Method for preparing diamond blade by using special metal bond
A metal bond, diamond cutting technology, used in manufacturing tools, stone processing tools, stone processing equipment, etc., can solve the problems of incomplete densification of sintering, insufficient element alloying, and inability to be widely used, and achieve excellent composition. The effect of uniformity, lower sintering temperature, and shorter sintering time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] (1) According to the mass percentage of pre-alloyed powder 15%, TFe (carbonyl iron powder) 10%, Cu 22%, Fe 40%, Sn 3%, Zn 3%, Mn 1.9%, W 5%, PFe 0.1% Take the raw materials, and then fully mix and ball-mill the above raw materials in a mechanical mixer to obtain a special metal bond; the mass percentage composition of the pre-alloyed powder is: Fe 45%, Ni 10%, Cu 35%, Co 10 %;
[0023] (2) Mix the special metal bond obtained in step (1) with diamond in a weight ratio of 1:0.125;
[0024] (3) Add the rubber molding agent whose mass is 8% of the mass of the special metal bond and diamond mixed powder obtained in step (2), mix evenly, and air dry;
[0025] (4) Put the air-dried powder in step (3) into the steel mold prepared in advance, and cold press at a pressure of 11Mpa;
[0026] (5) Sintering at high temperature for 5 hours at 765°C;
[0027] (6) Grinding the sheet to make a cutting sheet.
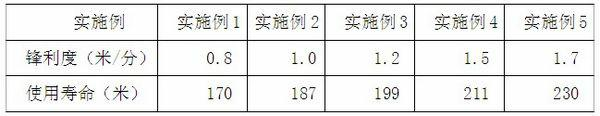
[0028] The sharpness and service life of the cutting disc of this embodim...
Embodiment 2
[0030] Except that the following parameters were changed, other steps were the same as in Example 1. In step (1), the mass percentage of raw materials is: pre-alloyed powder 17%, TFe 10%, Cu 30%, Fe 25%, Sn 3%, Zn 6%, Mn 3.8%, W 5%, PFe 0.2%; The mass percent composition of the pre-alloyed powder is: Fe 55%, Ni 10%, Cu 30%, Co 5%;
[0031] The ratio of the weight ratio of the special metal bond to the diamond in step (2) is 1: 0.175;
[0032] In step (5), the sintering temperature is 795°C, and the sintering time is 6 hours;
[0033] The molding agent in step (3) is a polyethylene glycol molding agent.
[0034] The sharpness and service life of the cutting disc of this embodiment were tested, and the test results are shown in Table 1.
Embodiment 3
[0036] Except that the following parameters were changed, other steps were the same as in Example 1. In step (1), the mass percentage of raw materials is: pre-alloyed powder 20%, TFe 15%, Cu 22%, Fe 25%, Sn 3%, Zn 3.8%, Mn 1%, W 10%, PFe 0.2%; The mass percent composition of the pre-alloyed powder is: Fe 55%, Ni 10%, Cu 25%, Co 10%;
[0037] In step (2), the weight ratio of the special metal bond to the diamond is 1:0.20;
[0038] In step (5), the sintering temperature is 780°C, and the sintering time is 5.5 hours;
[0039] The molding agent in step (3) is a polyethylene glycol molding agent.
[0040] The sharpness and service life of the cutting disc of this embodiment were tested, and the test results are shown in Table 1.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com