Methods of dynamically controlling film microstructure formed in a microcrystalline layer
A microcrystalline silicon layer, dynamic technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, coatings, crystal growth, etc., can solve the problems of undeveloped PV devices, insufficient film formation and crystallization rate, and reduced manufacturing yield
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
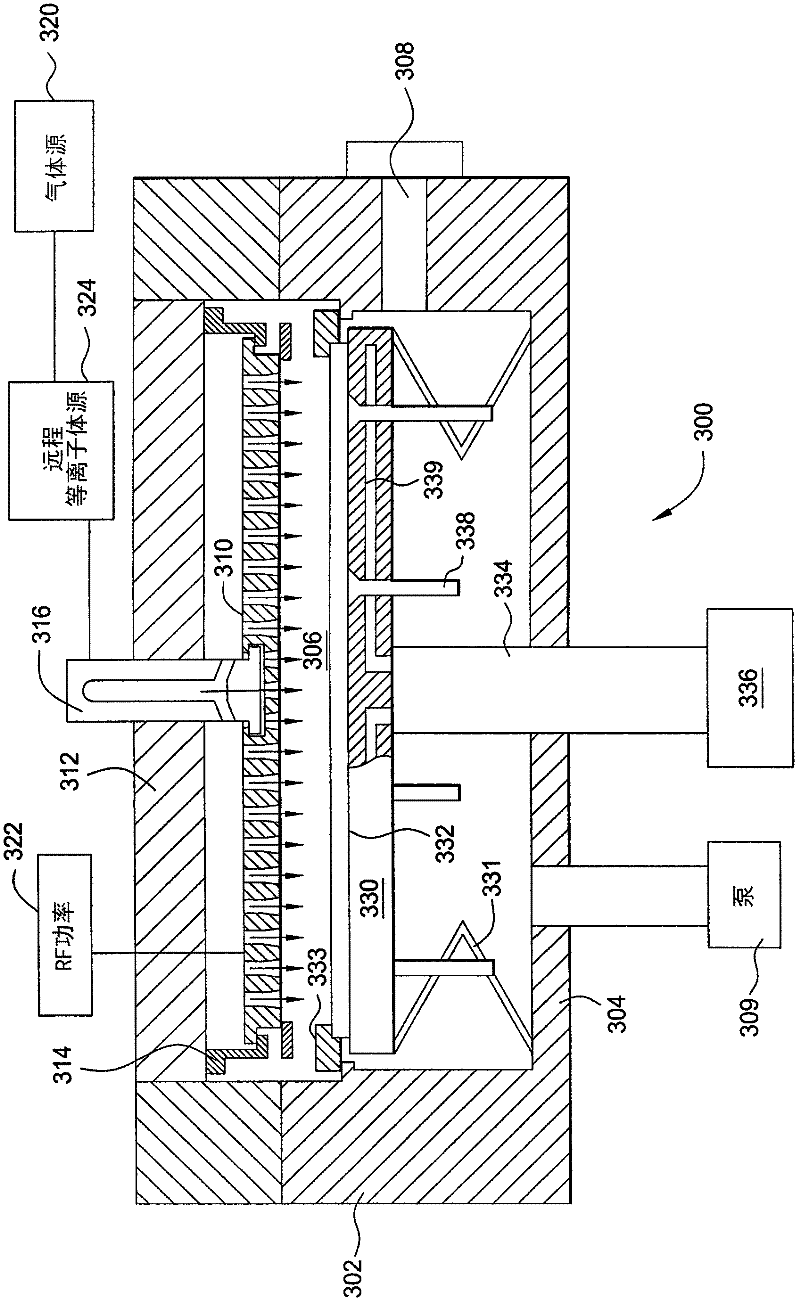
[0016] The present invention describes a method for depositing intrinsic microcrystalline silicon layers with high deposition rates and uniform crystallinity. In one embodiment, the intrinsic type microcrystalline silicon layer can be deposited by dynamically controlling the process parameters used during the deposition process, thereby dynamically controlling the film properties and microstructure formed in the final intrinsic type microcrystalline silicon layer. In one embodiment, the intrinsic microcrystalline silicon layer can be used in a multi-junction solar cell or a single-junction solar cell.
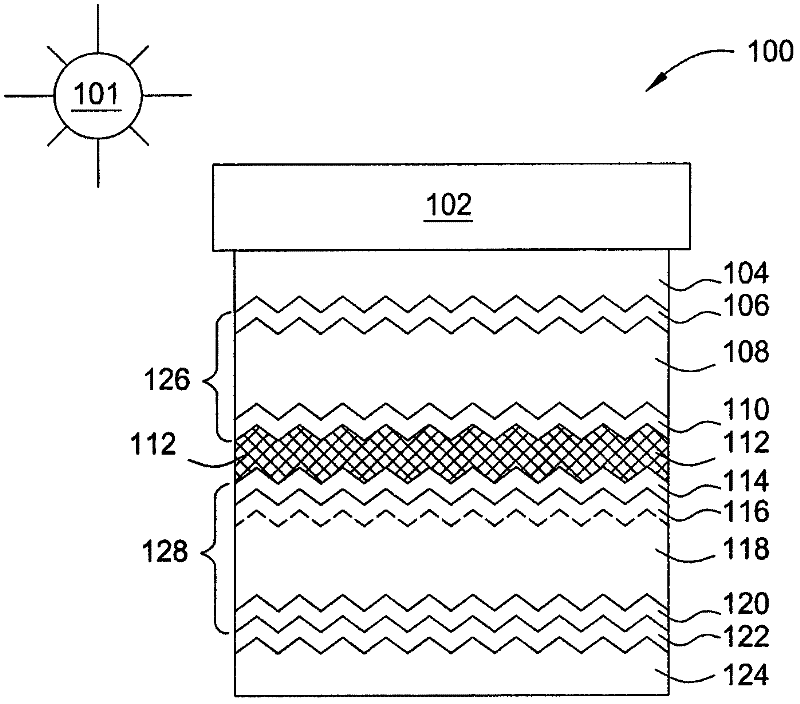
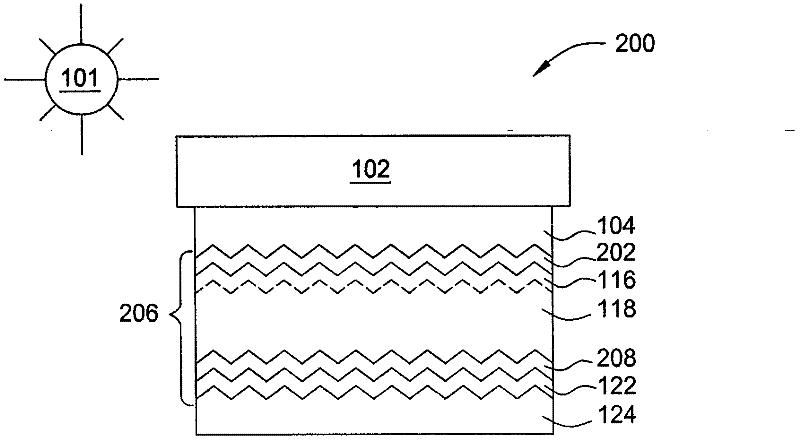
[0017] figure 1 is a schematic diagram of an embodiment of a multi-junction solar cell 100 oriented towards light or solar radiation 101 . The solar cell 100 includes a substrate 102, such as a glass substrate, a polymer substrate, a metal substrate, or other suitable substrate, over which a thin film is formed. The solar cell 100 also includes a first transparent conductive ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| band gap | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com