Hydrocarbon catalytic conversion method for producing propylene and light aromatic hydrocarbon
A catalytic conversion method and technology for light aromatic hydrocarbons, which are applied in the fields of hydrocarbon cracking to produce hydrocarbons, production of bulk chemicals, preparation of liquid hydrocarbon mixtures, etc., can solve the problem that the increase of catalytically cracked propylene is limited and does not involve improving the yield of catalytically cracked light aromatics. and other problems, to achieve the effect of improving the conversion rate of heavy oil, the yield of light products, the high content of light aromatics, the yield of propylene and the yield of BTX
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
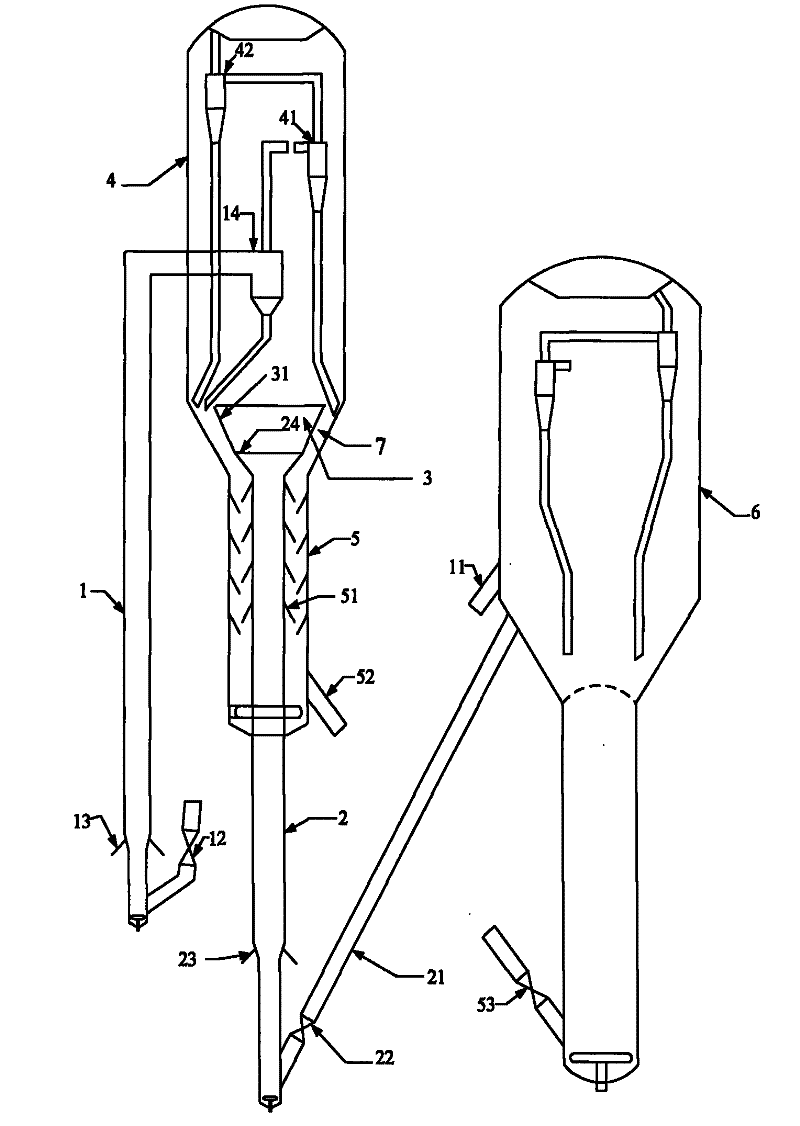
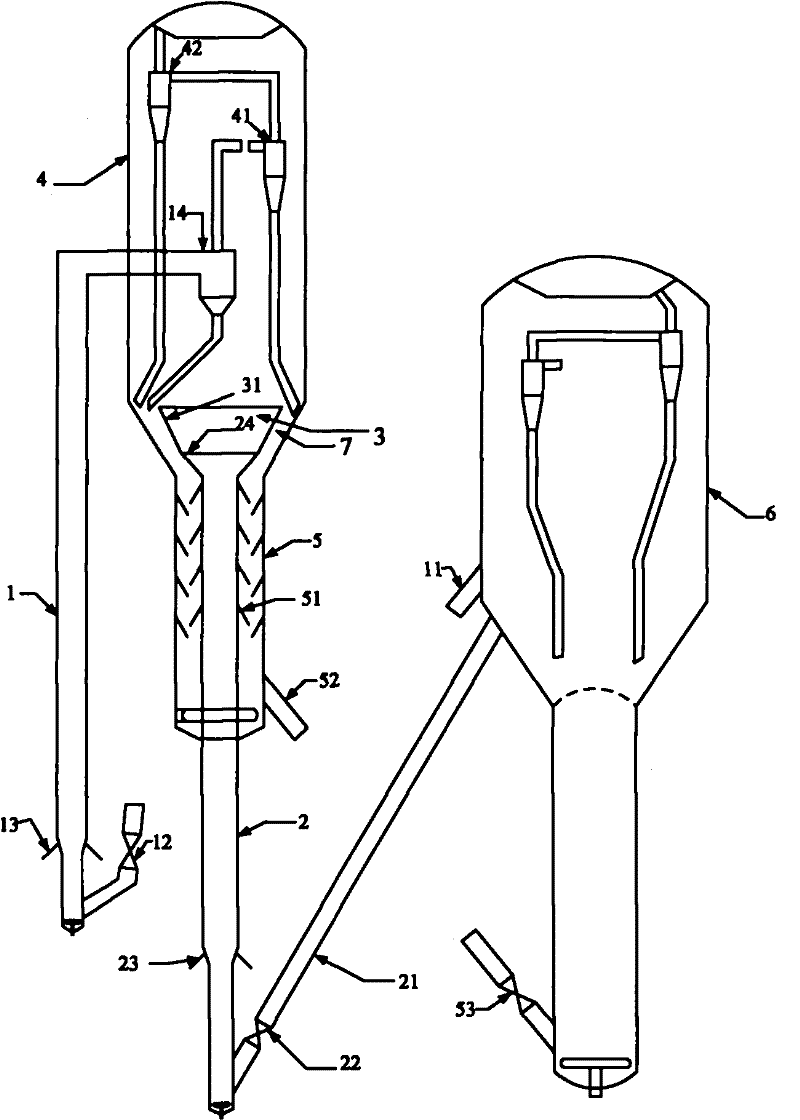
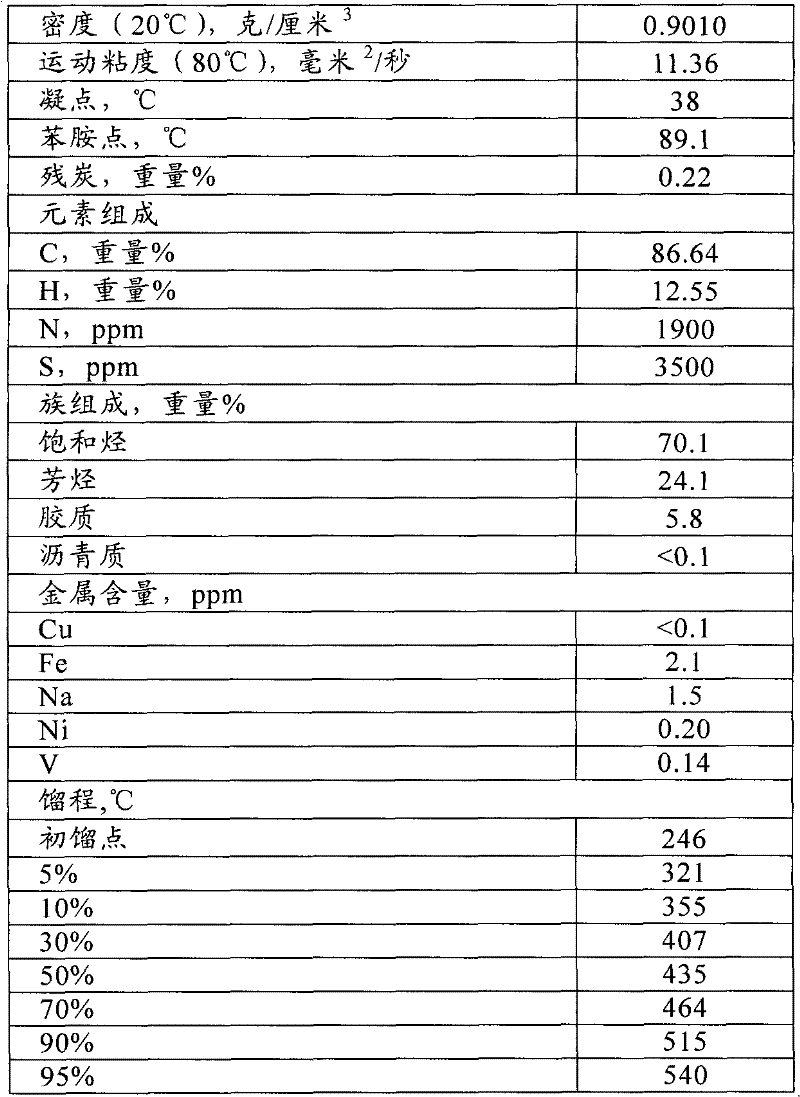
[0064] The heavy oil raw material (the first raw material, whose properties are shown in Table 1) is introduced into the riser reactor 1, and after contacting and reacting with the hot catalyst from the regenerator, the oil and gas products are separated from the catalyst, and the oil and gas products leave the reactor and are introduced into the fractionation device, separated The coke catalyst that obtains introduces stripper 5, is transported to regenerator after stripping and regenerates; Catalytic cracking C4 hydrocarbon and light gasoline fraction (the second raw material, its composition is shown in Table 2, and this light gasoline distillation range is 35 ℃~ 85°C) into the riser reactor 2, contact with the hot catalyst from the regenerator for reaction, the reacted oil-gas mixture and catalyst are introduced into the fluidized bed reactor 3 to continue the reaction, and the oil and gas products obtained by the reaction of the fluidized bed reactor 3 are introduced into t...
Embodiment 2
[0066] The process flow of this embodiment is the same as that of Example 1, and the difference from Example 1 is that light gasoline (properties are shown in Table 2) is 4: 1 under the reaction temperature of 40 ° C, reaction pressure 0.5 MPa, hydrogen and olefin molar ratio, in the catalyst (The trade name is RDD-1, produced by Sinopec Changling Catalyst Branch Company) on the upper surface through selective hydrogenation reaction, convert diolefins and alkynes into olefins and then introduce them into riser reactor 2. The amount of heavy oil introduced into riser 1 is the same as that of The light gasoline weight ratio of the riser 2 is 100:20. The reaction conditions and reaction results are shown in Table 3.
Embodiment 3
[0068] The heavy oil raw material (its properties are shown in Table 1) is introduced into the riser reactor 1, and after contacting with the hot catalyst from the regenerator, the oil and gas products are separated from the catalyst, and the oil and gas products leave the reactor and are introduced into the fractionation device to separate the obtained carbon deposits Catalyst is introduced into stripper 5, is transported to regenerator after steam stripping and regenerates; The catalytic cracking C4 cut that fractionation device fractionation of the present invention obtains and light gasoline cut (light gasoline distillation range is 35 ℃~85 ℃, and C4 cut accounts for 50% by weight %, the light gasoline fraction accounts for 50% by weight) on the RDD-1 catalyst at a reaction temperature of 40°C, a reaction pressure of 0.5MPa, and a hydrogen-to-gasoline molar ratio of 4:1 for selective hydrogenation and then introduced into the riser reactor 2. Contact and react with the hot ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com