Method for identifying induction characteristics of promoter by utilizing phenotype of transgenic plant
A technology for transgenic plants and promoters, which is applied in the field of identifying the characteristics of plant promoters, can solve the problems of fusion, restricting the process of plant genetic engineering and industrialization development, and quantitative difficulties, and achieves the effect of having identification results and intuitive identification results.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0020] 1. Construction of plant expression vectors:
[0021] 1. Experimental materials:
[0022] 1.1 Plant material:
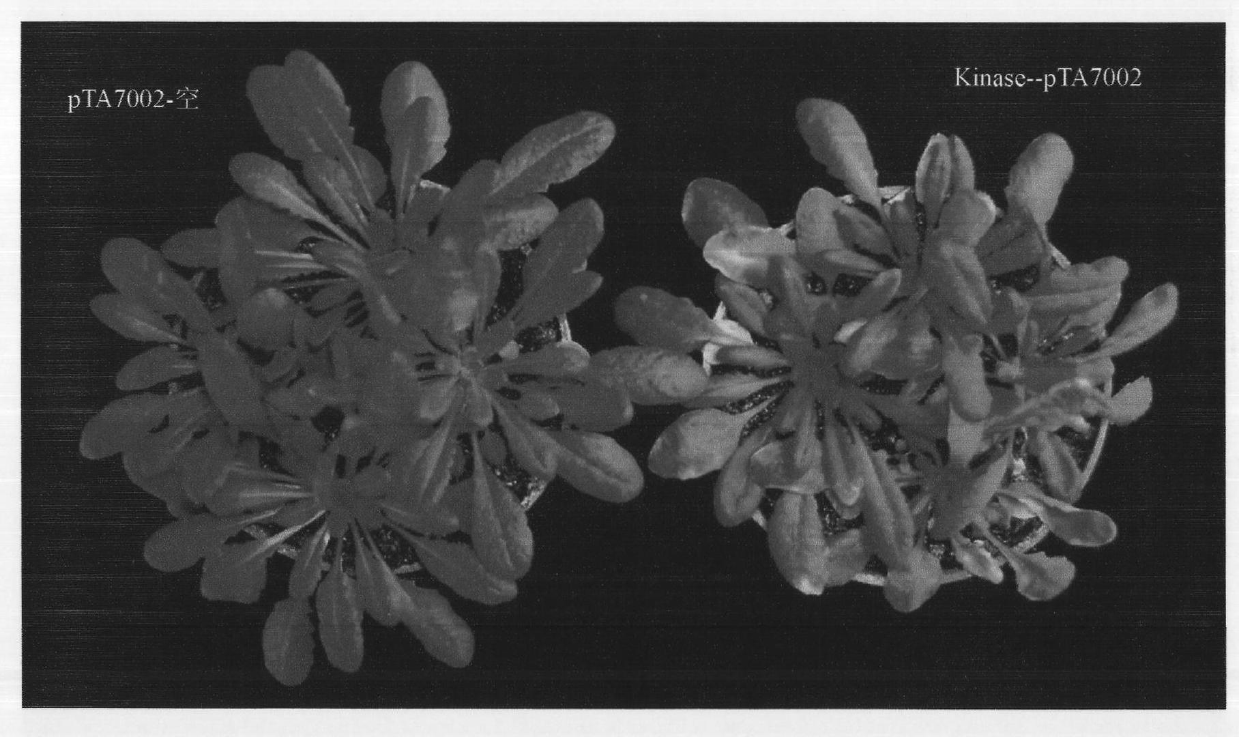
[0023] Wild-type Columbia ecotype (Col-O) Arabidopsis thaliana, "Innovation No. 1" tobacco
[0024] 1.2 Strains and plasmids:
[0025] Vector plasmid: pTA7002 was kindly provided by Professor Chua Nam-Hai, Rockefeller University, USA.
[0026] Strains: Escherichia coli DH5α, provided by the Laboratory of Plant Molecular Biology, Inner Mongolia Agricultural University; Agrobacterium GV3101, provided by the Laboratory of Plant Molecular Biology, Inner Mongolia Agricultural University.
[0027] 1.3 Reagents:
[0028] rTaq enzyme and DNA marker were purchased from TaKaRa Company, various restriction enzymes and T4 DNA ligase were purchased from NEB Company, RNaseA, pCF-T, DNA recovery kit and plasmid mini-prep kit were purchased from From Beijing Tiangen Company.
[0029] Ampicillin (Amp), Kanamycin (Kan), Gentamicin (Gent), X-gal, Isopropylthio-β-D-galactos...
Embodiment 2
[0143] Example 2: Preparation and transient expression of Agrobacterium-mediated tobacco:
[0144] 1. Reagents
[0145] 1.1 Configuration of reagents
[0146] 1M MgSO4 (Shanghai Sangong): Dissolve 3.009 grams of MgSO4 in 25ml of distilled water and autoclave;
[0147] 0.2M MES (BBI): Dissolve 1.0655g of MES in 25ml of distilled water, adjust the pH to 5.5, and sterilize by autoclaving;
[0148] 150mM AS (Proteco): Dissolve 0.0294g of AS in 1ml DMSO (Shanghai Sangong), dispense in 200μl, and store at -4°C;
[0149] 30mM DEX (Sigma): Dissolve 0.0058g of DEX in 500μl of absolute ethanol and dilute 1000 times when used;
[0150] 1.2 Configuration of the suspension
[0151] 10mM MgSO4: need 1M MgSO4 100μl
[0152] 10mM MES: 500μl of 0.2M MES is required
[0153] 150 μM AS: 100 μl of 150 mM AS is required
[0154] Dilute to 10ml with sterile water.
[0155] 2. Transient expression of tobacco:
[0156] ①. Put the Agrobacterium containing the target plasmid (pTA-Kinase1) stor...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com