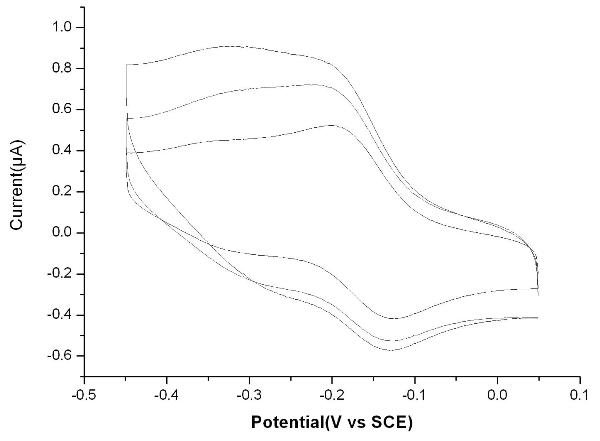
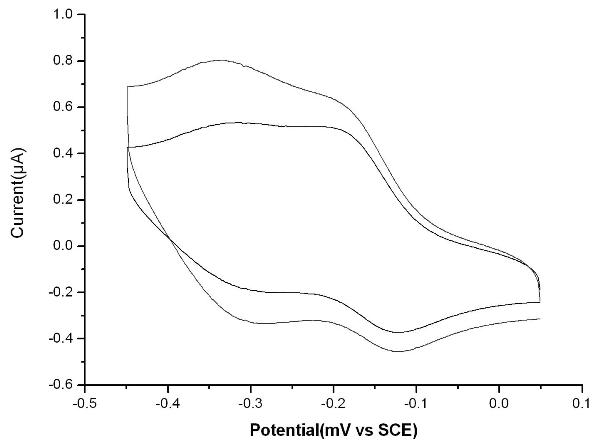
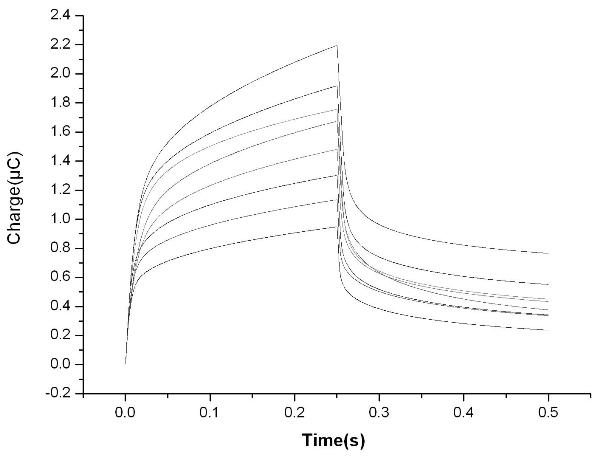
Bioelectrochemical sensor for detecting nuclear factor-kappab, its preparation method and application
A bioelectrochemical and sensor technology, applied in the field of new bioelectrochemical sensors, achieves the effects of broad application prospects, high sensitivity, rapid quantitative detection and convenience
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] Example 1: Modification of gold electrodes
[0032] The gold electrode was first ground on 5000-mesh metallographic sandpaper, and then polished with a suspension of alumina powder with a particle size ranging from 1.0 μm, 0.3 μm, and 0.05 μm to make the surface of the gold electrode into a smooth mirror surface. Sonicate in water ethanol and ultrapure water for 5 min, then put the gold electrode in 0.5 M H 2 SO 4 Cyclic voltammetry scan (0 - 1.5 V voltage range) was carried out in , the scan rate was set at 100 mV / s, and the stability was reached in about 20 cycles. Then dry the electrode in nitrogen to obtain a bare gold electrode with a clean surface, which can be used for the next step of DNA modification. The gold electrode was immersed in a solution containing 2 μM Capture DNA (10 mM Tris-HCl, 1 mM EDTA, 0.1 M NaCl, and 10 mM TCEP, pH 7.4) for 16 hours, and then immersed in 1 mM sulfhydryl Hexanol solution for 2 hours, then rinse the electrode with a sufficient...
Embodiment 2
[0033] Example 2: Preparation of gold nanoparticles and modification of Report DNA
[0034] The glass instruments used in the preparation of gold nanoparticles were soaked in aqua regia (hydrochloric acid: nitric acid = 3:1 (v / v)) for 30 minutes, rinsed with a large amount of tap water, washed with double distilled water and dried. Gold nanoparticles with a diameter of 13 nm were prepared by the sodium citrate reduction method (References: Grabar, K. C.; Freeman, R. G.; Hommer, M. B.; Natan, M. J. Anal. Chem. 1995 , 67 , 735-743.). In this method, sodium citrate is used as a reducing agent and a stabilizing agent to reduce chloroauric acid to generate gold nanoparticles under heating and boiling conditions. The specific method is to install a condenser tube in a round bottom flask with a volume of 250 ml, and add 100 ml of 0.01% HAuCl 4 , be heated to boiling, add 3.5 ml concentration rapidly and be 1% sodium citrate when vigorously stirring solution, continue stirrin...
Embodiment 3
[0036] Embodiment three: the preparation of the sample to be tested
[0037] Mix the Target DNA (1 μL, 2 μM) containing the NF-κB binding site and the complementary Complementary DNA (1 μL, 0.2 μM) in an Eppendorf tube, and hybridize at 37 °C for 30 min. Then, different concentrations of NF-κB (1 μL) were added to the sample system and incubated at 37 °C for 30 min. Finally, NEase (1 μL, 2 U) was added, and the final volume of the reaction sample was 10 μL, and incubated at 58 °C for 30 min.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com