Method for extracting sulforaphane from leaves of cauliflowers
An extraction method, the technology of sulforaphane, applied in the field of agriculture, can solve the problems of high cost and cumbersome steps, and achieve the effects of reducing production costs, simple extraction method, and simplified extraction steps
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
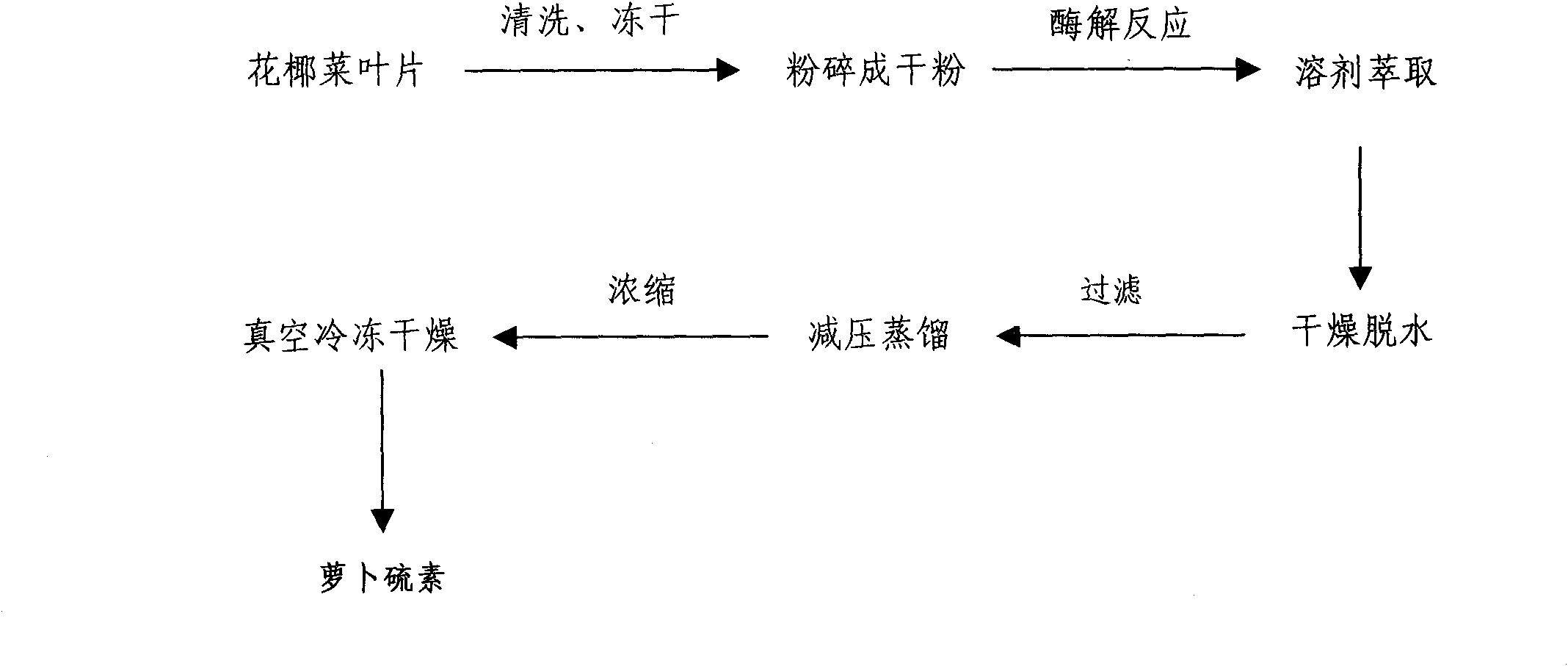
[0030] (1) Weigh 1.0 g of cauliflower leaf dry powder, add 8 mL of exogenous myrosinase (enzyme activity unit is 1.0 units, prepared with 0.05 mM, pH=7.0 PBS buffer) and 4 mL of deionized water or ultrapure water (pH7.0-8.0), fully mixed on a vortex instrument to form a homogenate, and treated in a water bath at 40°C for 30 minutes to complete the enzymolysis reaction.
[0031] (2) Solvent extraction, filtration
[0032] After the enzymolysis reaction, according to the actual amount of exogenous enzyme and deionized water or ultrapure water 12mL, quickly (3min) add 120mL of dichloromethane to the homogenate, mix and shake well, extract for 15min, and mix according to the amount of leaf dry powder and The weight ratio of anhydrous sodium sulfate is 5.0~8.0 (W 叶片干粉 :W 无水硫酸钠 =5.0~8.0) add 6.0g of anhydrous sodium sulfate to dry and dehydrate, filter with medical absorbent cotton, and collect the filtrate.
[0033] (3) Concentration, vacuum freeze-drying
[0034] The filtrate ...
Embodiment approach 2
[0036] (1) Weigh 50.0g of cauliflower leaf dry powder, add 500mL of exogenous myrosinase (enzyme activity unit is 1.0units, prepared with 0.05mM, pH=7.0 PBS buffer) and 200mL of deionized water or ultrapure water (pH7.0-8.0), fully mixed on a vortex instrument to form a homogenate, and treated in a water bath at 40°C for 40 minutes to complete the enzymolysis reaction.
[0037] (2) Solvent extraction, filtration
[0038] After the enzymatic hydrolysis reaction, add 5.6L of dichloromethane to the homogenate quickly (3min) according to the actual amount of 700mL of exogenous enzyme and deionized water or ultrapure water, mix and shake well, extract for 20min, and mix according to the amount of leaf dry powder The weight ratio with anhydrous sodium sulfate is 5.0~8.0(W 叶片干粉 :W 无水硫酸钠 =5.0~8.0) Add 300.0g of anhydrous sodium sulfate to dry and dehydrate, filter with medical absorbent cotton, and collect the filtrate.
[0039] (3) Concentration, vacuum freeze-drying
[0040] The...
Embodiment approach 3
[0042] (1) Weigh 15.0g to 25.0g of cauliflower leaf dry powder, add 100 to 250mL of exogenous myrosinase (enzyme activity unit is 1.0units, prepared with 0.05mM, pH=7.0 PBS buffer) and 60 to 150mL of Deionized water or ultrapure water (pH 7.0-8.0) is fully mixed on a vortex instrument to form a homogenate, and treated in a water bath at 40°C for 30-50 minutes to complete the enzymatic hydrolysis reaction.
[0043] (2) Solvent extraction, filtration
[0044] After the enzymatic hydrolysis reaction, according to the actual amount of exogenous enzyme and deionized water or ultrapure water, quickly (3min) add 1000mL ~ 4000mL of dichloromethane to the homogenate, mix and shake well, extract for 20 ~ 30min, and follow The weight ratio of leaf dry powder and anhydrous sodium sulfate is 5.0~8.0 (W 叶片干粉 :W 无水硫酸钠 =5.0~8.0) add anhydrous sodium sulfate to dry and dehydrate, filter with medical absorbent cotton, and collect the filtrate.
[0045] (3) Concentration, vacuum freeze-drying...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com