Precision current sensing element and manufacturing method thereof
A current sensing and precise technology, applied in resistor manufacturing, electrical components, resistor components, etc., can solve the problems of products unable to develop into miniaturization, reduce product performance, ceramic chip rupture, etc., to improve the current resistance capability, The effect of reducing product resistance and cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
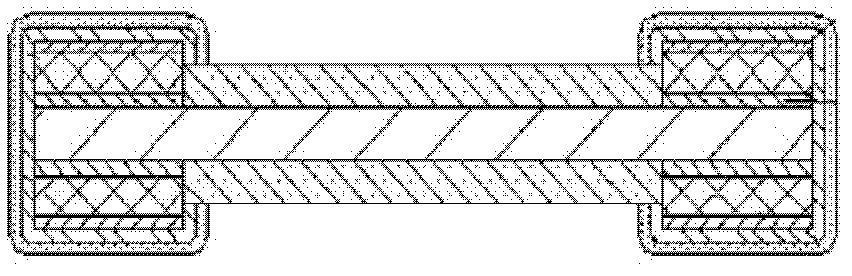
[0065] The inner layer is prepared by setting a sheet-shaped resistance alloy L6 on both sides of a piece of insulating heat-conducting adhesive, such as Figure 7 As shown, in this embodiment, L6 is closely combined with the insulating and thermally conductive adhesive C5 by pressing. The resistance alloy can be a material with a small temperature coefficient of resistance, and the resistivity is not limited; the insulating and heat-conducting adhesive can use a single high-molecular polymer glue with good heat resistance, insulation, thermal conductivity, and adhesion, or it can be passed through Glass fiber reinforced high molecular polymer glue with good heat resistance, insulation, thermal conductivity and adhesion. Then make the circuit on the inner layer after pressing, that is, the resistance alloy L6 is formed as Figure 9 The shown first resistor body C2, second resistor body C3, and resistor layer array division interval L5 have a specific shape. The shapes of the...
Embodiment 2
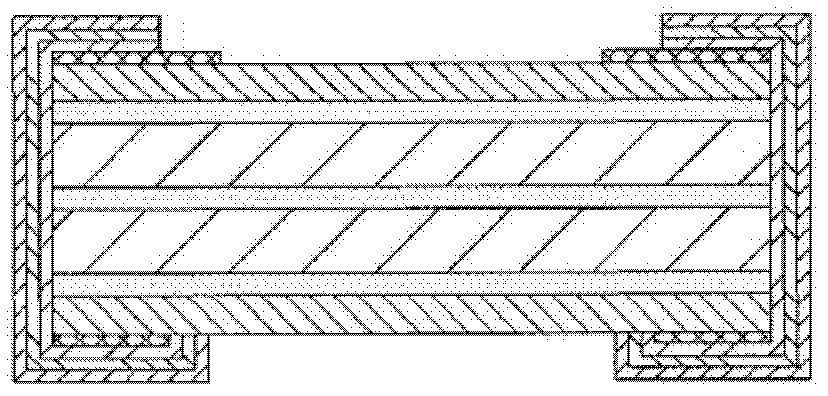
[0073] The inner layer is prepared by setting a sheet-shaped resistance alloy L6 and a sheet-shaped heat-conducting metal L7 on both sides of a piece of insulating heat-conducting adhesive, such as Figure 8 As shown, in this embodiment, the resistance alloy L6, the heat-conducting metal L7 and the insulating heat-conducting adhesive C5 are closely combined by pressing. The resistance alloy can be a material with a small temperature coefficient of resistance, and the resistivity is not limited; the heat-conducting metal is a metal material with a thermal conductivity greater than or equal to 200W / mK; the insulating heat-conducting adhesive can use a single material with good heat resistance, insulation, Thermally conductive, adhesive high-molecular polymer adhesives, or glass fiber-reinforced high-molecular polymer adhesives with good heat resistance, insulation, thermal conductivity, and adhesive properties. Then make the circuit on the inner layer after pressing, that is, fo...
Embodiment 3
[0081] If the resistance alloy and the heat-conducting metal itself have good rigidity, the following manufacturing methods can be followed:
[0082] Firstly, the resistive body is formed on the resistive alloy by etching, and the heat sink is formed on the thermally conductive metal.
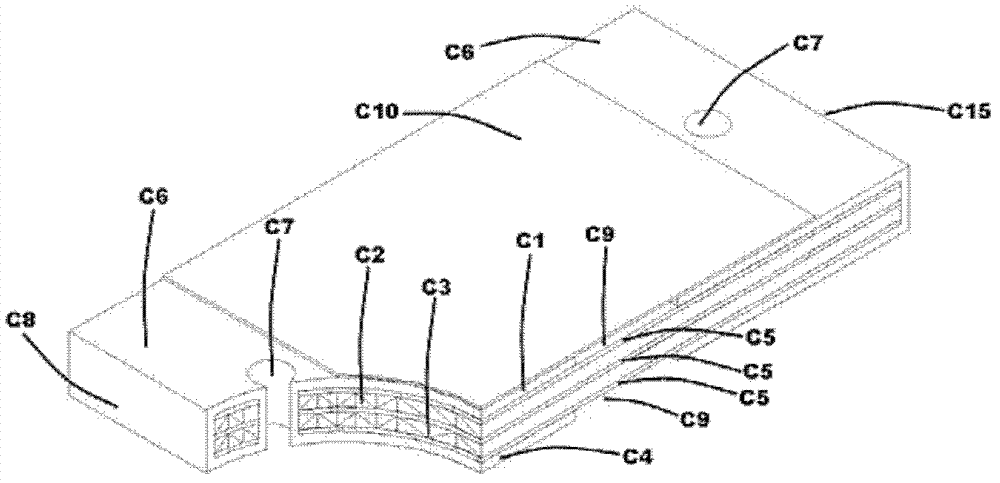
[0083] Then, the finished resistor body and heat sink are made according to the following steps: image 3 The method shown is stacked and pressed, and then slotted and drilled mechanically. Metallize the slotted and drilled parts. The method of metallization can be electroless plating and physical vapor deposition, so that the section of the slotted and drilled holes is first covered with a thin metal conductive layer, and then added by electroplating. Thick, so that the final product can withstand the impact of high current.
[0084] The forming of the outer layer circuit also adopts the method of chemical etching to form the pattern of the heat sink on the outer layer, and the pattern of th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com