Method for removing perchlorate in water
A perchlorate and water removal technology, applied in the field of water treatment, can solve the problems of high economic cost, low removal efficiency, and difficult removal, and achieve the effects of high adsorption efficiency, short reaction time, and strong practical value
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
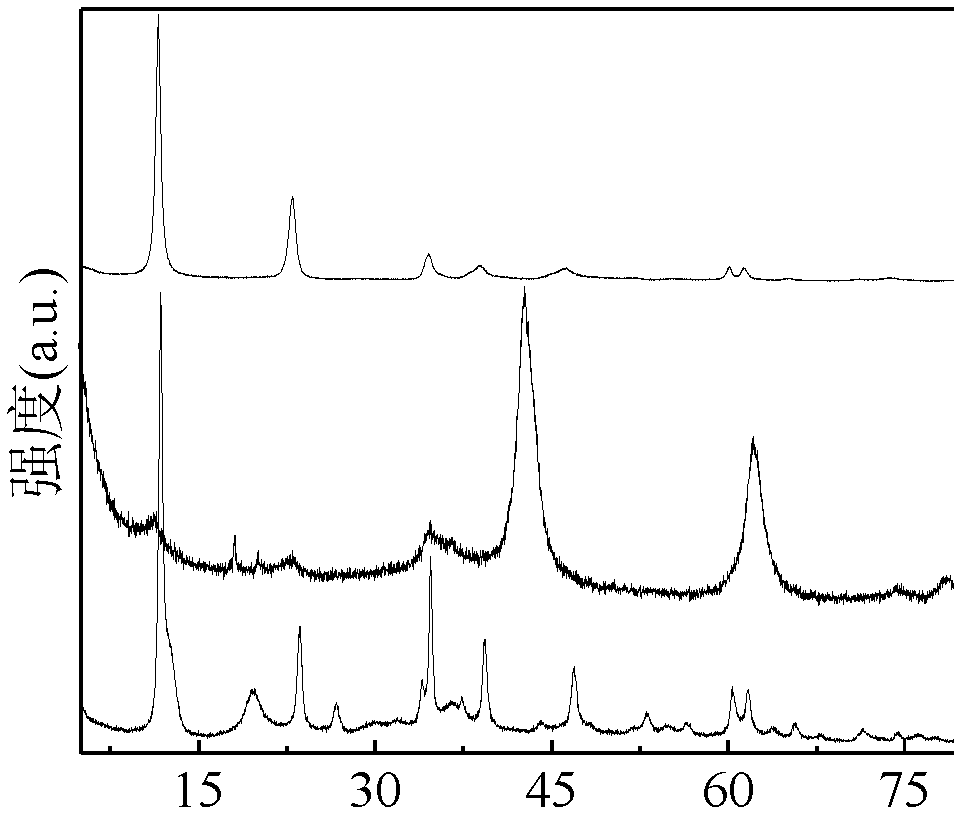
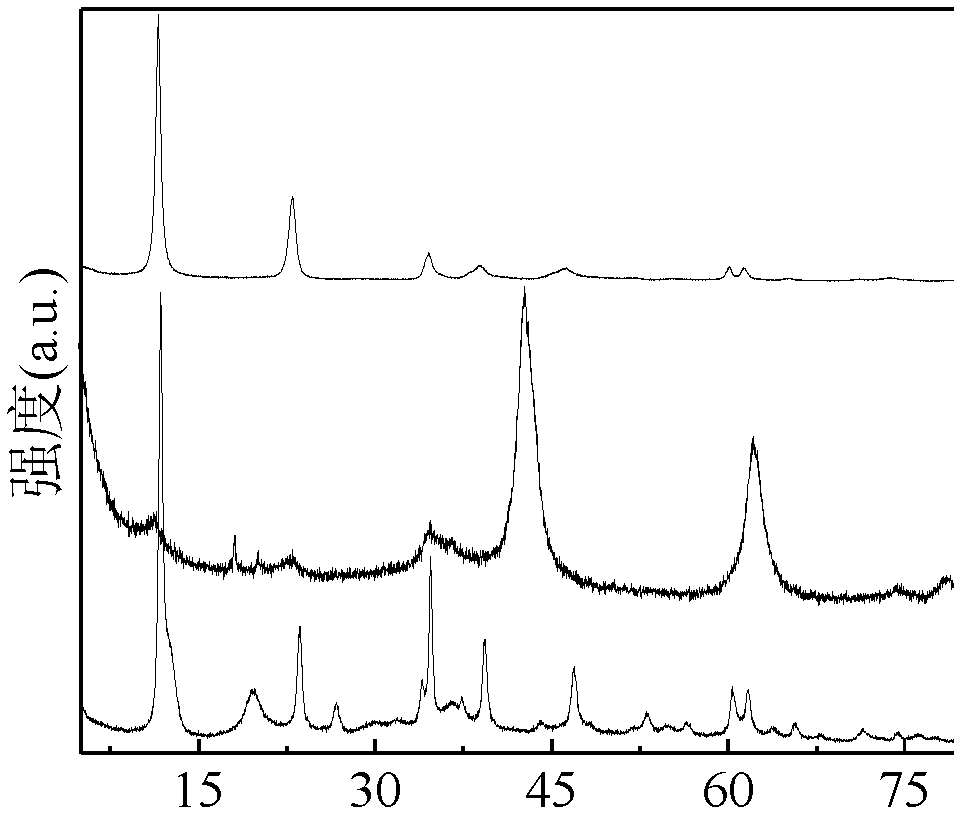
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] 1. Preparation of magnesium-aluminum layered double hydroxide:
[0040] (1) Weigh 192.3075g of magnesium nitrate hexahydrate and 93.7825g of aluminum nitrate nonahydrate, pour them into a 500mL conical flask, mix well and then add 150mL of deionized water to dissolve. If there are fine particles that cannot be dissolved, ultrasonication can be used for 3-5 minutes After stirring on an electromagnetic stirrer, the mixed solution that is completely dissolved after half an hour is called a;
[0041] Weigh 80.02g of anhydrous sodium hydroxide and 52.995g of anhydrous sodium carbonate respectively, pour them into another 500mL conical flask, quickly add 150mL of deionized water to dissolve them, if there are fine particles that cannot be dissolved, use ultrasonic After 3 to 5 minutes, electromagnetically stir evenly to obtain a completely dissolved solution b;
[0042] (2) Clean the two 150mL constant pressure funnels, dry them, and check their tightness. When ready, transf...
Embodiment 2
[0052] (1) The magnesium-aluminum bimetallic composite oxide Mg6Al that has reached saturation 2 o 9 Calcined at 550°C for 6h in a muffle furnace. Weigh 0.5g of regenerated adsorbent and put it into 200mL deionized water with an initial perchlorate concentration of 2000 μg / L (the mass ratio of adsorbent to polluted water is 1:400 respectively);
[0053] (2) Put it in a shaker at room temperature at 25°C with a rotation speed of 200rpm. After 12 hours, take 5mL of the mixed solution to pass through a 0.45μm filter membrane. The ion chromatography test shows that the removal rate can still reach more than 75% within 30 minutes, and the removal rate can reach 6 hours 85%, indicating that the adsorption functional material can be recycled.
Embodiment 3
[0055] (1) Weigh magnesium-aluminum bimetallic composite oxide Mg 6 Al 2 o 9 0.5g (the mass ratio of adsorbent to polluted water is 1:400), put into 200mL deionized in water;
[0056] (2) Put it in a shaker at room temperature at 25°C with a rotation speed of 200rpm. After reacting for 12 hours, the removal rates of perchlorate by the adsorbent are 29.84%, 69.79%, 86.33%, 89.32, and 87.68%, respectively. 60.54%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com