Process for improving corrosion-resisting property of magnesium alloy
A magnesium alloy and corrosion resistance technology, which is applied in the field of cryogenic treatment of magnesium alloy modification, can solve the problems of coatings that are easy to pollute the environment, corrode, and affect health, and achieve the effect of avoiding poor bonding and improving corrosion resistance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0020] (1) Solid solution treatment: Put the ceramic crucible with potassium nitrate into a box-type heat treatment furnace, and heat it up to 415°C to melt it; AZ91D magnesium alloy (Al 8.5wt%~9.5wt%, Zn 0.45wt %~0.9wt%, Mg 90~91wt%) sample is placed in the crucible, so that the surface of the sample is completely submerged in the molten salt, keep warm for 10b, take out the sample and put it in water to cool down, take it out and dry it for later use;
[0021] (2) Aging treatment: put the sample after the solid solution treatment in step (1) into a molten salt crucible at 220°C, keep it warm for 7 hours, take out the sample and wash and dry it for later use;
[0022] (3) Cryogenic treatment: the magnesium alloy sample after solid solution and aging treatment was placed in liquid nitrogen at -196°C, placed for 15 hours for cryogenic treatment, and then the sample was taken out.
Embodiment 2
[0024] (1) Solid solution treatment: put the ceramic crucible with potassium nitrate into the box-type heat treatment furnace, and heat it up to 415°C with the furnace to melt it; put the AZ91D magnesium alloy sample into the crucible, so that the surface of the sample is completely immersed In molten salt, keep warm for 10h, take out the sample and put it in water, take it out and dry it for later use;
[0025] (2) Aging treatment: put the sample after the solid solution treatment in step (1) into a molten salt crucible at 220°C, keep it warm for 7 hours, take out the sample and wash and dry it for later use;
[0026] (3) Cryogenic treatment: the magnesium alloy sample after solid solution and aging treatment was placed in liquid nitrogen at -196°C, placed for 72 hours for cryogenic treatment, and then the sample was taken out.
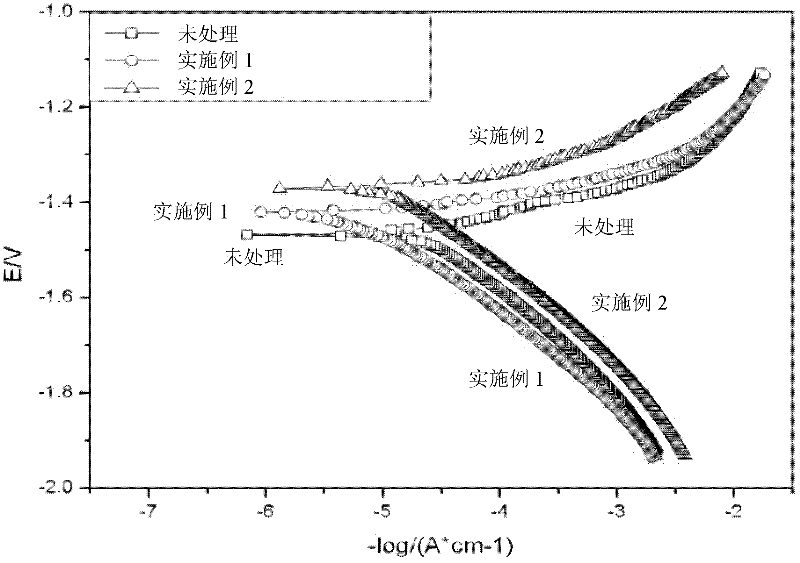
[0027] The reference substance was only processed through the steps (1) and (2) of Example 1, without cryogenic treatment. The corrosion resistance...
Embodiment 3
[0029] (1) Solid solution treatment: put the ceramic crucible containing potassium nitrate into the box-type heat treatment furnace, and heat it up to 430°C to melt it; put the AZ91D magnesium alloy sample into the crucible, so that the surface of the sample is completely immersed In molten salt, keep warm for 15 hours, take out the sample and put it in water to cool down, take it out and dry it for later use;
[0030] (2) Aging treatment: put the sample after the solid solution treatment in step (1) into a molten salt crucible at 260°C, keep it warm for 5 hours, take out the sample and wash and dry it for later use;
[0031] (3) Cryogenic treatment: the magnesium alloy sample after solid solution and aging treatment was placed in liquid nitrogen at -190° C., placed for 2 hours for cryogenic treatment, and then the sample was taken out.
[0032] Compared with the magnesium alloy without cryogenic treatment in step (3), the self-corrosion potential of the magnesium alloy after ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com