Plant endosperm specific expression promoter and use thereof
A specific, promoter technology, applied in applications, plant products, botanical equipment and methods, etc., can solve the problems of consuming bioenergy, the expression intensity cannot meet the needs of transgenic industrialization, and the growth and development of organisms adversely affect metabolites, etc. , to achieve great application prospects, increase the added value of science and technology, and improve the quality of seeds
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
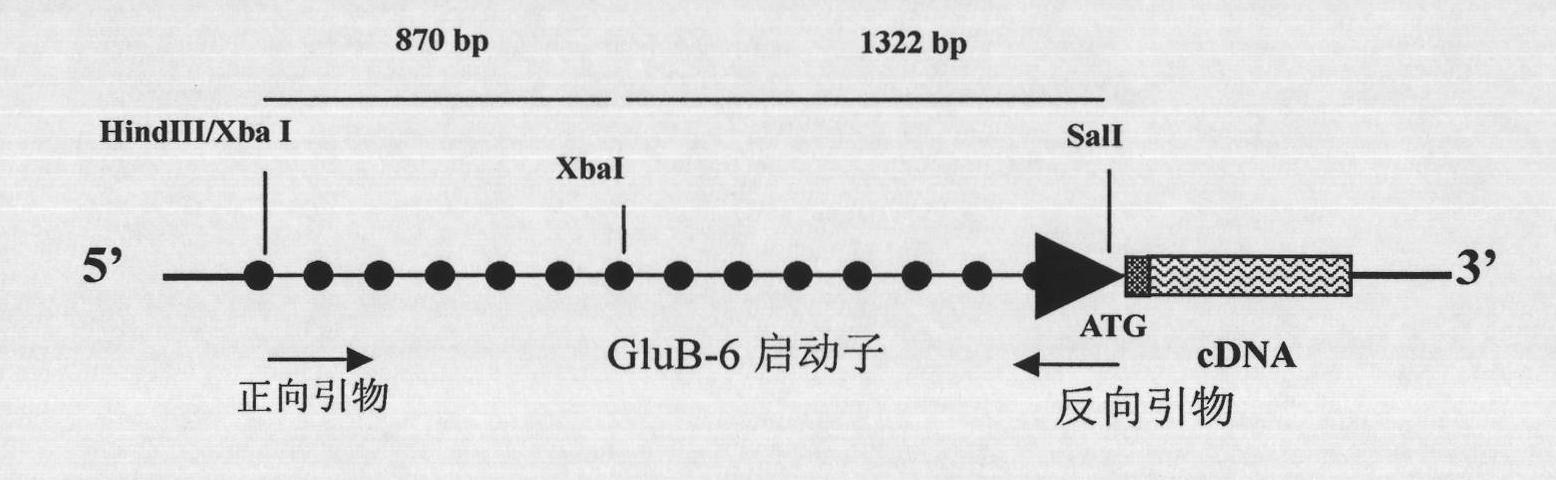
[0037] Embodiment 1, the acquisition of plant endosperm-specific expression promoter (GluB-6 promoter)
[0038] According to the report of Qu et al. (J. Exp. Bot. 2008, 59: 2417-2424), a glutenin gene (gene name Os02g0248800) was selected and named GluB-6. Search the upstream sequence of GluB-6 gene from GenBank, and design primers to amplify the GluB-6 promoter. To facilitate vector construction, two restriction sites (underlined) were sequentially added to the primers. The forward primer of the promoter is GluB-6HindF: 5'-TT AAGCTT TTCGCTGGATTAGAATTC-3'( Hind III ), the reverse primer is GluB-6SalR: 5'GC GTC GAC AGCTTTTGTATATACTAATAAAAC-3'( Sal I ).
[0039] The CTAB method was used to extract a small amount of genome from the leaves of rice (wild type rice Taichung No. 65, which was bred in Taiwan Province of my country in 1936; Qu Leqing et al., Acta Botany, 2001, 43: 1167-1171; preserved by the Institute of Botany, Chinese Academy of Sciences) Using the DNA as a ...
Embodiment 2
[0040] Embodiment 2, plant endosperm-specific expression promoter (GluB-6 promoter) expression vector construction and genetic transformation
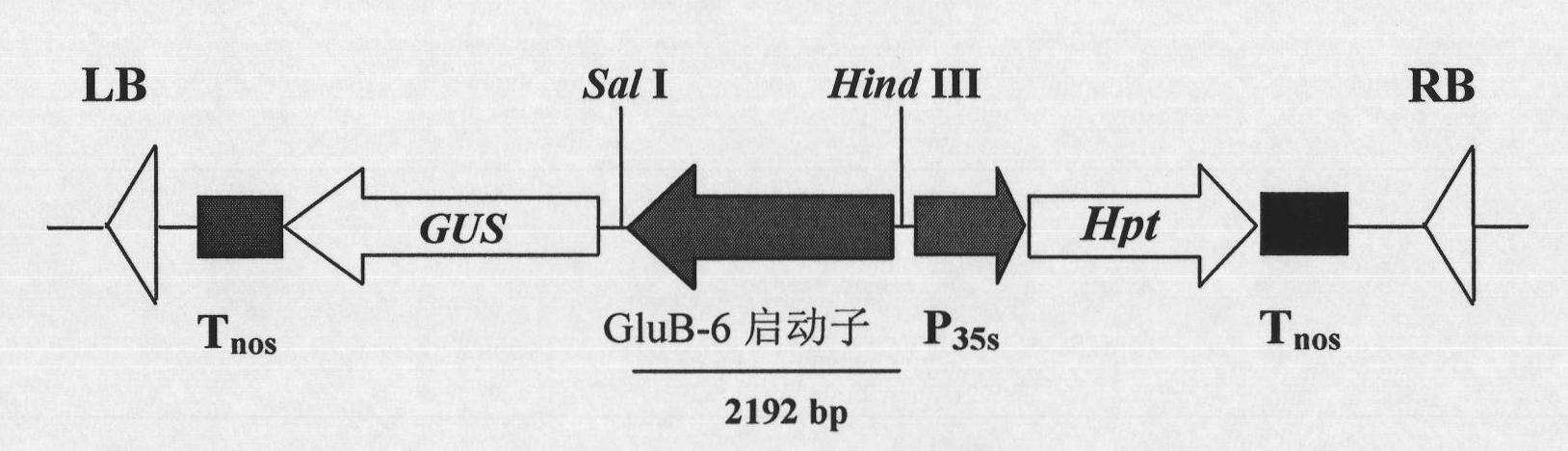
[0041] 1. Construction of plant expression vector with GluB-6 promoter fused to GUS gene
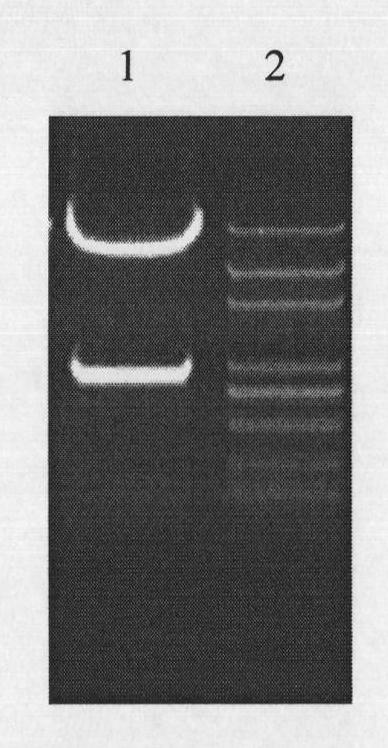
[0042] The binary expression vector pGPTV-35S-HPT was constructed according to the method described in the literature (Qu and Takaiwa, Plant Biotech J 2004, 2: 113-125), and was preserved by the Institute of Botany, Chinese Academy of Sciences. The pMD-GluB-6 plasmid and pGPTV-35S-HPT were digested with Sal I and Hind III. A 2192 bp restriction fragment containing the GluB-6 promoter was recovered, and this fragment was ligated between the Sal I and Hind III enzyme recognition sites of pGPTV-35S-HPT. On the basis of PCR identification, the obtained recombinant plasmid was identified by double enzyme digestion with Sal I and Hind III, and a fragment containing 2.2 kb GluB-6 promoter was obtained. The double-enzyme digestion identification shows ...
Embodiment 3
[0047] Example 3, Functional verification of plant endosperm-specific expression promoter (GluB-6 promoter)
[0048] Transgenic GluB-6-pGPTV-35S-HPT rice T 0 Plants were subjected to histochemical staining. Specific steps: Transplant GluB-6-pGPTV-35S-HPT rice T 0 Part of the leaves, roots, stem tissues of the generation plants, and the seeds at the filling stage 11 days, 15 days, and 17 days after flowering that were cut longitudinally from the middle with a scalpel were soaked in GUS reaction solution (0.1M NaPO 4 Buffer, pH7.0, 10mM EDTA, pH7.0, 5mM potassium ferricyanide, 5mM potassium ferrocyanide, 1.0mMX-Gluc, 0.1% Triton X-100), react at 37°C. The stained tissues were preserved in 70% ethanol, observed, and photographed under a dissecting microscope. The results showed that GUS expression was not observed in the roots, stems and leaves of transgenic GluB-6-pGPTV-35S-HPT rice. Image 6 Shown; the outer endosperm of the 11-day-after-anthesis seeds turned blue, but the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com