OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diode) device for increasing brightness
A device and metal technology, applied in the field of organic electroluminescence, can solve the problems of large power loss, few research documents, and limitations of the industrialization process of organic light-emitting devices, and achieve the effect of improving the brightness of the device and having little influence on the light transmittance.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
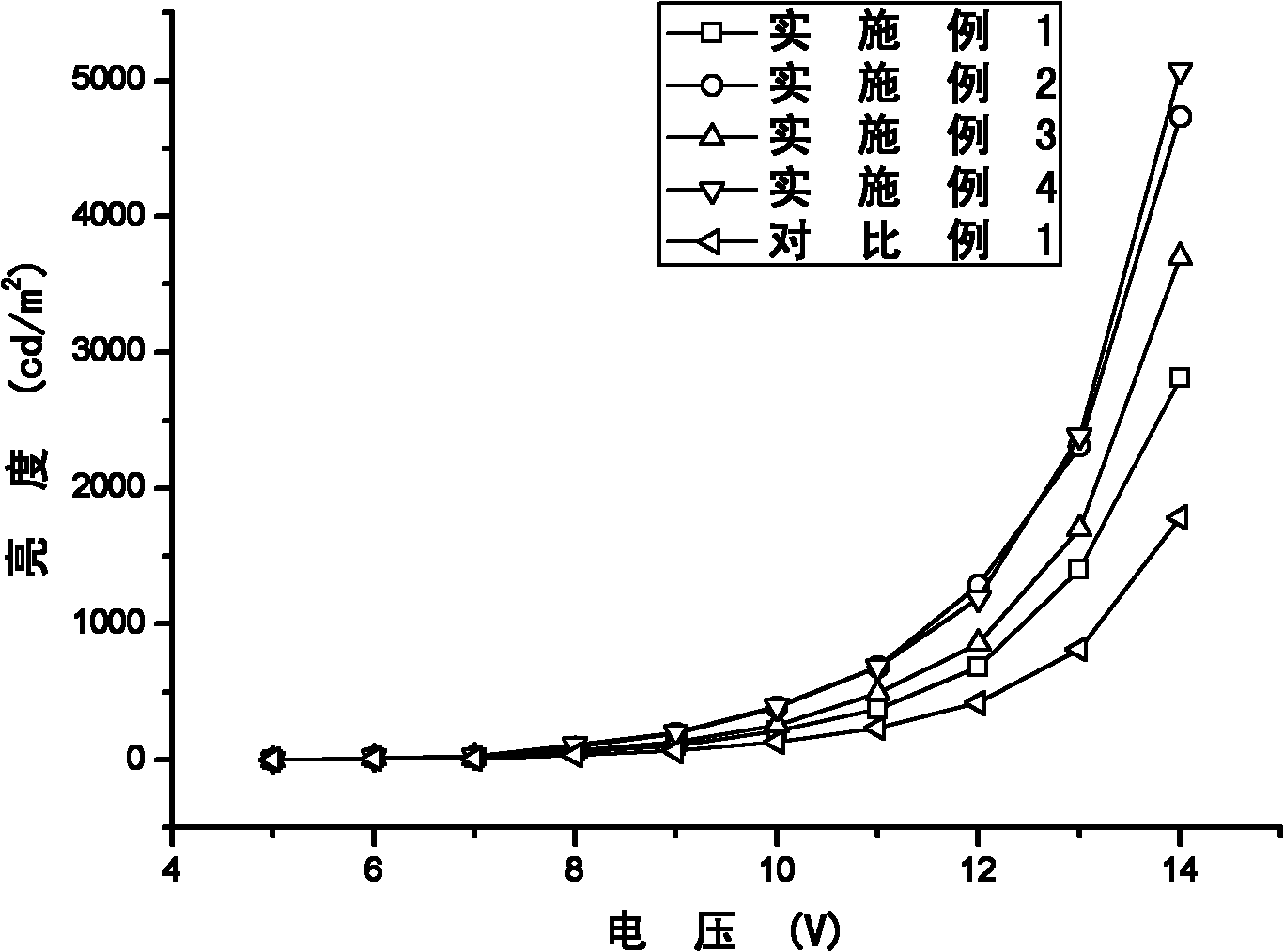
Examples
Embodiment 1
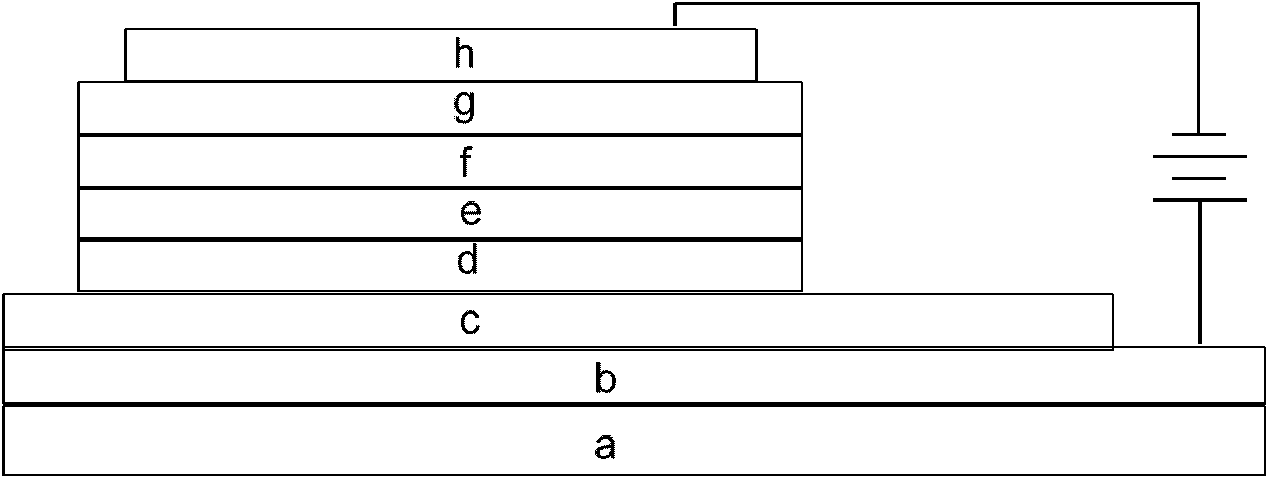
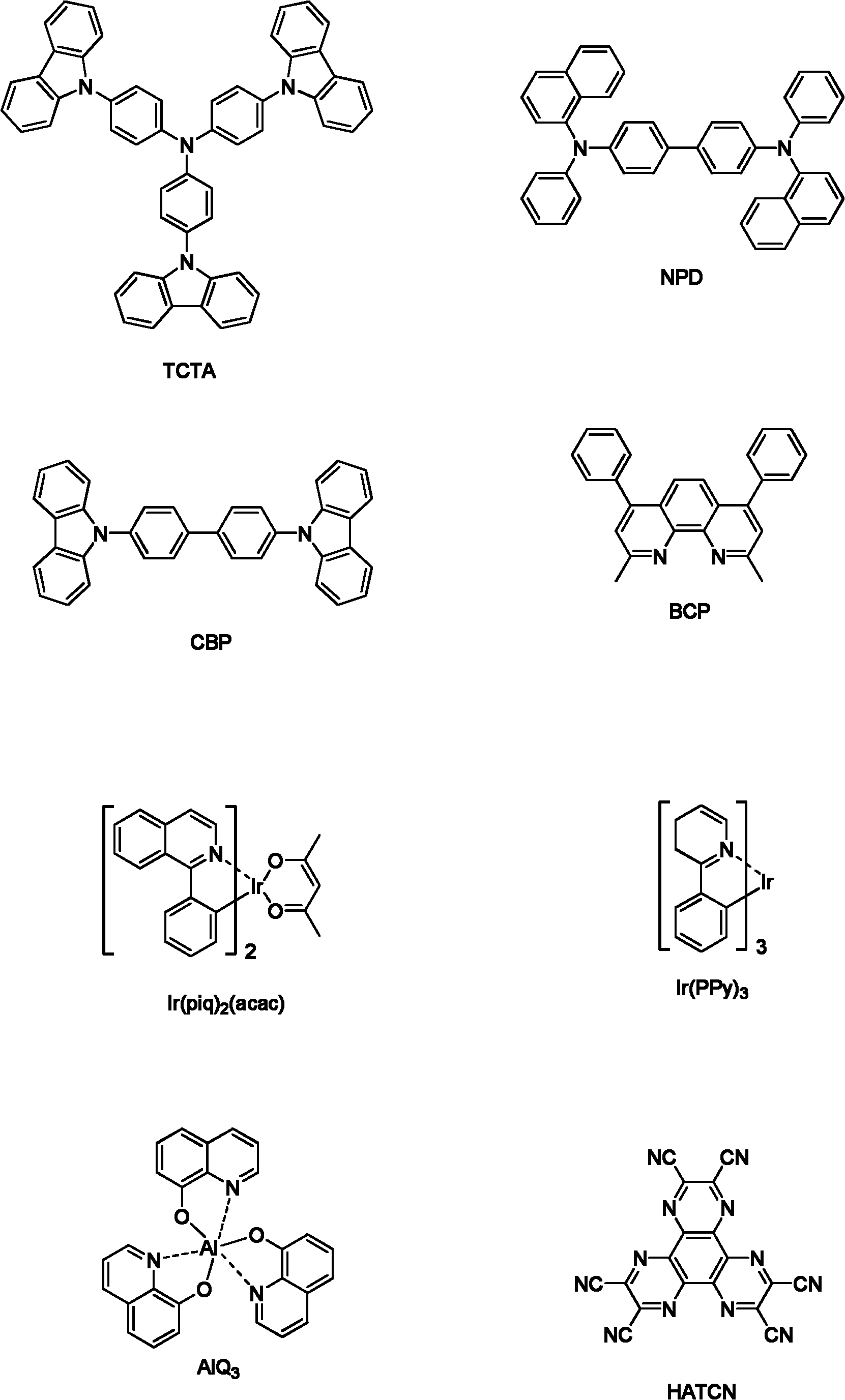
[0037] The flat glass substrate was cleaned with ultrasonic waves in an aqueous solution containing a decontamination agent, rinsed with distilled water and ethanol, and dried. Transfer the substrate to a vacuum thermal evaporation chamber. On the glass substrate, 15nm aluminum is thermally sublimated and evaporated as the anode; then MoO is thermally sublimated and evaporated on the anode in sequence. 3 20nm, NPD60nm, MoO 3 10nm, NPD50nm, CBP and Ir(piq) 2 (acac) 100:8 molar ratio mixed layer 50nm, BCP 15nm, AlQ 3 25nm, LiF 1nm; finally thermal sublimation evaporated aluminum 150nm to form the cathode. The deposition rate is kept at 2 angstroms / s for organic materials, 1 angstroms / s for LiF and molybdenum oxide, and 5 angstroms / s for aluminum. The final device structure is as follows:
[0038] Glass / Al(15nm) / MoO 3 (20nm) / NPD(60nm) / MoO 3 (10nm) / NPD(50nm) / CBP:Ir(piq) 2 (acac)100:8(50nm) / BCP(15nm) / AlQ 3(25nm) / LiF(1nm) / Al(150nm);
[0039] Two layers of MoO 3 The layer...
Embodiment 2
[0041] The flat glass substrate was cleaned with ultrasonic waves in an aqueous solution containing a decontamination agent, rinsed with distilled water and ethanol, and dried. Transfer the substrate to a vacuum thermal evaporation chamber. On the glass substrate, 15nm aluminum is thermally sublimated and evaporated as the anode; then MoO is thermally sublimated and evaporated on the anode in sequence. 3 10nm, SiO 2 1.5nm, MoO 3 10nm, SiO 2 1.5nm, MoO 3 10nm, NPD50nm, CBP and Ir(piq) 2 (acac) 100:8 molar ratio mixed layer 50nm, BCP 15nm, AlQ 3 25nm, LiF 1nm; finally thermal sublimation evaporated aluminum 150nm to form the cathode. The deposition rate is kept at 2 angstroms / s for organic materials, 1 angstroms / s for LiF, silicon oxide and molybdenum oxide, and 5 angstroms / s for aluminum. The final device structure is as follows:
[0042] Glass / Al(15nm) / MoO 3 (10nm) / SiO 2 (1.5nm) / MoO 3 (10nm) / SiO 2 (1.5nm) / MoO 3 (10nm) / NPD(50nm) / CBP:Ir(piq) 2 (acac)100:8(50nm)...
Embodiment 3
[0045] The flat glass substrate was cleaned with ultrasonic waves in an aqueous solution containing a decontamination agent, rinsed with distilled water and ethanol, and dried. Transfer the substrate to a vacuum thermal evaporation chamber. On the glass substrate, 15nm thermally sublimated evaporated aluminum is used as the anode; then thermally sublimated evaporated 10nm titanium cyanine copper, MoO 3 30nm, NPD50nm, CBP and Ir(piq) 2 (acac) 100:8 molar ratio mixed layer 50nm, BCP 15nm, AlQ 3 25nm, LiF 1nm; finally thermal sublimation evaporated aluminum 150nm to form the cathode. The deposition rate is kept at 2 angstroms / s for organic materials, 1 angstroms / s for LiF and molybdenum oxide, and 5 angstroms / s for aluminum. The final device structure is as follows:
[0046] Glass / Al(15nm) / Titanium Copper(10nm) / MoO 3 (30nm) / NPD(50nm) / CBP:Ir(piq) 2 (acac)100:8(50nm) / BCP(15nm) / AlQ 3 (25nm) / LiF(1nm) / Al(150nm);
[0047] where MoO 3 For hole injection and hole transport laye...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Total thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Brightness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com