Preservation method of biological enzyme preparation
A biological enzyme and preparation technology, applied in the field of bioengineering, can solve the problems of high production cost, low activity of immobilized enzyme, affecting reaction speed and production efficiency, etc., to maintain continuity, realize repeated long-term use, and convenient cleaning and disinfection and save the effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
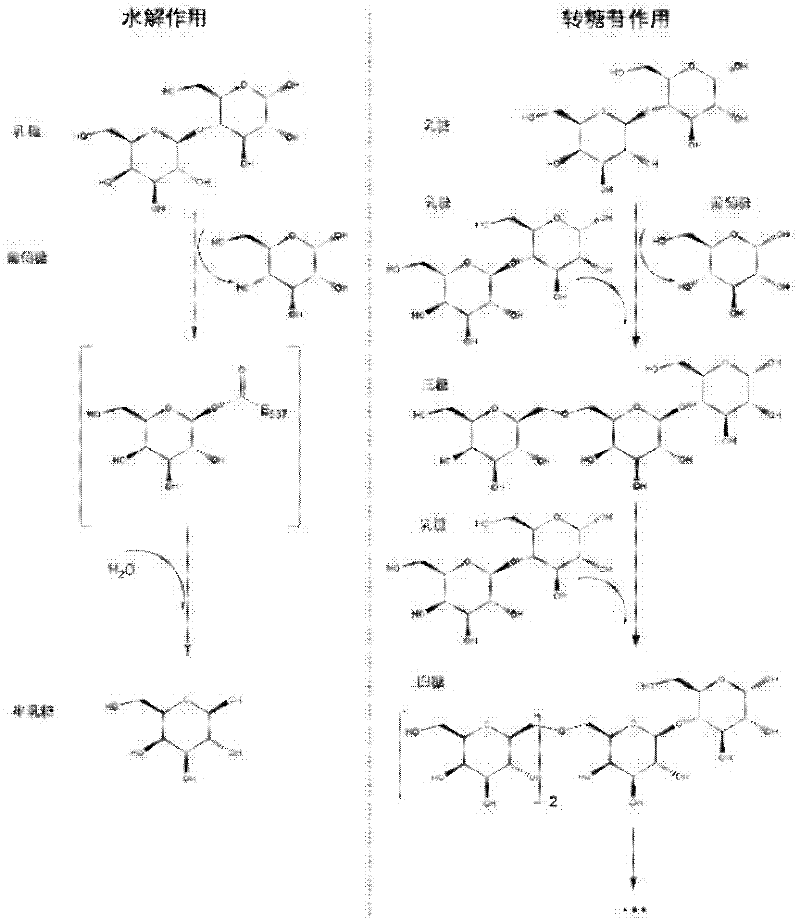
[0040] Example 1: Application Results of Immobilized β-Galactosidase for Production of Lactose Decomposed Milk
[0041] Immobilization method of β-galactosidase: Weigh 2g chitosan beads → add 20ml 0.5% glutaraldehyde → cross-link for 40min (30°C, 80rpm) → wash to get activated chitosan beads → add 10ml of 1mg / ml enzyme solution, fix overnight → wash with water → store at 4°C.
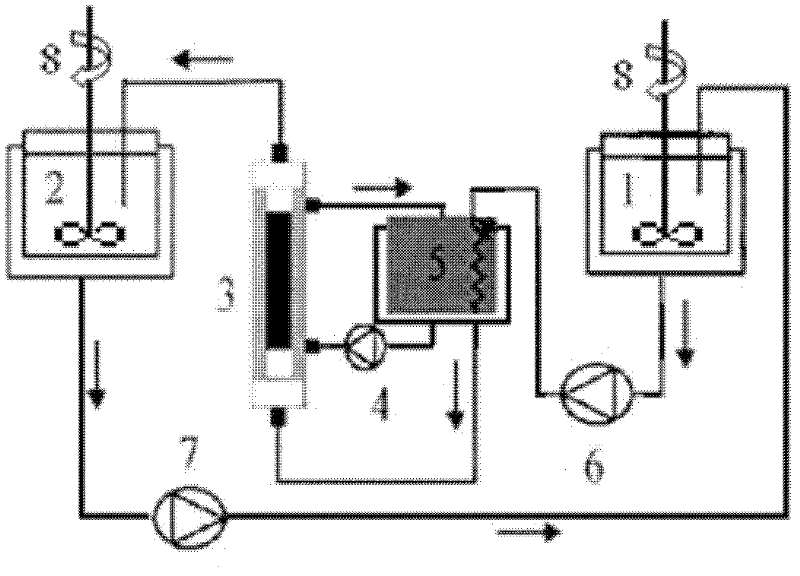
[0042] Production of lactose-decomposed milk with immobilized β-galactosidase: use skim milk, after ultra-high temperature (140°C, 4s) sterilization treatment, determine the content of lactose, protein and fat, and cool it as the reaction substrate. Make the substrate milk pass through the reactor at a flow rate of 1L / h to react with the immobilized enzyme. After 4-5 cycles, the lactose is decomposed, the remaining lactose content is measured, and the lactose decomposition rate is calculated. When the decomposition of lactose reaches more than 80%, change to a new batch of substrate milk and operate a...
Embodiment 2
[0054] Example 2: Results of application of immobilized β-galactosidase to whey
[0055] The immobilization method of β-galactosidase is the same as that in Example 1.
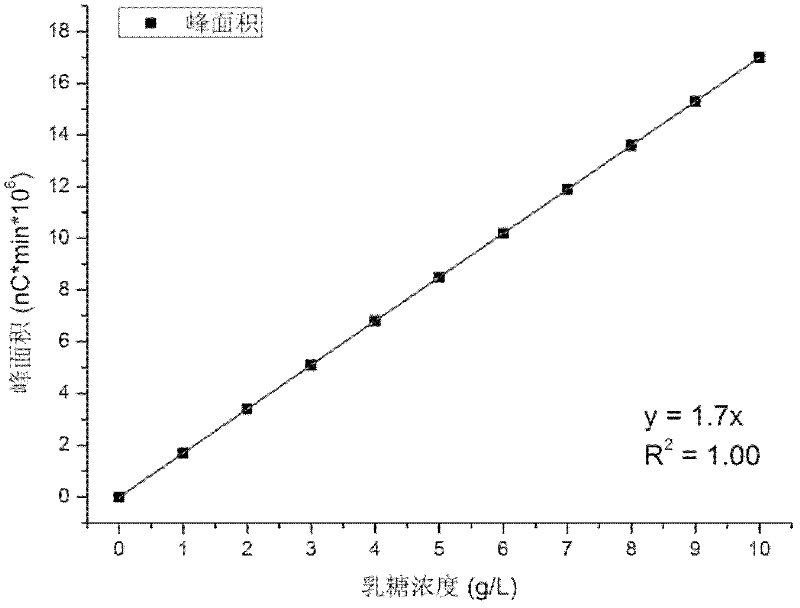
[0056] Treat whey with immobilized β-galactosidase to produce galacto-oligosaccharides: Use desalted whey powder to prepare a whey solution with a lactose content of 10%, and after ultra-high temperature (140°C, 4s) sterilization, determine Lactose and protein content, cooled as reaction substrates. The substrate whey is passed through the reactor at a flow rate of 1 L / h to react with the immobilized enzyme, and after 4-5 cycles, lactose is decomposed to generate galacto-oligosaccharides. Using ion chromatography, using ion exchange and gradient elution methods, combined with pulsed amperometric detection system to detect lactose and galactooligosaccharides. When the decomposition of lactose reaches more than 80%, change to a new batch of substrate whey and then operate, continuous operation every day 12 hou...
Embodiment 3
[0059] Example 3: Application Results of Immobilized β-Galactosidase for Processing Lactose Solution
[0060] The immobilization method of β-galactosidase is the same as that in Example 1.
[0061] Process the lactose solution with immobilized β-galactosidase to produce galacto-oligosaccharides: use lactose to prepare a solution with a lactose content of 10%, after ultra-high temperature (140°C, 4s) sterilization, measure the lactose content, and cool it as Reaction substrate. The substrate whey is passed through the reactor at a flow rate of 1 L / h to react with the immobilized enzyme, and after 4-5 cycles, lactose is decomposed to generate galacto-oligosaccharides. Using ion chromatography, using ion exchange and gradient elution methods, combined with a pulsed amperometric detection system to detect lactose and galactooligosaccharides. When the decomposition of lactose reaches more than 80%, a new batch of substrate whey is used for operation, and the operation is continue...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com