Method for producing 1,3-dioleoyl-2-palmitoyl triglyceride
A technology of palmitic acid triglyceride and production method, which is applied in the direction of fatty acid esterification, fat production, edible oil/fat, etc., and can solve problems such as increased cholesterol content, increased risk of cardiovascular disease, and unfavorable health
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
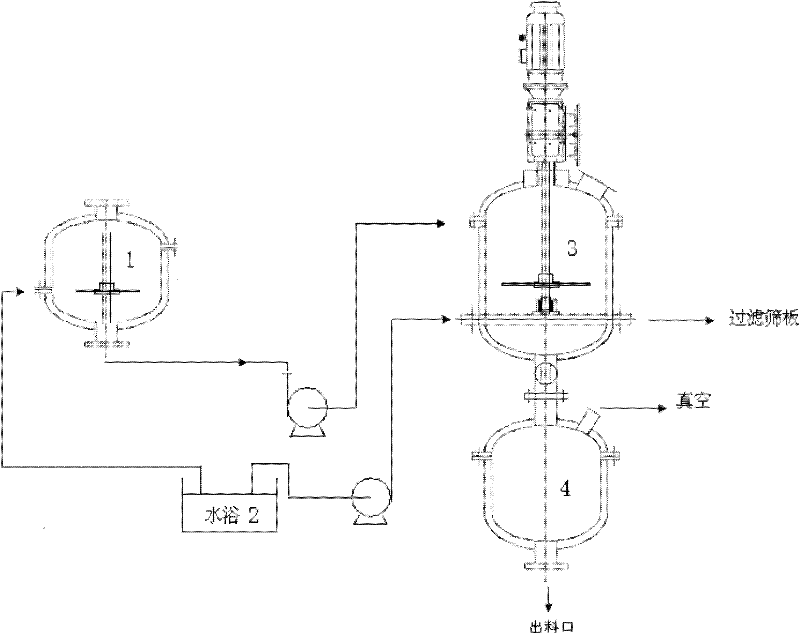
[0037] Example 1 combined figure 1 illustrate
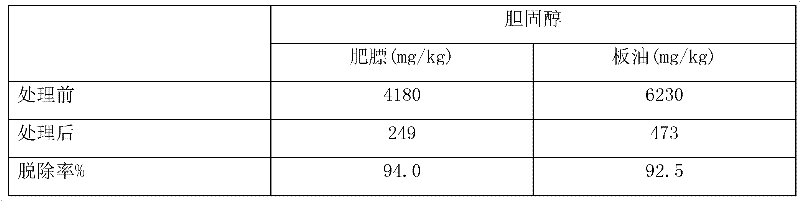
[0038] Step 1 Lard raw material is obtained by boiling fat and suet from commercially available healthy pigs over medium heat; heat the boiled lard to about 32°C, add 2% (w / w) β-cyclodextrin, Then add 40% (w / v) ethanol aqueous solution (80%), vigorously shake and mix, then let stand for 30 minutes, discard the water phase in layers, and extract the oil phase twice according to the above process, the results are as follows:
[0039]
[0040] Step 2 Add 2 mol / L NaOH-ethanol solution to commercially available olive oil, reflux at 80°C for 4 hours, extract twice with n-hexane to remove unsaponifiable matter; separate the n-hexane phase, add 1 mol / L hydrochloric acid to the water phase to acidify to pH 1 -2, add n-hexane to extract the organic phase for 3 times, discard the water phase, add activated clay to the n-hexane phase for decolorization, remove the activated clay by filtration, remove the solvent, dehydrate and dry to ob...
Embodiment 2
[0049] Example 2 combined figure 1 Description, step 1-2 is the same as embodiment 1
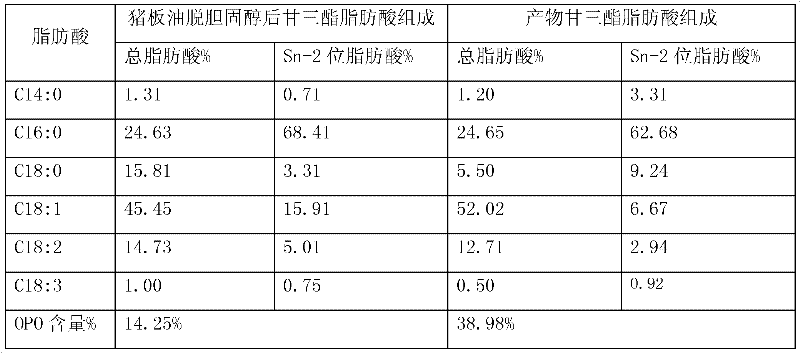
[0050] Step 3-4 Put the lard decholesterolated in the above step 1 and the fatty acid refined in the step 2 into the tank 1 at a ratio of 0.5:1, heat to 42°C, dissolve and mix well, and then pump into the above reactor 3, Heat to 80°C, add RMIM lipase with 8% total weight of lard and fatty acid, react at constant temperature for 40min, then cool down to 37°C at a rate of 5°C / min, keep constant temperature for 60min, then turn on the vacuum, remove lipase by centrifugal filtration, The product was molecularly distilled (6mmHg, 150°C) to remove free fatty acids. The product goes into 4. HPLC-ELSD analysis of OPO content, GC analysis of fatty acid composition, as follows:
[0051]
[0052] The content of OPO increased from 13.75% to 35.48% of the raw material of pig fat oil, and the change rate of palmitic acid content in the composition of sn-2 fatty acid was 3.9%.
[0053] Step 5 Add t...
Embodiment 3
[0055] Step 1-2 is basically the same as embodiment 1
[0056] Step 3-4 Put the lard decholesterolated in the above step 1 and the fatty acid refined in the step 2 into the tank 1 at a ratio of 0.8:1, heat to 42°C, dissolve and mix well, and then pump into the above reactor 3, Heat to 80°C, add RMIM lipase with 3% total weight of lard and fatty acid, react at constant temperature for 40min, then cool down to 37°C at a rate of 3°C / min, keep constant temperature for 60min, then turn on the vacuum, and remove lipase by centrifugal filtration. The product was molecularly distilled (6mmHg, 150°C) to remove free fatty acids. The product goes into 4. OPO content was analyzed by HPLC-ELSD, and fatty acid composition was analyzed by GC. OPO content increased from 13.75% to 45.48% of the lard oil raw material, and the change rate of palmitic acid content in the sn-2 fatty acid composition was 4.3%.
[0057] Step 5 Add the triglyceride obtained above into a container with a stirring de...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com