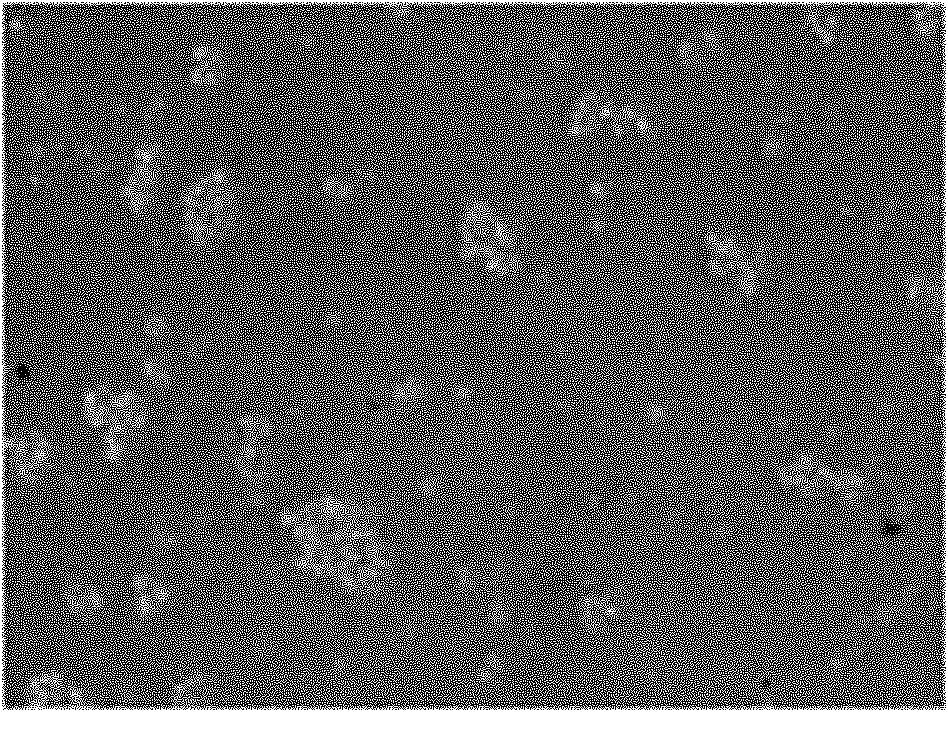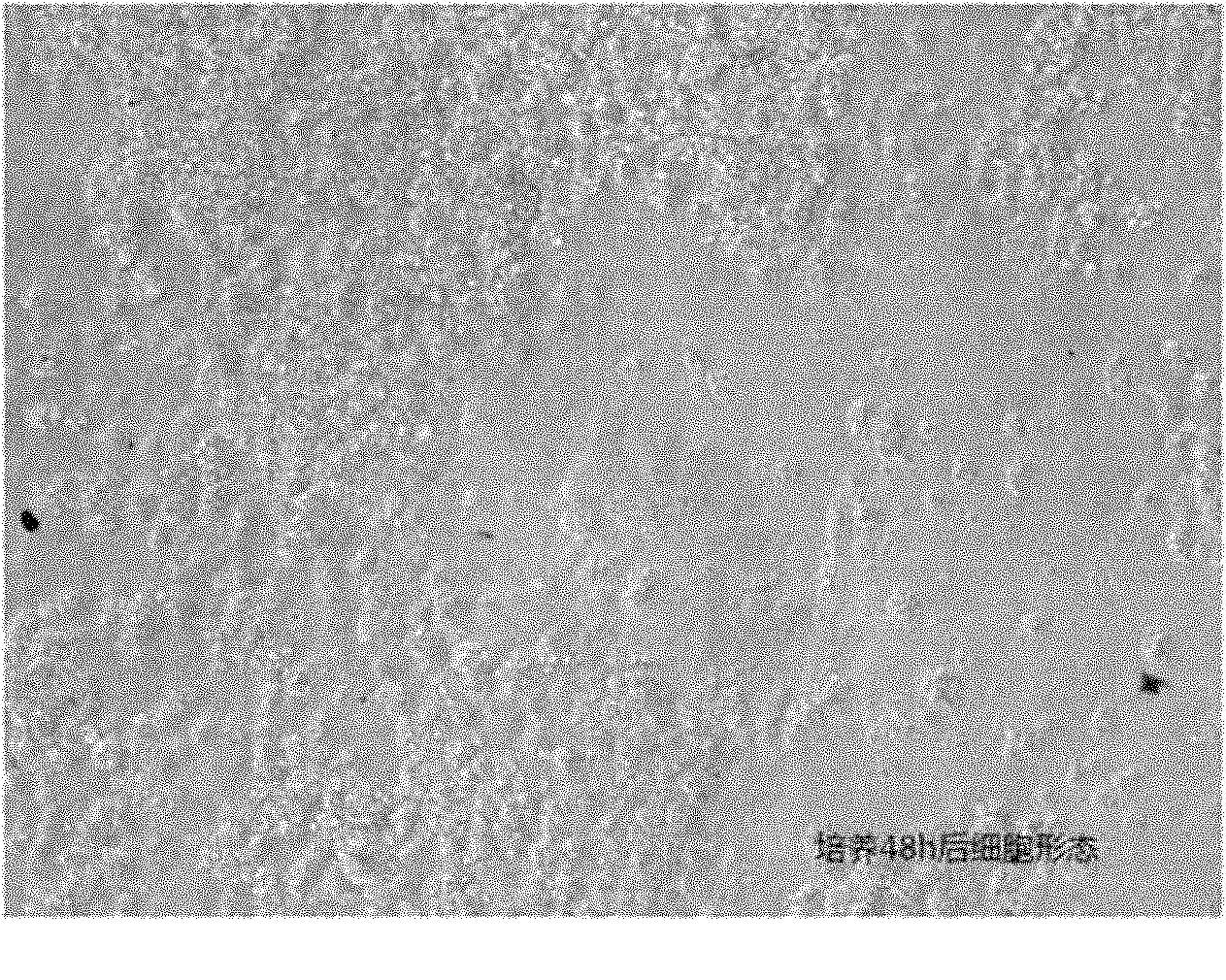Method for separation and primary culture of intestinal mucosal cells of fishes
A technology of intestinal mucosa and primary culture, applied in animal cells, vertebrate cells, artificial cell constructs, etc., can solve the problem of cells, tissue blocks, mixed dead cells, incomplete application of aquatic temperature-changing animals, and difficulty in cell separation Large and other problems, to achieve the effect of good cultivation and growth, good digestion and separation, and good growth
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] A method for the isolation and primary culture of fish intestinal mucosal cells, comprising the following steps:
[0033] ⑴Choose the intestinal tract of the test material fish that has been cultivated for 2 to 3 weeks with feed that has strengthened the growth of intestinal mucosal cells. After disinfection, use scissors to mash the brain of the fish body in a sterile room, quickly cut open the belly of the fish, take out the intestine, and remove extra-intestinal fat;
[0034] ⑵The intestinal tract is made into intestinal sacs or turned over and then digested to effectively separate intestinal mucosal cells; then centrifuge at a speed of 300r / min to 500r / min for 3 to 5 minutes to obtain intestinal mucosal cell clusters: the ratio of mucosal cells reaches 1: The mixed cell suspension of 2.5-5 can meet the inoculation concentration requirements of subsequent experiments.
[0035] The process of making the intestinal tract into an intestinal capsule and then digesting i...
Embodiment 2
[0054] Step 1: The surface of the material fish is disinfected with alcohol with a mass fraction of 75%.
[0055] Step 2: Take out the intestinal tract of the fish body by routine dissection, and remove the extra-intestinal fat.
[0056] Step 3: Inject the fish into the intestinal tract with a syringe and rinse with normal saline for 3 to 4 times to clean the contents of the intestinal tract.
[0057] Step 4: Turn the intestine completely over, with the mucosa facing outward and the intestinal wall facing inward. Use antibiotic-containing D-Hanks solution to wash the intestinal mucosal surface to remove mucus and debris on the intestinal mucosal surface, and then ligate both ends of the intestinal tract. The D-Hanks solution containing antibiotics was 200,000 U / L of penicillin, 200,000 U / L of gentamicin, and 200 mg / L of streptomycin.
[0058]Step 5: Submerge the inverted intestinal sac in the mixed digestive solution, digest in a water bath at 25-30°C for 20-40 minutes, then...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com