcium carbide under normal pressure
A technology for calcining magnesite and calcium carbide, which is applied in the field of calcium carbide reducing calcined magnesite at atmospheric pressure, which can solve the problems of long production cycle, discontinuous, low magnesium output, etc., and achieve cost saving, low price and easy availability Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
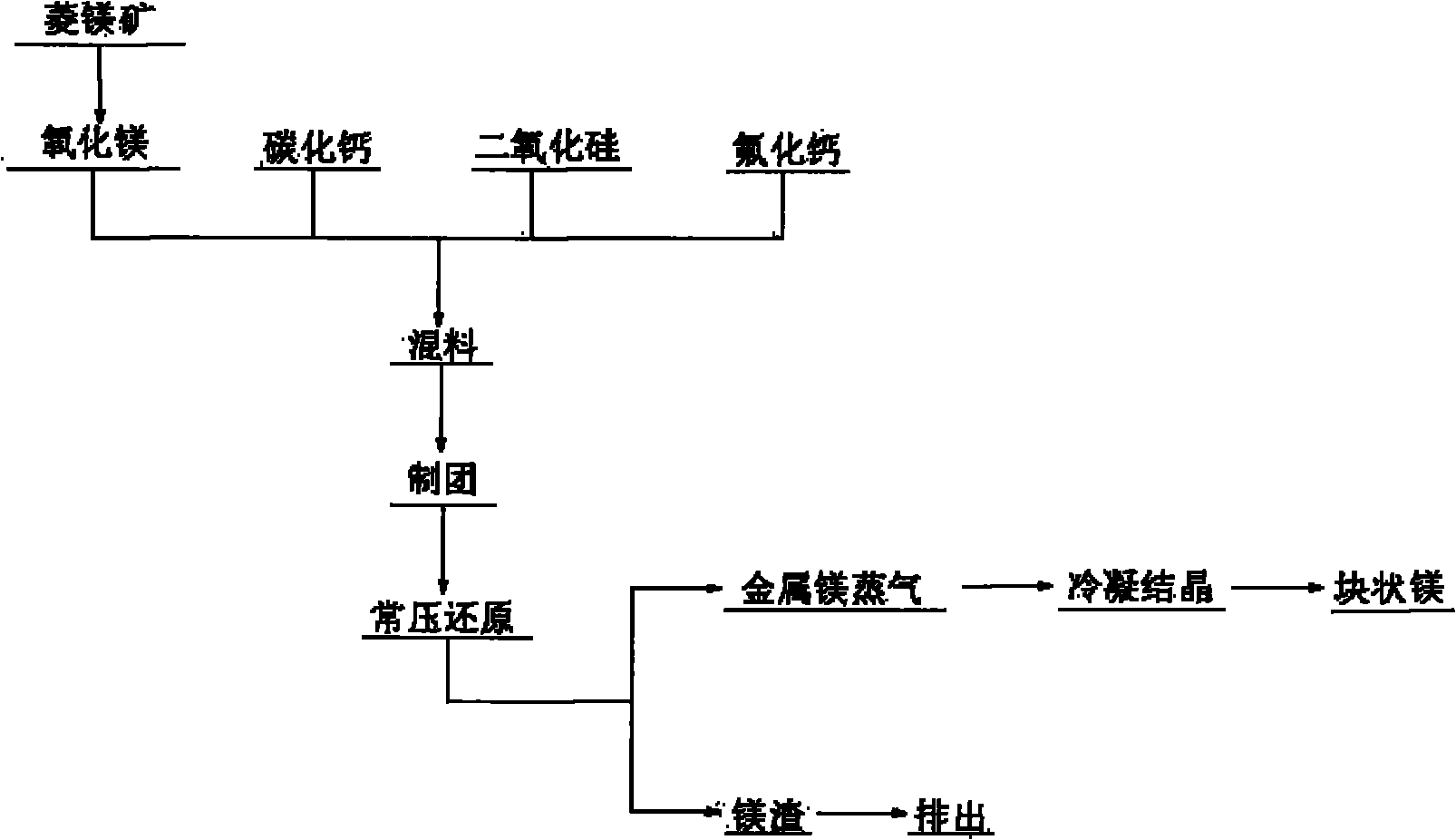
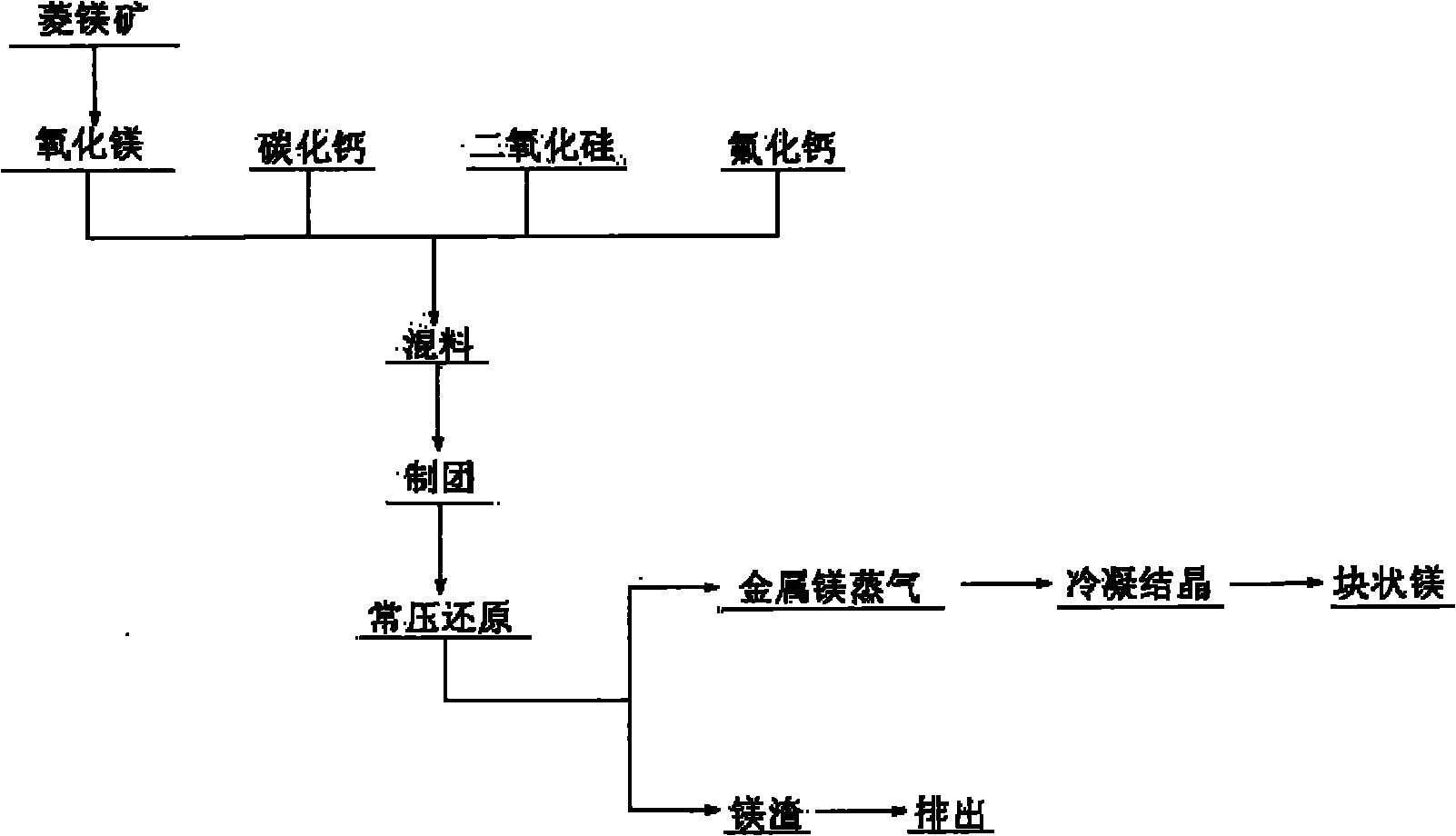
[0022] figure 1 It is a process flow chart of a method for reducing calcined magnesite with calcium carbide atmospheric pressure of the present invention, as figure 1 Shown: Calcined magnesite (magnesite content above 99%) is prepared with calcium carbide and silicon dioxide in molar equivalents of 1:1:0.75, and calcium fluoride, a catalyst accounting for 8% of the total material amount, is added and then mixed uniform. Under the pressure of 30MPa, it is pressed into a material ball with a diameter of 3cm. Before putting in the material ball, the air in the reaction system is exhausted, and then a certain amount of inert gas is introduced to keep the system at normal pressure. The induced draft fan condenses the generated magnesium vapor into crystalline magnesium on the condenser at 200-550°C. After 6 hours of reaction, continuous slagging and feeding are carried out, and the crystalline magnesium is taken out.
Embodiment 2
[0024] Calcined magnesite (magnesia content over 99%) is prepared with calcium carbide and silicon dioxide in a molar equivalent ratio of 1:1.2:0.8, and calcium fluoride, a catalyst accounting for 9% of the total material amount, is added and mixed evenly. Under the pressure of 35MPa, it is pressed into a material ball with a diameter of 3cm. Before putting in the material ball, the air in the reaction system is exhausted, and then a certain amount of inert gas is introduced to keep the system at normal pressure. The temperature is raised to the reaction temperature of 1200 ° C. The induced draft fan condenses the generated magnesium vapor into crystalline magnesium on the condenser at 200-550°C. After 7 hours of reaction, continuous slagging and feeding are carried out, and the crystalline magnesium is taken out.
Embodiment 3
[0026] Calcined magnesite (magnesia content above 99%) is prepared with calcium carbide and silicon dioxide in a molar equivalent ratio of 1:1.5:1, and calcium fluoride, a catalyst accounting for 10% of the total material amount, is added and mixed evenly. Under the pressure of 45MPa, it is pressed into a material ball with a diameter of 3cm. Before putting in the material ball, the air in the reaction system is exhausted, and then a certain amount of inert gas is introduced to keep the system at normal pressure. The temperature is raised to a reaction temperature of 1250 ° C. The induced draft fan condenses the generated magnesium vapor into crystalline magnesium on the condenser at 200-550°C. After 8 hours of reaction, continuous slagging and feeding are carried out, and the crystalline magnesium is taken out.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com