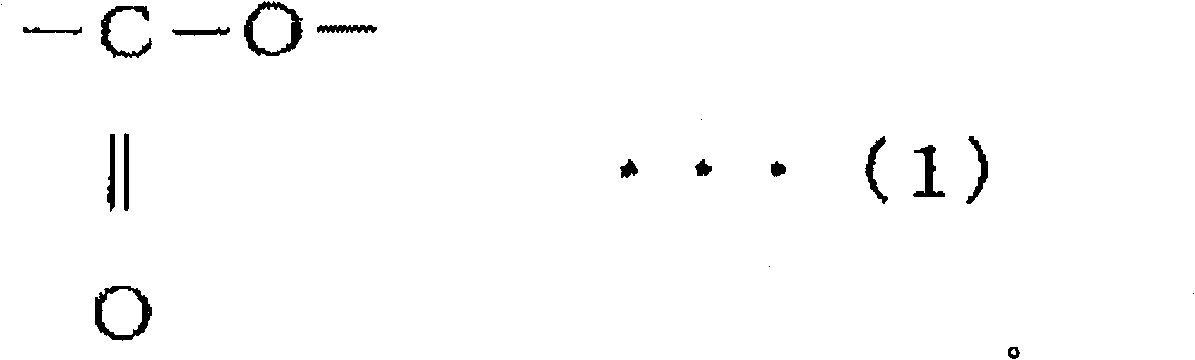Aqueous dispersion for treatment of fibers
A technology of fiber treatment and dispersion, applied in the direction of fiber treatment, carbon fiber, fiber type, etc., to achieve the effects of excellent adhesion, excellent softness, and excellent mechanical strength
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
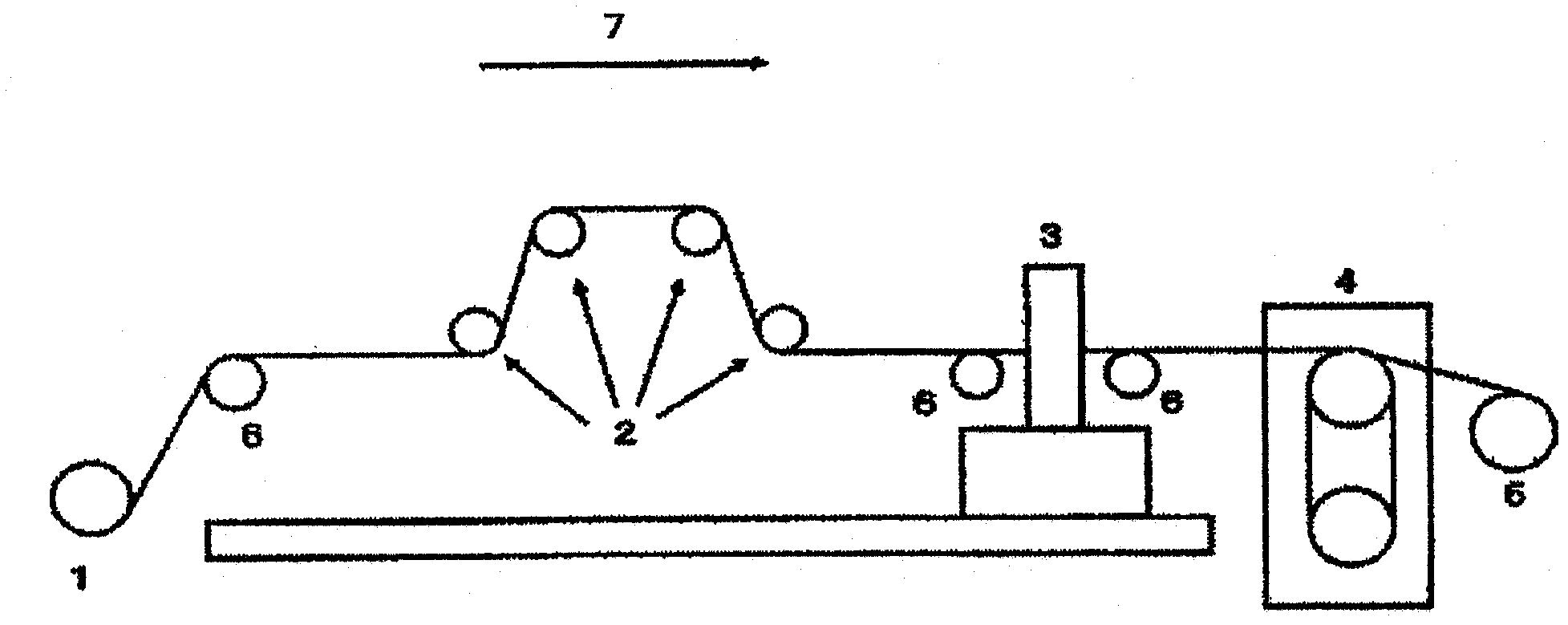
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0136] (1) Preparation of water dispersion
[0137] 91 parts by weight of propylene-butene-ethylene copolymer (A-1) (structural unit derived from propylene (hereinafter also referred to as "C3") = 66 mol %, weight average molecular weight ( hereinafter also referred to as "Mw") = 90,000, MI (melt index: 230° C.) (hereinafter also abbreviated as "MI") = 700), 9 parts by weight of maleic anhydride as a raw material of the propylene resin (B) A modified propylene / ethylene copolymer (C3 = 98 mol%, Mw = 25,000, acid content = 0.81 mmol) and 3 parts by weight of potassium oleate as a surfactant (C) were mixed. The above-mentioned mixture was put into a pressurized kneader, and melt-kneaded at 180° C. for 30 minutes. A 20% potassium hydroxide aqueous solution in an amount necessary to neutralize all the carboxylic acids was poured into the kneader, and kneaded for 30 minutes. This was taken out, poured into hot water, and fully stirred to obtain an aqueous dispersion. The obtained...
Embodiment 2
[0150] (1) Preparation of water dispersion
[0151] 91 parts by weight of propylene-butylene-ethylene copolymer (A-1) (C3=66 mol%, Mw=90,000, MI=700) as propylene-based resin (A), 9 parts by weight as propylene-based resin ( A maleic anhydride-modified propylene-ethylene copolymer (C3 = 98 mol%, Mw = 25,000, acid content = 0.81 mmol) and 3 parts by weight of potassium oleate as a surfactant (C) were mixed. . The above-mentioned mixture was supplied at a rate of 3,000 g / hour from the feed hopper of a twin-screw extruder (manufactured by Ikegai Iron Works Co., Ltd., PCM-30, L / D=40). A 20% aqueous solution of potassium hydroxide was continuously supplied at a rate of 90 g / hour from the supply port of the part, and extrusion was performed continuously at a heating temperature of 210°C. The extruded resin mixture was cooled to 110° C. in a jacketed static mixer installed at the same extruder port, and then poured into 80° C. hot water to obtain an aqueous dispersion. The yield o...
Embodiment 3
[0156] An aqueous dispersion was obtained in the same manner as in Example 2, except that a propylene-ethylene copolymer (C3=70 mol%, Mw=130,000, MI=80) was used as the propylene-based resin (A-1). The yield of the obtained aqueous dispersion was 99%, the solid content concentration was 45%, the pH was 12, and the average particle diameter was 0.4 μm (measured by a microtrac particle size analyzer).
[0157] Using the obtained aqueous dispersion, a test piece was prepared by the method described in (2) of Example 1, and evaluated by the method described in [1. Evaluation method of carbon fiber treated material]. The results are shown in Table 1.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Tensile modulus of elasticity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| The average particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com