Polishing composition and polishing method using the same
A technology of polishing composition and compound, which is applied in the field of polishing composition, can solve the problems of high smooth surface for a long time, unable to provide sufficient polishing rate, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1 and 2 and comparative example 1
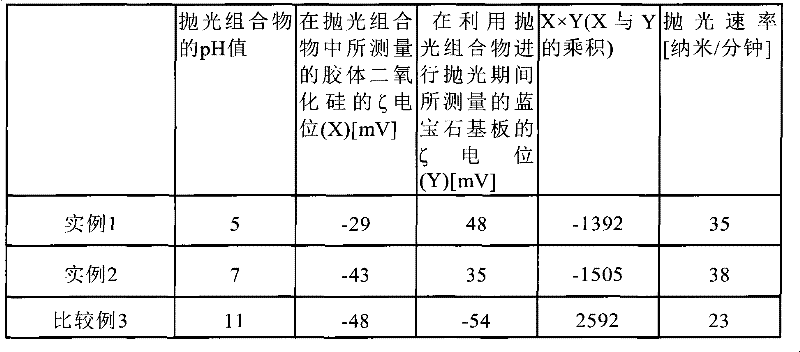
[0032]The polishing compositions of Examples 1 and 2 and Comparative Example 1 were prepared by diluting a colloidal silica sol containing colloidal silica having an average primary particle diameter of 80 nm with water, and adding a pH adjuster as necessary. Each of the polishing compositions of Examples 1 and 2 and Comparative Example 1 contained 20% by mass of colloidal silica. Hydrochloric acid or potassium hydroxide is suitably used as a pH adjuster. Using each of the polishing compositions of Examples 1 and 2 and Comparative Example 1, the surface (c-plane ()) of the sapphire substrate was polished under the conditions shown in Table 1. All sapphire substrates used were of the same type, with a diameter of 52 millimeters (about 2 inches).
[0033] Table 2 shows the pH value of the polishing composition, the zeta potential value of colloidal silica measured in the polishing composition, and the zeta potential value of the sapphire substrate measured during polishing with...
example 3 and comparative example 2
[0040] The polishing compositions of Example 3 and Comparative Example 2 were prepared by diluting the colloidal silica sol containing colloidal silica having an average primary particle size of 80 nm with water, and adding a pH adjuster as needed. Each of the polishing compositions of Example 3 and Comparative Example 2 contained 20% by mass of colloidal silica. Hydrochloric acid or potassium hydroxide is suitably used as a pH adjuster. Using the polishing compositions of Example 3 and Comparative Example 2, the surface (Ga surface) of the gallium nitride substrate was polished under the conditions shown in Table 3. All GaN substrates used are of the same type and have an area of 10 mm.
[0041] The pH values of the polishing compositions, the sign of the colloidal silica zeta potential measured in each polishing composition, and the sign of the gallium nitride substrate zeta potential measured during polishing with each polishing composition are shown in Table 4. Befor...
example 4 and 5 and comparative example 3 and 4
[0048] The polishing compositions of Examples 4 and 5 and Comparative Examples 3 and 4 were prepared by diluting a colloidal silica sol containing colloidal silica having an average primary particle diameter of 35 nm with water, and adding a pH adjuster as necessary. Each of the polishing compositions of Examples 4 and 5 and Comparative Examples 3 and 4 contained 5% by mass of colloidal silica. Acetic acid or potassium hydroxide is suitably used as a pH adjuster. Using each of the polishing compositions of Examples 4 and 5 and Comparative Examples 3 and 4, the surface ((100) plane) of the indium arsenide substrate was polished under the conditions shown in Table 5. All of the indium arsenide substrates used were of the same type, with a diameter of 52 mm (approximately 2 inches).
[0049] The pH values of the polishing compositions, the sign of the colloidal silica zeta potential measured in each polishing composition, and the sign of the indium arsenide substrate zeta pote...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com